a) Water is a good solvent – all molecules in a living things are
... 2.1.1. Monomers are similar unit structures (organic molecules) of polymers. The monomers link with each other by the covalent bonds to form the chains of oligomers and polymers. The oligomers contain small number of monomers (from two to twenty), the polymers contain from hundreds to millions monom ...
... 2.1.1. Monomers are similar unit structures (organic molecules) of polymers. The monomers link with each other by the covalent bonds to form the chains of oligomers and polymers. The oligomers contain small number of monomers (from two to twenty), the polymers contain from hundreds to millions monom ...
Rapid Sample Preparation and HPLC-ESI- TOFMS Analysis of Derivatized Amino Acids Introduction
... Due to poor resolution of the isomeric pairs 1MHIS/3MHIS and LEU/ILE these compounds were reported as single peaks. In addition, THR was found to exactly coelute with GPR and so could not be automatically found. However, this compound could be detected by manual inspection of the mass spectral data ...
... Due to poor resolution of the isomeric pairs 1MHIS/3MHIS and LEU/ILE these compounds were reported as single peaks. In addition, THR was found to exactly coelute with GPR and so could not be automatically found. However, this compound could be detected by manual inspection of the mass spectral data ...
Assaying
... Highly susceptible to contamination by buffers, biological materials and salts Protein amino acid composition is extremely important, thus the choice of a standard is very difficult, especially for purified proteins Absorbance is heavily influence by pH and ionic strength of the solution. This is of ...
... Highly susceptible to contamination by buffers, biological materials and salts Protein amino acid composition is extremely important, thus the choice of a standard is very difficult, especially for purified proteins Absorbance is heavily influence by pH and ionic strength of the solution. This is of ...
Medical Biochemistry: Course content 2016/2017
... (substrate, products, enzyme and coenzyme) and its regulation. Lipoproteins. Which are the common lipoproteins and how do they differ regarding the lipid composition? What is their function? Why are the lipids contained in chylomicrons and VLDL mainly taken up by extrahepatic tissues (primarily adip ...
... (substrate, products, enzyme and coenzyme) and its regulation. Lipoproteins. Which are the common lipoproteins and how do they differ regarding the lipid composition? What is their function? Why are the lipids contained in chylomicrons and VLDL mainly taken up by extrahepatic tissues (primarily adip ...
1 - contentextra
... Monosaccharide Simple sugar with the formula CnH2nOn. They are soluble molecules. Examples include glucose and fructose. Monounsaturated fat Fat containing fatty acids which have one carbon–carbon double bond. Ninhydrin A locating reagent used in chromatography and electrophoresis to detect the posi ...
... Monosaccharide Simple sugar with the formula CnH2nOn. They are soluble molecules. Examples include glucose and fructose. Monounsaturated fat Fat containing fatty acids which have one carbon–carbon double bond. Ninhydrin A locating reagent used in chromatography and electrophoresis to detect the posi ...
Unit 3 Biochemistry - The Naked Science Society
... Biochemistry is the study of the chemical interactions of living things. Biochemists study the structures and physical properties of biological molecules. ...
... Biochemistry is the study of the chemical interactions of living things. Biochemists study the structures and physical properties of biological molecules. ...
Biochemical Thermodynamics
... Identities of the R groups Nineteen of the twenty ribosomally encoded amino acids fit this form The only variation is in the identity of the R group (the side chain extending off the alpha carbon) Complexity ranging from glycine (R=H) to tryptophan (R=-CH2-indole) ...
... Identities of the R groups Nineteen of the twenty ribosomally encoded amino acids fit this form The only variation is in the identity of the R group (the side chain extending off the alpha carbon) Complexity ranging from glycine (R=H) to tryptophan (R=-CH2-indole) ...
The Synthesis and Expression of Peptide CbnY Thomas Doerksen
... The King’s University ORAL Collaboration Bacteriocins are small antimicrobial peptides produced by bacteria, and have great potential in the food industry as an alternative to antibiotics. The two-component bacteriocins, produced by various strains of lactic acid bacteria, display optimal activity w ...
... The King’s University ORAL Collaboration Bacteriocins are small antimicrobial peptides produced by bacteria, and have great potential in the food industry as an alternative to antibiotics. The two-component bacteriocins, produced by various strains of lactic acid bacteria, display optimal activity w ...
Chemistry of Life - El Camino College
... Chemical reactions: atoms change partners By breaking existing bonds and forming new ones 2 H + O 2H O + energy Reactants Products Is matter or energy created during a chemical reaction? Matter and energy can not be created nor destroyed ONLY transformed! ...
... Chemical reactions: atoms change partners By breaking existing bonds and forming new ones 2 H + O 2H O + energy Reactants Products Is matter or energy created during a chemical reaction? Matter and energy can not be created nor destroyed ONLY transformed! ...
Transcription and Translation
... base sequence can cause an alteration in amino acid sequence (think back to sickle cell anaemia – this is caused by a mutation which results in the sixth amino acid of the β polypeptide of haemoglobin being replaced by valine). Why are there three nucleotides in the code? There are four bases in DNA ...
... base sequence can cause an alteration in amino acid sequence (think back to sickle cell anaemia – this is caused by a mutation which results in the sixth amino acid of the β polypeptide of haemoglobin being replaced by valine). Why are there three nucleotides in the code? There are four bases in DNA ...
Chapter 2: Biochemistry
... Proteins are compounds that consist of nitrogen, in addition to carbon, hydrogen and oxygen. They serve as enzymes, antibodies, contractile material, hormones, pigments and structural parts in cells and tissues. Proteins also contain one or more chains of amino acids, the structural units of prote ...
... Proteins are compounds that consist of nitrogen, in addition to carbon, hydrogen and oxygen. They serve as enzymes, antibodies, contractile material, hormones, pigments and structural parts in cells and tissues. Proteins also contain one or more chains of amino acids, the structural units of prote ...
Building Monomers of Macromolecules
... Atoms join together to form molecules. These molecules are held together by bonds. In this lab you will use toothpicks to represent the bonds. Important note: use one toothpick to represent a single covalent bond, and two toothpicks to represent a double covalent bond. Remember, covalent bonds are b ...
... Atoms join together to form molecules. These molecules are held together by bonds. In this lab you will use toothpicks to represent the bonds. Important note: use one toothpick to represent a single covalent bond, and two toothpicks to represent a double covalent bond. Remember, covalent bonds are b ...
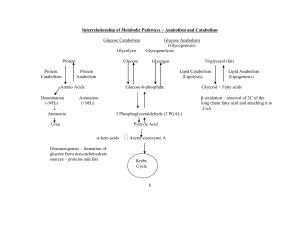
3.DCP I Year BCP Metabolism Notes
... Ammonia and this ammonia is toxic to our body cells. This should be excrete from body this is happen by the urea cycle in this cycle the ammonia from amino acid metabolism converted into urea and this urea will be excrete trough kidneys from our body. Catabolism of Amino acids takes place by followi ...
... Ammonia and this ammonia is toxic to our body cells. This should be excrete from body this is happen by the urea cycle in this cycle the ammonia from amino acid metabolism converted into urea and this urea will be excrete trough kidneys from our body. Catabolism of Amino acids takes place by followi ...
Biomolecules PPT
... hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom are removed from the monomers to form water, and the two monomers are joined together. ...
... hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom are removed from the monomers to form water, and the two monomers are joined together. ...
Protein Synthesis Simulation
... 5. Look at the “Universal Genetic Code Chart.” Which codon (set of 3 bases) in RNA codes for the “Met” amino acid? Write the correct bases below. ___ ___ ___ 6. The “Met” amino acid is the “start” codon and allows protein synthesis to begin. Find this codon on the RNA strand. Position the green wind ...
... 5. Look at the “Universal Genetic Code Chart.” Which codon (set of 3 bases) in RNA codes for the “Met” amino acid? Write the correct bases below. ___ ___ ___ 6. The “Met” amino acid is the “start” codon and allows protein synthesis to begin. Find this codon on the RNA strand. Position the green wind ...
nucleic acids
... Macromolecule: a larger molecule--there are 4 types that make up all living things!! ...
... Macromolecule: a larger molecule--there are 4 types that make up all living things!! ...
Biological Macromolecules
... be there, like certain bacteria, antibodies find the invader and stick themselves onto it. **White Blood cells destroy the invaders (hopefully) ...
... be there, like certain bacteria, antibodies find the invader and stick themselves onto it. **White Blood cells destroy the invaders (hopefully) ...
Macromolecules 2015 16
... • Lipids consist of chains of carbon atoms bonded to each other and to hydrogen atoms. This structure makes lipids repel water. ...
... • Lipids consist of chains of carbon atoms bonded to each other and to hydrogen atoms. This structure makes lipids repel water. ...
Organic and Inorganic Molecules - Cal State LA
... enzymes (catalyze reactions in the body; makes them easier to happen) ...
... enzymes (catalyze reactions in the body; makes them easier to happen) ...























