Central Dogma
... http://highered.mcgrawhill.com/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=swf::535::535::/si tes/dl/free/0072437316/120077/micro06.swf::Protein Synthesis ...
... http://highered.mcgrawhill.com/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=swf::535::535::/si tes/dl/free/0072437316/120077/micro06.swf::Protein Synthesis ...
Document
... B2.5.2 Enzymes Relate the shape of an enzyme to its function Describe how high temperatures affect enzymes Describe how enzymes work at different pH values Describe examples of enzymes that work outside of body cells, such as digestive enzymes, including details of where they are produced, where the ...
... B2.5.2 Enzymes Relate the shape of an enzyme to its function Describe how high temperatures affect enzymes Describe how enzymes work at different pH values Describe examples of enzymes that work outside of body cells, such as digestive enzymes, including details of where they are produced, where the ...
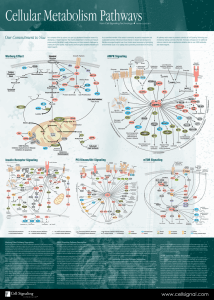
Cellular Metabolism Pathways
... Most cells use glucose as a fuel source. Glucose is metabolized by glycolysis in a multi-step set of reactions resulting in the creation of pyruvate. In typical cells, much of this pyruvate enters the mitochondria where it is oxidized by the Krebs Cycle to generate ATP to meet the cell’s energy dema ...
... Most cells use glucose as a fuel source. Glucose is metabolized by glycolysis in a multi-step set of reactions resulting in the creation of pyruvate. In typical cells, much of this pyruvate enters the mitochondria where it is oxidized by the Krebs Cycle to generate ATP to meet the cell’s energy dema ...
bodybuilding supplements
... Steroids are synthetic substances associated with male growth hormones. Whereas, bodybuilding supplements generally consist of natural or synthetic ingredients from plants, herbs, vitamins, minerals and amino acids. Bodybuilding supplements are not steroids. Anabolic steroids are a class of steroid ...
... Steroids are synthetic substances associated with male growth hormones. Whereas, bodybuilding supplements generally consist of natural or synthetic ingredients from plants, herbs, vitamins, minerals and amino acids. Bodybuilding supplements are not steroids. Anabolic steroids are a class of steroid ...
Enzymes - كنانة أونلاين
... The region that contains these catalytic residues, binds the substrate, and then carries out the reaction is known as the active site. Enzymes can also contain sites that bind cofactors, which are needed for catalysis. Some enzymes also have binding sites for small molecules, which are often direct ...
... The region that contains these catalytic residues, binds the substrate, and then carries out the reaction is known as the active site. Enzymes can also contain sites that bind cofactors, which are needed for catalysis. Some enzymes also have binding sites for small molecules, which are often direct ...
Contributions of direct incorporation from diet and microbial amino
... and (ii) the protein content of diet. Other factors such as growth rate and metabolic state are also important considerations, because several amino acids (e.g. proline) can be conditionally indispensable when de novo synthesis does not meet requirements for growth (Ball, Atkinson & Bayley 1986; Chu ...
... and (ii) the protein content of diet. Other factors such as growth rate and metabolic state are also important considerations, because several amino acids (e.g. proline) can be conditionally indispensable when de novo synthesis does not meet requirements for growth (Ball, Atkinson & Bayley 1986; Chu ...
PDF
... the organic FET can be applied to analyte detection in water. Then, we used the extended-gate type organic transistor as a sensor for cysteine detection. An Ag/AgCl electrode was employed as a reference electrode. A HEPES (4-(2-hydroxyethyl)-1-piperazineethanesulfonic acid) buffer solution of cystei ...
... the organic FET can be applied to analyte detection in water. Then, we used the extended-gate type organic transistor as a sensor for cysteine detection. An Ag/AgCl electrode was employed as a reference electrode. A HEPES (4-(2-hydroxyethyl)-1-piperazineethanesulfonic acid) buffer solution of cystei ...
CHAPTER 5 THE STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF MACROMOLECULES
... – Polymers consist of many similar or identical building blocks linked by covalent bonds. ...
... – Polymers consist of many similar or identical building blocks linked by covalent bonds. ...
Glycolysis is the major oxidative pathway for glucose
... NADH are formed when pyruvate is produced (aerobic glycolysis), whereas NADH is reconverted to NAD+ when lactate is the end product (anaerobic glycolysis). ...
... NADH are formed when pyruvate is produced (aerobic glycolysis), whereas NADH is reconverted to NAD+ when lactate is the end product (anaerobic glycolysis). ...
lecture11&12-RS_Major Metabolic Pathways of
... NADH are formed when pyruvate is produced (aerobic glycolysis), whereas NADH is reconverted to NAD+ when lactate is the end product (anaerobic glycolysis). ...
... NADH are formed when pyruvate is produced (aerobic glycolysis), whereas NADH is reconverted to NAD+ when lactate is the end product (anaerobic glycolysis). ...
Cellular respiration
... 2. What is another name for the Aerobic System? 3. Describe the conditions under which an athlete would be relying mostly on the Aerobic System to produced ATP. 4. What must proteins and fats be converted into in order to be used as fuel for the Aerobic System? ...
... 2. What is another name for the Aerobic System? 3. Describe the conditions under which an athlete would be relying mostly on the Aerobic System to produced ATP. 4. What must proteins and fats be converted into in order to be used as fuel for the Aerobic System? ...
Malonyl-CoA: the regulator of fatty acid synthesis and oxidation
... published a study in the JCI noting the surprising realization that malonylCoA, the substrate of fatty acid synthesis, was also an inhibitor of fatty acid oxidation. Subsequent experiments have borne out this finding and furthered our understanding of molecular metabolism. Ketogenesis, the productio ...
... published a study in the JCI noting the surprising realization that malonylCoA, the substrate of fatty acid synthesis, was also an inhibitor of fatty acid oxidation. Subsequent experiments have borne out this finding and furthered our understanding of molecular metabolism. Ketogenesis, the productio ...
REVIEW: Bio 139 Lab Practical #1 All labs from beginning of the
... ATP production). White = colorless reaction / reduction of litmus (bacteria use litmus as terminal electron acceptor). May be pink at surface where oxygen in the air oxidizes the litmus. Solids/ppt = curd formation. {We’ll learn this later in the semester: Pink with solid chunk: milk protein precipi ...
... ATP production). White = colorless reaction / reduction of litmus (bacteria use litmus as terminal electron acceptor). May be pink at surface where oxygen in the air oxidizes the litmus. Solids/ppt = curd formation. {We’ll learn this later in the semester: Pink with solid chunk: milk protein precipi ...
Chapter 5 - Biology 210A - Introduction to the Biological Sciences
... Four Levels of Protein Structure • The primary structure of a protein is its unique sequence of amino acids • Secondary structure, found in most proteins, consists of coils and folds in the polypeptide ...
... Four Levels of Protein Structure • The primary structure of a protein is its unique sequence of amino acids • Secondary structure, found in most proteins, consists of coils and folds in the polypeptide ...
Enzyme Activity
... Inhibitors are chemicals that reduce the rate of enzymic reactions. The are usually specific and they work at low concentrations. They block the enzyme but they do not usually destroy it. ...
... Inhibitors are chemicals that reduce the rate of enzymic reactions. The are usually specific and they work at low concentrations. They block the enzyme but they do not usually destroy it. ...
Evaluation of volatile compounds produced by Lactobacillus
... Chromatographic analysis Volatile compounds retained on the fiber-coating phase were thermally desorbed in the injection port (250 °C, splitless mode) equipped with a narrow-bore glass liner (Supelco, Bellefonte, USA) of a gas chromatograph (PerkinElmer model 9000, USA). The compounds were separated ...
... Chromatographic analysis Volatile compounds retained on the fiber-coating phase were thermally desorbed in the injection port (250 °C, splitless mode) equipped with a narrow-bore glass liner (Supelco, Bellefonte, USA) of a gas chromatograph (PerkinElmer model 9000, USA). The compounds were separated ...
ENZYME KINETICS - University of Pennsylvania
... Implicit in all of the preceding discussions has been the idea that we can somehow isolate enzymes at will for study. In practice this is not always so easy. Biochemists obtain enzymes and measure their activities by various methods. The enzyme to be investigated is first extracted from some living ...
... Implicit in all of the preceding discussions has been the idea that we can somehow isolate enzymes at will for study. In practice this is not always so easy. Biochemists obtain enzymes and measure their activities by various methods. The enzyme to be investigated is first extracted from some living ...
Chapter 5 Bacterial Metabolism
... Krebs Cycle (Citric Acid Cycle) • The new molecule is called acetyl coenzyme A (Acetyl CoA) • The removal of the CO2 also produces another NADH molecule for the electron transport chain • The remaining 2 carbons from the 3 carbon pyruvate are now able to enter the Krebs cycle • This happens when a ...
... Krebs Cycle (Citric Acid Cycle) • The new molecule is called acetyl coenzyme A (Acetyl CoA) • The removal of the CO2 also produces another NADH molecule for the electron transport chain • The remaining 2 carbons from the 3 carbon pyruvate are now able to enter the Krebs cycle • This happens when a ...
Slide 1
... • How are proteins digested and absorbed into the blood? How do other tissues and organs get the amino acids out of the blood? • What are plasma proteins and why are they important? Be able to give an example of a plasma protein. • Learn how amino acids can be used in • The synthesis of new proteins ...
... • How are proteins digested and absorbed into the blood? How do other tissues and organs get the amino acids out of the blood? • What are plasma proteins and why are they important? Be able to give an example of a plasma protein. • Learn how amino acids can be used in • The synthesis of new proteins ...
complete
... • How are proteins digested and absorbed into the blood? How do other tissues and organs get the amino acids out of the blood? • What are plasma proteins and why are they important? Be able to give an example of a plasma protein. • Learn how amino acids can be used in • The synthesis of new proteins ...
... • How are proteins digested and absorbed into the blood? How do other tissues and organs get the amino acids out of the blood? • What are plasma proteins and why are they important? Be able to give an example of a plasma protein. • Learn how amino acids can be used in • The synthesis of new proteins ...
Lecture 6
... standard free energy required to synthesize GTP from GDP and Pi is + 30.5 kJ/mole. If we couple these two reactions together than the standard free energy change is -3.3 kJ/mole. This enzyme catalyzes a substrate level phosphorylation to generate the only NTP produced directly in the citric acid cyc ...
... standard free energy required to synthesize GTP from GDP and Pi is + 30.5 kJ/mole. If we couple these two reactions together than the standard free energy change is -3.3 kJ/mole. This enzyme catalyzes a substrate level phosphorylation to generate the only NTP produced directly in the citric acid cyc ...
Module 1 : Introduction to the study of man
... Explain why this pathway is referred to as a shunt. ...
... Explain why this pathway is referred to as a shunt. ...