KREBS CYCLE Definition Krebs cycle (aka tricarboxylic acid cycle
... 9. L-malate is oxidised regenerating oxaloacetate, and NAD + is reduced to NADH. Oxaloacetate can be used to combine with acetyl-CoA and the cycle is repeated. ...
... 9. L-malate is oxidised regenerating oxaloacetate, and NAD + is reduced to NADH. Oxaloacetate can be used to combine with acetyl-CoA and the cycle is repeated. ...
U4L21 fuel oxidation - The University of Sydney
... This material has been reproduced and communicated to you by or on behalf of the University of Sydney pursuant to Part VB of the Copyright Act 1968 (the Act). The material in this communication may be subject to copyright under the Act. Any further reproduction or communication of this material by y ...
... This material has been reproduced and communicated to you by or on behalf of the University of Sydney pursuant to Part VB of the Copyright Act 1968 (the Act). The material in this communication may be subject to copyright under the Act. Any further reproduction or communication of this material by y ...
Fructose-1,6 - LSU School of Medicine
... Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase is regulated at the level of ...
... Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase is regulated at the level of ...
Genomic characterization and phylogenetic analysis
... helicase motif (located at amino acids 1377-1486) were found in this deduced amino acid sequence. Interestingly, a calicivirus coat protein motif was found at amino acids 439-564, which was the first time this motif has been identified in the SBV encoded protein. These results indicate that structur ...
... helicase motif (located at amino acids 1377-1486) were found in this deduced amino acid sequence. Interestingly, a calicivirus coat protein motif was found at amino acids 439-564, which was the first time this motif has been identified in the SBV encoded protein. These results indicate that structur ...
powerpoint
... Same substrate with two separate enzymes. Higher the Km the lower the affinity. Differences in first order and mixed order ...
... Same substrate with two separate enzymes. Higher the Km the lower the affinity. Differences in first order and mixed order ...
Searching for Binding Partners for the Novel PHKG1 Variant, PhKγ
... NOVEL PHKG1 VARIANT, PhK-γ181 ...
... NOVEL PHKG1 VARIANT, PhK-γ181 ...
2nd Phase of Glycolysis
... loss of CO2 to produce acetyl-CoA and NADH. AcetylCoA then enters the citric acid cycle where it is completely oxidized into CO2 and H2O. Under aerobic conditions the NADH produced from glycolysis and the citric acid cycle are reoxidized into NAD+ in the ...
... loss of CO2 to produce acetyl-CoA and NADH. AcetylCoA then enters the citric acid cycle where it is completely oxidized into CO2 and H2O. Under aerobic conditions the NADH produced from glycolysis and the citric acid cycle are reoxidized into NAD+ in the ...
Nutrition
... results in the formation of ketones (ketoacids) which can be deadly because they lower the blood pH resulting in ketoacidosis ...
... results in the formation of ketones (ketoacids) which can be deadly because they lower the blood pH resulting in ketoacidosis ...
Standard Assays Offered by the Lipomics Laboratory. • Lipid
... preparation methodology, with the goal of ensuring maximum metabolite recovery with minimum disruption to the metabolome. A typical extraction protocol for recovery of polar metabolites from tissue begins with cryo-pulverization to yield a fine powder. Ice-cold extraction solvent, typically 75% 9:1 ...
... preparation methodology, with the goal of ensuring maximum metabolite recovery with minimum disruption to the metabolome. A typical extraction protocol for recovery of polar metabolites from tissue begins with cryo-pulverization to yield a fine powder. Ice-cold extraction solvent, typically 75% 9:1 ...
CARBOHYDRATE METABOLISM - UNAIR | E
... oxidation of glucose energy It can function either aerobically or anaerobically pyruvate Occurs in the cytosol of all cell AEROBICALLY GLYCOLYSIS : Pyruvate Mitochondria Asetil CoA Kreb’s Cycle ...
... oxidation of glucose energy It can function either aerobically or anaerobically pyruvate Occurs in the cytosol of all cell AEROBICALLY GLYCOLYSIS : Pyruvate Mitochondria Asetil CoA Kreb’s Cycle ...
الشريحة 1
... A plate assay was further designed to detect bacterial lipases in a medium containing trioleylglycerol and the fluorescent dye rhodamine ...
... A plate assay was further designed to detect bacterial lipases in a medium containing trioleylglycerol and the fluorescent dye rhodamine ...
ACID - TeacherWeb
... Acids taste sour (e.g. vinegar, lemon juice). Acids are harmful to living cells. Aqueous solutions of all acids contain hydrogen ions. Acid turns blue litmus red. Strong acids are corrosive. ...
... Acids taste sour (e.g. vinegar, lemon juice). Acids are harmful to living cells. Aqueous solutions of all acids contain hydrogen ions. Acid turns blue litmus red. Strong acids are corrosive. ...
FMOC The solid phase peptide synthesis (SPPS) was first
... human parathyroid hormone (84 residues), HIV-1 aspartyl protease (99 residues) and interleukin-3 (140 residues). The developments in Fmoc SPPS (Fields and Noble, 1990) can be summarized by the following categories: solid supports, linkers, the first residue attachment, protecting groups, Fmoc depro ...
... human parathyroid hormone (84 residues), HIV-1 aspartyl protease (99 residues) and interleukin-3 (140 residues). The developments in Fmoc SPPS (Fields and Noble, 1990) can be summarized by the following categories: solid supports, linkers, the first residue attachment, protecting groups, Fmoc depro ...
Continued..
... over a span of 150 or more amino acids, they are probably significantly related. If we consider an alignment of just 70 amino acids, it is popular to consider the two sequences significantly related if they share 25% amino acid identity. In 1998, Brenner et al., have shown that this may be erroneo ...
... over a span of 150 or more amino acids, they are probably significantly related. If we consider an alignment of just 70 amino acids, it is popular to consider the two sequences significantly related if they share 25% amino acid identity. In 1998, Brenner et al., have shown that this may be erroneo ...
Condensation Polymerisation
... of glucose molecules. A condensation polymer is a polymer formed by the removal of atoms from adjacent monomer molecules to allow them to join together. Small molecules are produced as well as the polymer molecule and the process is known as condensation polymerisation. Formation of starch from gluc ...
... of glucose molecules. A condensation polymer is a polymer formed by the removal of atoms from adjacent monomer molecules to allow them to join together. Small molecules are produced as well as the polymer molecule and the process is known as condensation polymerisation. Formation of starch from gluc ...
Cell Quiz Review
... 19) Regarding enzyme kinetics, the substrate concentration at which the reaction velocity is equal to 0.5 Vmax is referred to as: 20) Zero-order kinetics occurs during the beginning of an enzyme-catalyzed reaction when a substrate concentration is high and the rate of the reaction is _____ on the __ ...
... 19) Regarding enzyme kinetics, the substrate concentration at which the reaction velocity is equal to 0.5 Vmax is referred to as: 20) Zero-order kinetics occurs during the beginning of an enzyme-catalyzed reaction when a substrate concentration is high and the rate of the reaction is _____ on the __ ...
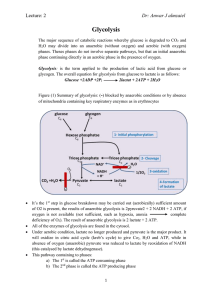
Dr: Anwar J almzaiel Glycolysis
... Under aerobic condition, lactate no longer produced and pyruvate is the major product. It will oxidize in citric acid cycle (kreb’s cycle) to give Co2, H2O and ATP, while in absence of oxygen (anaerobic) pyruvate was reduced to lactate by reoxidation of NADH (this catalysed by lactate dehydrogenase) ...
... Under aerobic condition, lactate no longer produced and pyruvate is the major product. It will oxidize in citric acid cycle (kreb’s cycle) to give Co2, H2O and ATP, while in absence of oxygen (anaerobic) pyruvate was reduced to lactate by reoxidation of NADH (this catalysed by lactate dehydrogenase) ...
Applied and Environmental Microbiology
... abolished nitrogenase activity in the presence of malate. A. amazonense strains grew best with glutamate and alanine (Table 1). All amino acids that were tested inhibited the nitrogen fixation ability of A. amazonense at high concentrations. In contrast, A. brasiliense strains did not grow as well o ...
... abolished nitrogenase activity in the presence of malate. A. amazonense strains grew best with glutamate and alanine (Table 1). All amino acids that were tested inhibited the nitrogen fixation ability of A. amazonense at high concentrations. In contrast, A. brasiliense strains did not grow as well o ...
effect of arsenic stress on amino acid profile
... (R=0.236) in roots of HARG. On the other hand, the induction in Gly synthesis was linearly correlated in both the genotypes upon AsIII and AsV exposure. Proline content was especially significantly correlated to As accumulations in LARG shoots and roots (R=0.919*** and R=0.924** respectively), while ...
... (R=0.236) in roots of HARG. On the other hand, the induction in Gly synthesis was linearly correlated in both the genotypes upon AsIII and AsV exposure. Proline content was especially significantly correlated to As accumulations in LARG shoots and roots (R=0.919*** and R=0.924** respectively), while ...
Document
... assumption is that this group will (randomly) adopt one of 4 possible structures helix, sheet, turn or loop (other). The program then asks whether this assumed “ministructure” is energetically suited to the six amino acids on either side. The program then moves on to the next (overlapped) set of res ...
... assumption is that this group will (randomly) adopt one of 4 possible structures helix, sheet, turn or loop (other). The program then asks whether this assumed “ministructure” is energetically suited to the six amino acids on either side. The program then moves on to the next (overlapped) set of res ...
Lab Module 8: Phenol-Red Carbohydrate Fermentation Broths
... convert that carb to glucose (Step One, above). Among those bacteria that can ferment a particular carbohydrate, there are also a variety of types of by-products. Lactobacillus (and human muscle cells) forms lactic acid as a fermentation by-product. Acetobacter forms acetic acid. Many bacteria form ...
... convert that carb to glucose (Step One, above). Among those bacteria that can ferment a particular carbohydrate, there are also a variety of types of by-products. Lactobacillus (and human muscle cells) forms lactic acid as a fermentation by-product. Acetobacter forms acetic acid. Many bacteria form ...