Nucleoside Phosphoramidate Monoesters: Potential
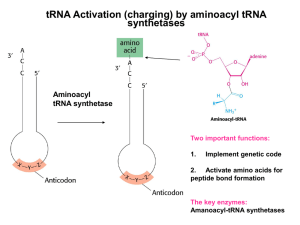
... The accuracy of protein synthesis depends on correct charging of tRNAs with amino acids 1. tRNA synthetases must link tRNAs with their correct amino acids. 2. tRNA synthetases recognize correct amino acids by specific binding to the active site and proofreading. 3. tRNA synthetases recognize correc ...
... The accuracy of protein synthesis depends on correct charging of tRNAs with amino acids 1. tRNA synthetases must link tRNAs with their correct amino acids. 2. tRNA synthetases recognize correct amino acids by specific binding to the active site and proofreading. 3. tRNA synthetases recognize correc ...
Camp 1 - Dr. Paul J. McElligott
... no enzyme activity • it becomes active only after a six-amino acid fragment is hydrolyzed from the N-terminal end of its chain • removal of this small fragment changes in not only the primary structure but also the tertiary structure, allowing the molecule to achieve its active form © 2003 Thomson L ...
... no enzyme activity • it becomes active only after a six-amino acid fragment is hydrolyzed from the N-terminal end of its chain • removal of this small fragment changes in not only the primary structure but also the tertiary structure, allowing the molecule to achieve its active form © 2003 Thomson L ...
comparison free energy binding sites
... that hosts cell hold in this site when there is not inhibitor Sialic acid , on the other hand is inhibitor binding site [16].( Sialic acid active site = Inhibitor site ) There are 4 amino acid involved with altering or drug that include: Asp151,Glu276,Arg152 and Arg371[9,14] .That introduced as bind ...
... that hosts cell hold in this site when there is not inhibitor Sialic acid , on the other hand is inhibitor binding site [16].( Sialic acid active site = Inhibitor site ) There are 4 amino acid involved with altering or drug that include: Asp151,Glu276,Arg152 and Arg371[9,14] .That introduced as bind ...
Force Field
... The null-model is the model that assumes that there is no signal in the input data. In case of our Chou-and-Fasman example, the null model assumes that there is no relation between the amino acid type and the secondary structure. So, if 7% (0.07) of all amino acids are of type Ala, and ~34% (0.34) o ...
... The null-model is the model that assumes that there is no signal in the input data. In case of our Chou-and-Fasman example, the null model assumes that there is no relation between the amino acid type and the secondary structure. So, if 7% (0.07) of all amino acids are of type Ala, and ~34% (0.34) o ...
Amino Acid Composition of Enzymatically Hydrolysed Potato Protein
... Flavourzyme, it contributed to a further but slight increase in nitrogen solubility (up to 67.60% in PII preparation), particularly in preparations obtained in laboratory conditions. It was confirmed that the enzyme coming from the Aspergillus oryzae strain (enzyme F) is active both as an endo- as w ...
... Flavourzyme, it contributed to a further but slight increase in nitrogen solubility (up to 67.60% in PII preparation), particularly in preparations obtained in laboratory conditions. It was confirmed that the enzyme coming from the Aspergillus oryzae strain (enzyme F) is active both as an endo- as w ...
Enzymes: Principles of Catalysis
... • The enzyme lowers the activation barrier compared to the uncatalyzed aqueous reaction • In theory, the enzyme may also facilitate the tunneling through the barrier. This may be important for ...
... • The enzyme lowers the activation barrier compared to the uncatalyzed aqueous reaction • In theory, the enzyme may also facilitate the tunneling through the barrier. This may be important for ...
Document
... one morning that his right big toe was swollen and painful to touch. He attributed the pain to “stubbing” his toe two days earlier on a coffee table. He initially took aspirin and Tylenol with some minimal improvement in the pain, but over the past week the pain has increased and now the big toe is ...
... one morning that his right big toe was swollen and painful to touch. He attributed the pain to “stubbing” his toe two days earlier on a coffee table. He initially took aspirin and Tylenol with some minimal improvement in the pain, but over the past week the pain has increased and now the big toe is ...
The activity reaction core and plasticity of metabolic networks
... To examine the utilization and relative flux rates of each metabolic reaction in a wide range of simulated environmental conditions ...
... To examine the utilization and relative flux rates of each metabolic reaction in a wide range of simulated environmental conditions ...
Biochemistry 2EE3 Metabolism and Physiological Chemistry 2002
... Purpose: To provide a brief introduction to proteins, enzymes and gene expression followed by a more detailed treatment of energy and intermediary metabolism with emphasis on physiological chemistry Learning objectives: Understanding principles of structure and function of biological macromolecules, ...
... Purpose: To provide a brief introduction to proteins, enzymes and gene expression followed by a more detailed treatment of energy and intermediary metabolism with emphasis on physiological chemistry Learning objectives: Understanding principles of structure and function of biological macromolecules, ...
Chapter 13 - TCA Cycle
... NADH that is used in numerous other biochemical reactions. Its central importance to many biochemical pathways suggests that it was one of the earliest established components of cellular metabolism. ...
... NADH that is used in numerous other biochemical reactions. Its central importance to many biochemical pathways suggests that it was one of the earliest established components of cellular metabolism. ...
Chapter 4 powerpoint file
... They only perform one specific reaction While they change the reactants into new products enzymes themselves are not changed during a reaction They can be re-used multiple times They may be permanently or temporarily inhibited ...
... They only perform one specific reaction While they change the reactants into new products enzymes themselves are not changed during a reaction They can be re-used multiple times They may be permanently or temporarily inhibited ...
Metabolism and Glycolysis
... 3) Place where it happens (organs, types of cell, subcellular compartments). 4) Regulatory enzymes. (Metabolic conditions that stimulate or inhibit the pathway). 5) Organization of the pathway and the formulas of the compounds involved. (The map of the pathway). 6) Relationship with other pathways. ...
... 3) Place where it happens (organs, types of cell, subcellular compartments). 4) Regulatory enzymes. (Metabolic conditions that stimulate or inhibit the pathway). 5) Organization of the pathway and the formulas of the compounds involved. (The map of the pathway). 6) Relationship with other pathways. ...
Appendix C - Detailed Research ...
... and store glycogen, the resulting acetyl-CoA units derived from carbohydrates (and under some conditions, also proteins) are turned into fatty acids and cholesterol at the first step of the Krebs Cycle. Acetyl-CoA, the primary substrate for fatty acid biosynthesis, is a product of pyruvate oxidation ...
... and store glycogen, the resulting acetyl-CoA units derived from carbohydrates (and under some conditions, also proteins) are turned into fatty acids and cholesterol at the first step of the Krebs Cycle. Acetyl-CoA, the primary substrate for fatty acid biosynthesis, is a product of pyruvate oxidation ...
Representations of 3D Structures
... A b-strand is distinguished by strong CaHi-NHi+1contacts and long range nOes connecting the strands. A long range nOe connects residues more than 5 residues apart in the chain. ...
... A b-strand is distinguished by strong CaHi-NHi+1contacts and long range nOes connecting the strands. A long range nOe connects residues more than 5 residues apart in the chain. ...
WP4 - Hamish Collin
... There is evidence in the literature that some purified cysteine synthase type enzymes are multifunctional and amongst other reactions can take allyl thiol and attach it to an amino acid skeleton to make Allyl cysteine Some other ß-substituted alanines (secondary plant products such as mimosine) are ...
... There is evidence in the literature that some purified cysteine synthase type enzymes are multifunctional and amongst other reactions can take allyl thiol and attach it to an amino acid skeleton to make Allyl cysteine Some other ß-substituted alanines (secondary plant products such as mimosine) are ...
Lipids General function
... Secretion of lipids from intestine mucosal cell: A disease called chyle= leakage of the lipid rich lymph into: a.abdominal cavity (chylo abdomen) b.pleural cavity (chylo thorax) c. urine cavity (chyluria) result from obstruction to transportation in the lymphatics intestinal resynthesis of triglycer ...
... Secretion of lipids from intestine mucosal cell: A disease called chyle= leakage of the lipid rich lymph into: a.abdominal cavity (chylo abdomen) b.pleural cavity (chylo thorax) c. urine cavity (chyluria) result from obstruction to transportation in the lymphatics intestinal resynthesis of triglycer ...
Ultrasonic velocity and density values of L
... zwitterions to the bulk water. The larger partial molal compressibilities of L-phenylalanine, L-leucine, L-glutamic acid and L-proline in 2.0 M aqueous NaCl and 2.0 M aqueous NaNOs solutions than the corresponding values of ^l in water have been attributed to the formation of 'zwitterion-ion' and 'i ...
... zwitterions to the bulk water. The larger partial molal compressibilities of L-phenylalanine, L-leucine, L-glutamic acid and L-proline in 2.0 M aqueous NaCl and 2.0 M aqueous NaNOs solutions than the corresponding values of ^l in water have been attributed to the formation of 'zwitterion-ion' and 'i ...
Daily Essential Electrolytes, Protein, and Probiotics
... “family” of enzymes called metalloenzymes. They are named such because one or more metallic minerals play an essential role in their function. For example, copper is a key element in many enzymes that build or tear down body tissue. Manganese is used by enzymes needed to utilize several vitamins. Zi ...
... “family” of enzymes called metalloenzymes. They are named such because one or more metallic minerals play an essential role in their function. For example, copper is a key element in many enzymes that build or tear down body tissue. Manganese is used by enzymes needed to utilize several vitamins. Zi ...
Supplemental Table 1 A survey of AAS prediction methods and their
... et al. (2003) (58) ●Altering tree structure decreases performance; altering branch lengths does not affect performance as much. Herrgard et al. ●Using sequence and structure, this prediction method focuses on ...
... et al. (2003) (58) ●Altering tree structure decreases performance; altering branch lengths does not affect performance as much. Herrgard et al. ●Using sequence and structure, this prediction method focuses on ...
Daily Essential Electrolytes, Protein, and Probiotics
... “family” of enzymes called metalloenzymes. They are named such because one or more metallic minerals play an essential role in their function. For example, copper is a key element in many enzymes that build or tear down body tissue. Manganese is used by enzymes needed to utilize several vitamins. Zi ...
... “family” of enzymes called metalloenzymes. They are named such because one or more metallic minerals play an essential role in their function. For example, copper is a key element in many enzymes that build or tear down body tissue. Manganese is used by enzymes needed to utilize several vitamins. Zi ...
Biochemistry Lit Exam Concepts Soluble/Membrane protein function
... Metabolism: Be able to explain the chemical logic of a metabolic pathway, particularly those from primary metabolism (e.g. glycolysis, citric acid cycle, fatty acid biosynthesis, etc.). be able to adapt the chemical logic from a primary metabolic pathway to that of a secondary metabolic pathway. DNA ...
... Metabolism: Be able to explain the chemical logic of a metabolic pathway, particularly those from primary metabolism (e.g. glycolysis, citric acid cycle, fatty acid biosynthesis, etc.). be able to adapt the chemical logic from a primary metabolic pathway to that of a secondary metabolic pathway. DNA ...























