One amino acid makes the difference: the formation of ent
... the CPS and KS gene families have expanded in other plant species. Rice, for example, contains four CPS/CPSlike genes and eleven KS/KS-like genes involved in the production of a large variety of different labdane-type diterpenes [6, 18, 19]. Here, class I terpene synthases not mediating ent-kaurene ...
... the CPS and KS gene families have expanded in other plant species. Rice, for example, contains four CPS/CPSlike genes and eleven KS/KS-like genes involved in the production of a large variety of different labdane-type diterpenes [6, 18, 19]. Here, class I terpene synthases not mediating ent-kaurene ...
Anaerobic Respiration
... What would happen if the bucket was empty? How does the bucket normally stay full? ...
... What would happen if the bucket was empty? How does the bucket normally stay full? ...
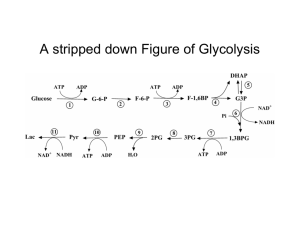
Glycolysis and gluconeogenesis
... Fatty acid biosynthesis and ketone bodies Pyruvate dehydrogenase, citric acid cycle and anaplerotic reactions Amino acid degradation and urea cycle Nitrogen metabolism: biosynthesis of amino acids, nucleotides and related molecules Oxidative phosphorylation and ATP synthesis Photosynthesis (light re ...
... Fatty acid biosynthesis and ketone bodies Pyruvate dehydrogenase, citric acid cycle and anaplerotic reactions Amino acid degradation and urea cycle Nitrogen metabolism: biosynthesis of amino acids, nucleotides and related molecules Oxidative phosphorylation and ATP synthesis Photosynthesis (light re ...
213lec6
... sequence of amino acids (primary structure). Hydrogen bonding within or between amino acids causes bending or coiling (secondary structure). Interactions between the side groups of the amino acids determine the three-dimensional shape of the protein (tertiary structure). Finally, the quaternary stru ...
... sequence of amino acids (primary structure). Hydrogen bonding within or between amino acids causes bending or coiling (secondary structure). Interactions between the side groups of the amino acids determine the three-dimensional shape of the protein (tertiary structure). Finally, the quaternary stru ...
SACE2 Chemistry Workbook Sample Chapter
... Figure 3.95: Hydrolysis of a triglyceride molecule in an alkaline solution. The hydrolysis of a triglyceride occurs inside the cells of living organisms including animals and plants. The hydrolysis reaction is catalysed by a class of enzymes called lipases. Lipases are present in the saliva and othe ...
... Figure 3.95: Hydrolysis of a triglyceride molecule in an alkaline solution. The hydrolysis of a triglyceride occurs inside the cells of living organisms including animals and plants. The hydrolysis reaction is catalysed by a class of enzymes called lipases. Lipases are present in the saliva and othe ...
No Slide Title
... The BLOSUM matrices (BLOcks SUbstitution Matrix) are based on the BLOCKS database. The BLOCKS database utilizes the concept of blocks (ungapped amino acid pattern), which act as signatures of a family of proteins. Substitution frequencies for all pairs of amino acids were then calculated and this us ...
... The BLOSUM matrices (BLOcks SUbstitution Matrix) are based on the BLOCKS database. The BLOCKS database utilizes the concept of blocks (ungapped amino acid pattern), which act as signatures of a family of proteins. Substitution frequencies for all pairs of amino acids were then calculated and this us ...
BS 11 First Mid-Term Answer Key Spring 1998
... Circle the residue(s) which is likely to be phosphorylated. Ans: The E. Of these amino acids, only the Glu is a good nucleophile. (2 pt) L) Mutation of S195, H57 and D102 of chymotrypsin to alanine residues yields an enzyme that enhances proteolysis rates by ~5x104 over the uncatalyzed reaction. The ...
... Circle the residue(s) which is likely to be phosphorylated. Ans: The E. Of these amino acids, only the Glu is a good nucleophile. (2 pt) L) Mutation of S195, H57 and D102 of chymotrypsin to alanine residues yields an enzyme that enhances proteolysis rates by ~5x104 over the uncatalyzed reaction. The ...
Chapter 2 ppt B
... – Displacement reactions occur forming water and a salt – Neutralization reaction • Joining of H+ and OH– to form water neutralizes ...
... – Displacement reactions occur forming water and a salt – Neutralization reaction • Joining of H+ and OH– to form water neutralizes ...
Plant and soil
... chromosome (Kaneko et al. 2010). To analyze the contribution of AAT1 to IAA biosynthesis, we constructed an AAT1 mutant by inserting a gusA-smrR cassette in the natural KpnI site found in the hisC1 sequence. The correct cassette orientation relative to the promoter was created in strain 7445, and st ...
... chromosome (Kaneko et al. 2010). To analyze the contribution of AAT1 to IAA biosynthesis, we constructed an AAT1 mutant by inserting a gusA-smrR cassette in the natural KpnI site found in the hisC1 sequence. The correct cassette orientation relative to the promoter was created in strain 7445, and st ...
Ch 3 Notes
... • Describe the induced fit model of enzyme action. • Compare the structure and function of each of the different types of lipids. • Compare the nucleic acids DNA and RNA. ...
... • Describe the induced fit model of enzyme action. • Compare the structure and function of each of the different types of lipids. • Compare the nucleic acids DNA and RNA. ...
Higher Human Biology HW 3
... (b) During Stage A, glucose is converted to pyruvate. Name the molecule that provides phosphate for this conversion. _________________________________________________________ ...
... (b) During Stage A, glucose is converted to pyruvate. Name the molecule that provides phosphate for this conversion. _________________________________________________________ ...
mb_ch03
... • Describe the induced fit model of enzyme action. • Compare the structure and function of each of the different types of lipids. • Compare the nucleic acids DNA and RNA. ...
... • Describe the induced fit model of enzyme action. • Compare the structure and function of each of the different types of lipids. • Compare the nucleic acids DNA and RNA. ...
Gregory Moy - University of Pennsylvania
... The first step in the experiment was the determination of the solubility of ovalbumin. By taking a five-gram sample of ovalbumin and submersing it in 100mL of deionized water, microfuging, and dessicating for a week, the solubility was obtained. After the dessication process, the final sample was we ...
... The first step in the experiment was the determination of the solubility of ovalbumin. By taking a five-gram sample of ovalbumin and submersing it in 100mL of deionized water, microfuging, and dessicating for a week, the solubility was obtained. After the dessication process, the final sample was we ...
Biomolecular chemistry 4. From amino acids to proteins
... • A: Histidine is very good at donating and accepting protons at physiological pH. This is a very important part of many enzyme mechanisms. I may have mentioned that histidine is not such a good nucleophile. For enzyme mechanisms that involve a nucleophilic attack on the substrate, cysteine would be ...
... • A: Histidine is very good at donating and accepting protons at physiological pH. This is a very important part of many enzyme mechanisms. I may have mentioned that histidine is not such a good nucleophile. For enzyme mechanisms that involve a nucleophilic attack on the substrate, cysteine would be ...
Principles of BIOCHEMISTRY
... • Muscles lack pyruvate dehydrogenase and cannot produce ethanol from pyruvate • Muscle lactate dehydrogenase converts pyruvate to lactate • This reaction regenerates NAD+ for use by glyceraldehyde 3phosphate dehydrogenase in glycolysis • Lactate formed in skeletal muscles during exercise is transpo ...
... • Muscles lack pyruvate dehydrogenase and cannot produce ethanol from pyruvate • Muscle lactate dehydrogenase converts pyruvate to lactate • This reaction regenerates NAD+ for use by glyceraldehyde 3phosphate dehydrogenase in glycolysis • Lactate formed in skeletal muscles during exercise is transpo ...
Enhancement of the Essential Amino Acid Composition of Food
... Glycolysis is finely adjusted [13] at irreversible reaction steps (pyruvate kinase, phosphoglycerate kinase, phosphofructokinase, hexokinase) that command large negative changes in free energy; the big picture being that the flow of carbon intermediary compounds through glycolysis and citric acid cy ...
... Glycolysis is finely adjusted [13] at irreversible reaction steps (pyruvate kinase, phosphoglycerate kinase, phosphofructokinase, hexokinase) that command large negative changes in free energy; the big picture being that the flow of carbon intermediary compounds through glycolysis and citric acid cy ...
Cellular Respiration - LaPazColegioWiki2013-2014
... Lactic acid fermentation ONLY ATP gained comes from glycolysis (the step ...
... Lactic acid fermentation ONLY ATP gained comes from glycolysis (the step ...
Protein quality measures - essential amino acids (EAAs
... vegetarian diets d. Rule of thumb: Regardless of protein sources, if tryptophan, lysine and sulfur (S)-amino acid (*) intake is sufficient (“limiting amino acids”), the remaining EAAs are likely to be adequate in the overall daily diet ...
... vegetarian diets d. Rule of thumb: Regardless of protein sources, if tryptophan, lysine and sulfur (S)-amino acid (*) intake is sufficient (“limiting amino acids”), the remaining EAAs are likely to be adequate in the overall daily diet ...
Chapter 5 Polypeptides Geometry of Peptide Bond
... cyclic disulfide is formed as the product, and equilibrium lies toward this product even at lower dithiothreitol concentrations. The reduced cysteine residues would quickly re-form disulfide bonds by air oxidation unless they are modified by the alkylation reactions. Note—when amino acid analysis is ...
... cyclic disulfide is formed as the product, and equilibrium lies toward this product even at lower dithiothreitol concentrations. The reduced cysteine residues would quickly re-form disulfide bonds by air oxidation unless they are modified by the alkylation reactions. Note—when amino acid analysis is ...
Figure 17-3 Degradation of glucose via the glycolytic pathway.
... which must be generated in the mitochondria. OAA cannot be transported out so it must be converted to PEP or malate (or Asp but lets ignore that). Gluconeogenesis requires NADH so reducing equivalents must be generated for that purpose; cytoplasmic [NADH]/[NAD] is very low. ...
... which must be generated in the mitochondria. OAA cannot be transported out so it must be converted to PEP or malate (or Asp but lets ignore that). Gluconeogenesis requires NADH so reducing equivalents must be generated for that purpose; cytoplasmic [NADH]/[NAD] is very low. ...
Method to protect a targeted amino acid residue during random mutagenesis
... resulting in pUC-crtN. crtB was removed from previously constructed pUC-crtE-crtB-crtI (5), resulting in pUC-crtEcrtI. From these two plasmids, genes and promoters (lacP-crtN and lacP-crtE-crtI) were PCR ampli®ed and subcloned into the SalI site of pACYC184, resulting in pAC-crtN and pACcrtI-crtE, r ...
... resulting in pUC-crtN. crtB was removed from previously constructed pUC-crtE-crtB-crtI (5), resulting in pUC-crtEcrtI. From these two plasmids, genes and promoters (lacP-crtN and lacP-crtE-crtI) were PCR ampli®ed and subcloned into the SalI site of pACYC184, resulting in pAC-crtN and pACcrtI-crtE, r ...