Frederick Sanger - Nobel Lecture
... could be well separated since they were the only acidic peptides present. At this pH, - COOH groups are uncharged, -SO,H groups carry a negative and -NH2 groups a positive charge. Peptides without cysteic acid were all positively charged, those with one cysteic acid were neutral and could be separat ...
... could be well separated since they were the only acidic peptides present. At this pH, - COOH groups are uncharged, -SO,H groups carry a negative and -NH2 groups a positive charge. Peptides without cysteic acid were all positively charged, those with one cysteic acid were neutral and could be separat ...
Albumin from chicken egg white (A7641) - Product - Sigma
... Sigma-Aldrich, Inc. warrants that its products conform to the information contained in this and other Sigma-Aldrich publications. Purchaser must determine the suitability of the product(s) for their particular use. Additional terms and conditions may apply. Please see reverse side of the invoice or ...
... Sigma-Aldrich, Inc. warrants that its products conform to the information contained in this and other Sigma-Aldrich publications. Purchaser must determine the suitability of the product(s) for their particular use. Additional terms and conditions may apply. Please see reverse side of the invoice or ...
Higher Human Biology unit 1 section 5 ENZYMES
... • A 1 molar solution is produced when 138g are dissolved in 1 litre of water. • A 0.1 molar solution is produced when 13.8g are dissolved in 100ml of water • A 0.01 molar solution is produced when 1.38g are dissolved in 100ml of water Work out what weights of sodium phosphate need to be added to 100 ...
... • A 1 molar solution is produced when 138g are dissolved in 1 litre of water. • A 0.1 molar solution is produced when 13.8g are dissolved in 100ml of water • A 0.01 molar solution is produced when 1.38g are dissolved in 100ml of water Work out what weights of sodium phosphate need to be added to 100 ...
Enzymes
... Competitive inhibition • Competitive inhibitor „competes“ with a substrate S for binding at enzyme´s active site. • It is bound to an active site but not converted by the enzyme. • Vmax value is unchanged. • KM value is elevated (it is necessary to add more S to reach the original enzyme activity) ...
... Competitive inhibition • Competitive inhibitor „competes“ with a substrate S for binding at enzyme´s active site. • It is bound to an active site but not converted by the enzyme. • Vmax value is unchanged. • KM value is elevated (it is necessary to add more S to reach the original enzyme activity) ...
The Genetic Code: Yesterday, Today, and Tomorrow
... machinery including tRNAs, aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases, elongation factors, and tRNA modification enzymes [13]. Even before the advent of genome sequencing, it was evident that the genetic code changed during evolution [14]. In currently known organisms, over 20 examples are known where individual or ...
... machinery including tRNAs, aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases, elongation factors, and tRNA modification enzymes [13]. Even before the advent of genome sequencing, it was evident that the genetic code changed during evolution [14]. In currently known organisms, over 20 examples are known where individual or ...
ATP citrate lyase – biology and implication in human
... The primary sequence of rat liver ACLY has been obtained from a cDNA clone and its amino acid sequence was showed to have a high similarity with the alpha chain of succinyl-CoA synthetase of Escherichia coli7. Both enzymes catalyse similar reactions. The first reaction step for both of them is autop ...
... The primary sequence of rat liver ACLY has been obtained from a cDNA clone and its amino acid sequence was showed to have a high similarity with the alpha chain of succinyl-CoA synthetase of Escherichia coli7. Both enzymes catalyse similar reactions. The first reaction step for both of them is autop ...
The Mucopeptides of Bacterial Cell Walls. A Review
... were grown in a basal salts and glucose medium with lysine and diaminopimelic acid, but in each experiment either the glucose, lysine or diaminopimelic acid was totally labelled with 14C. The cell walls were fractionated with phenol, and the insoluble portions, containing most of the mucopeptide, we ...
... were grown in a basal salts and glucose medium with lysine and diaminopimelic acid, but in each experiment either the glucose, lysine or diaminopimelic acid was totally labelled with 14C. The cell walls were fractionated with phenol, and the insoluble portions, containing most of the mucopeptide, we ...
Nomenclature and Symbolism for Amino, Acids and Peptides
... Semisystematic names of substituted a-amino acids are formed according to the general principles of organic nomenclature [14], by attaching the name of the substituent group to the trivial name of the amino acid. The position of the substitution is indicated by locants (see 3AA-2.2). The configurati ...
... Semisystematic names of substituted a-amino acids are formed according to the general principles of organic nomenclature [14], by attaching the name of the substituent group to the trivial name of the amino acid. The position of the substitution is indicated by locants (see 3AA-2.2). The configurati ...
Chapter 3
... chiral center extend toward the viewer, vertical bonds extend away from the viewer • Abbreviations can be one letter or three letters • Amino acids are grouped by the properties of their side chains (R groups) • Classes: Aliphatic, Aromatic, Sulfur-containing, Alcohols, Bases, Acids and Amides Prent ...
... chiral center extend toward the viewer, vertical bonds extend away from the viewer • Abbreviations can be one letter or three letters • Amino acids are grouped by the properties of their side chains (R groups) • Classes: Aliphatic, Aromatic, Sulfur-containing, Alcohols, Bases, Acids and Amides Prent ...
Optimal dietary amino acid ratio for broilers based on dietary amino
... except the EAA under study. In all experimental diets, the remaining nutrient and energy contents were the same respectively. The nitrogen balance trials were divided into adaptation period (5 days) and two consecutive periods of excreta collection (5 days each). During this period the experimental ...
... except the EAA under study. In all experimental diets, the remaining nutrient and energy contents were the same respectively. The nitrogen balance trials were divided into adaptation period (5 days) and two consecutive periods of excreta collection (5 days each). During this period the experimental ...
Chapter 17 End?of?Chapter Problems Key
... stomach. (Obj #21) The acidic conditions in the stomach weaken the links between amino acids that hold the protein molecules in their tertiary structure. When the tertiary structure of proteins is relaxed, they are more easily digested. One way this is done is by disrupting salt bridges due to the r ...
... stomach. (Obj #21) The acidic conditions in the stomach weaken the links between amino acids that hold the protein molecules in their tertiary structure. When the tertiary structure of proteins is relaxed, they are more easily digested. One way this is done is by disrupting salt bridges due to the r ...
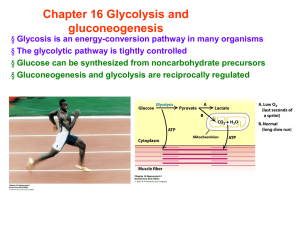
Chapter 16 Glycolysis and gluconeogenesis
... p. 452 There is a high incidence of cataract formation with age in populations that consume substantial amounts of milk into adulthood. ...
... p. 452 There is a high incidence of cataract formation with age in populations that consume substantial amounts of milk into adulthood. ...
Additional file 11 cd00120: MCM1, Agamous, Deficiens, and SRF
... and regulators (e.g. Regulator of G protein signaling (RGS) domains). Multiple sequence alignment were obtained from Pei et al., 2006 (19), where the main four subtypes are further divided into 11 subfamilies depending either on the taxonomy (like, plant, animal, fungal G proteins) and type of funct ...
... and regulators (e.g. Regulator of G protein signaling (RGS) domains). Multiple sequence alignment were obtained from Pei et al., 2006 (19), where the main four subtypes are further divided into 11 subfamilies depending either on the taxonomy (like, plant, animal, fungal G proteins) and type of funct ...
How to Find a Specific Gene or Protein to Study
... The initial search option, which is presented in the header as a text box with a "Go" button, is a keyword search against the text of the data records. Thus, it suffers from the same limitations as all keyword searches, such as misspellings and synonyms. Most genes and gene products can be described ...
... The initial search option, which is presented in the header as a text box with a "Go" button, is a keyword search against the text of the data records. Thus, it suffers from the same limitations as all keyword searches, such as misspellings and synonyms. Most genes and gene products can be described ...
Inhibition of Serine Amidohydrolases by Complexes of Vanadate
... Department of Chemistry, Wesleyan University, Middletown, Connecticut 06459 ...
... Department of Chemistry, Wesleyan University, Middletown, Connecticut 06459 ...
... b) the binding of the first ligand raises the KD for binding of the second. c) the binding of the first ligand raises the KA for binding of the second. d) cannot bind more than one ligand. 10. The hormones, glucagon and epinephrine, stimulate glycogen breakdown to G-6-P a) directly, by binding to gl ...
... Identify ATP as the high energy compound which transfers energy, and is produced when ADP combines with phosphate in phosphorylation, building up energy, and releases energy when broken down into ADP and phosphate once more. State that cells use high energy electrons to pump hydrogen ions across a m ...
Function of Biomolecules Worksheet
... Use the information in the diagrams to determine which biomolecules are being compared 12. Which set of biomolecules is being compared in the diagram to the right? A carbohydrates and proteins B n ...
... Use the information in the diagrams to determine which biomolecules are being compared 12. Which set of biomolecules is being compared in the diagram to the right? A carbohydrates and proteins B n ...
Ch 19 - Chemistry Courses: About
... Glucose Entry into Cells • Tissues have unique function • Isozymes of glucose transporter, GLUT – Insulin dependent in muscle – Higher [glucose] required for liver uptake ...
... Glucose Entry into Cells • Tissues have unique function • Isozymes of glucose transporter, GLUT – Insulin dependent in muscle – Higher [glucose] required for liver uptake ...
Name: __ Date: Homework: The Function of Biomolecules Answer
... Answer the following questions about the biomolecules. 1. Both complex carbohydrates and lipids can provide energy to your body as they are broken down. However, only carbohydrates are broken down into which of the following subunits? A sugars B amino acids C nucleotides D fats 2. Amino acids and su ...
... Answer the following questions about the biomolecules. 1. Both complex carbohydrates and lipids can provide energy to your body as they are broken down. However, only carbohydrates are broken down into which of the following subunits? A sugars B amino acids C nucleotides D fats 2. Amino acids and su ...