Presentation
... in this pocket to ensure tight binding We also looked for other potential binding sites in nearby amino acids ...
... in this pocket to ensure tight binding We also looked for other potential binding sites in nearby amino acids ...
Microbiology - Chapter 7 & 8
... Note: ATP is a ribonucleotide, it has ribose, a nitogenous base (adenine), and phosphate. The high energy bond of the terminal of the three phosphates is the one cyclically broken and regenerated. Sugars like glucose can be broken down in a catabolic pathway controlled by many cellular enzymes. Some ...
... Note: ATP is a ribonucleotide, it has ribose, a nitogenous base (adenine), and phosphate. The high energy bond of the terminal of the three phosphates is the one cyclically broken and regenerated. Sugars like glucose can be broken down in a catabolic pathway controlled by many cellular enzymes. Some ...
Topic 9: Respiration
... Understand basic process for recovering energy from sugar and other organic molecules. ...
... Understand basic process for recovering energy from sugar and other organic molecules. ...
Protein Synthesis
... tRNA • If the 3 base anticodon of the tRNA complements the 3 base codon of the mRNA, they briefly combine. • The amino acid is left behind when the tRNA leaves. • As each codon is read, the next tRNA brings in a new amino acid and the polypeptide (protein) chain grows. • This requires enzymes and A ...
... tRNA • If the 3 base anticodon of the tRNA complements the 3 base codon of the mRNA, they briefly combine. • The amino acid is left behind when the tRNA leaves. • As each codon is read, the next tRNA brings in a new amino acid and the polypeptide (protein) chain grows. • This requires enzymes and A ...
Ch. 13 end of chapter review
... Years ago geneticists discovered a fly gene they called eyeless. Mutations that inactivate this gene cause flies to develop without eyes. Geneticists later discovered a mouse gene, called Pax6, that was homologous to eyeless. Transplanting an activated Pax6 gene into a fruit fly can cause the fly to gro ...
... Years ago geneticists discovered a fly gene they called eyeless. Mutations that inactivate this gene cause flies to develop without eyes. Geneticists later discovered a mouse gene, called Pax6, that was homologous to eyeless. Transplanting an activated Pax6 gene into a fruit fly can cause the fly to gro ...
USMLE STEP 1 Review: Week 3, Biochemistry
... Acquired (liver disease) or hereditary (urea enzyme deficiencies) Results in excess NH4+, depletes αketoglutarate, inhibits TCA cycle Tremor, slurring speech, somnolence, vomiting, cerebral edema, blurred vision Treat with benzoate, phenylbutyrate ...
... Acquired (liver disease) or hereditary (urea enzyme deficiencies) Results in excess NH4+, depletes αketoglutarate, inhibits TCA cycle Tremor, slurring speech, somnolence, vomiting, cerebral edema, blurred vision Treat with benzoate, phenylbutyrate ...
Insights From The Molecular Docking Of
... 9], DNA binding proteins [2, 4, 10], Rhodopsin family [11], metal binding proteins [12], sugar metabolizing proteins [13] and receptors [14] carrying out complex functions. However, the precise function of these palindromic sequences has not yet been fully understood. Palindromic sequences in protei ...
... 9], DNA binding proteins [2, 4, 10], Rhodopsin family [11], metal binding proteins [12], sugar metabolizing proteins [13] and receptors [14] carrying out complex functions. However, the precise function of these palindromic sequences has not yet been fully understood. Palindromic sequences in protei ...
Chapter 15 The Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle
... becomes acyl-CoA inside mitochodria, which is utilized for acetyl-CoA by -oxidation. : Carnitine acyltransferase I, carrior protein and carnitine acyltransferase II Multienzyme complexes in TCA cycle : pyruvate dehydrogenase, -ketoglutarate dehydrogenase ...
... becomes acyl-CoA inside mitochodria, which is utilized for acetyl-CoA by -oxidation. : Carnitine acyltransferase I, carrior protein and carnitine acyltransferase II Multienzyme complexes in TCA cycle : pyruvate dehydrogenase, -ketoglutarate dehydrogenase ...
Chapter 3: The Chemical Basis for Life Lesson 2: Organic Compounds
... usually occur within organic compounds in smaller groups of elements called functional groups. When organic compounds react with other compounds, generally just the functional groups are involved. Therefore, functional groups generally determine the nature and functions of organic compounds. You can ...
... usually occur within organic compounds in smaller groups of elements called functional groups. When organic compounds react with other compounds, generally just the functional groups are involved. Therefore, functional groups generally determine the nature and functions of organic compounds. You can ...
Purification and amino acid sequence of sakacin A, a
... the calculated and the determined M , values indicated that the cysteine residues existed in the reduced state and were not engaged in intramolecular cystine bridging. Furthermore, when sakacin A was heated with 1 mM-Pmercaptoethanol at 80 "C for 10 min to ensure that the thiol residues existed in t ...
... the calculated and the determined M , values indicated that the cysteine residues existed in the reduced state and were not engaged in intramolecular cystine bridging. Furthermore, when sakacin A was heated with 1 mM-Pmercaptoethanol at 80 "C for 10 min to ensure that the thiol residues existed in t ...
Prebiotic synthesis from CO atmospheres: Implications for the
... gen (350 Torr; 99.8% 15N, Shoko, Tokyo) was enclosed in a glass tube (400 ml) containing liquid water (5 ml). 15N2 was used to identify possible contamination. The gas mixture was irradiated with protons generated by a van de Graaff accelerator (Tokyo Institute of Technology, Tokyo) at 297 K for 3 h ...
... gen (350 Torr; 99.8% 15N, Shoko, Tokyo) was enclosed in a glass tube (400 ml) containing liquid water (5 ml). 15N2 was used to identify possible contamination. The gas mixture was irradiated with protons generated by a van de Graaff accelerator (Tokyo Institute of Technology, Tokyo) at 297 K for 3 h ...
Assessment of grapevine nitrogen status and optimized nitrogen
... Wines made from two treatments from the Sauvignon blanc at Glen Manor Vineyards in 2013 were subjected to a trained consumer preference panel at the University of Arkansas in June 2014. The two treatments were the control (no N) and the 30 kg N/ha rate of N applied to the foliage of the vines. The p ...
... Wines made from two treatments from the Sauvignon blanc at Glen Manor Vineyards in 2013 were subjected to a trained consumer preference panel at the University of Arkansas in June 2014. The two treatments were the control (no N) and the 30 kg N/ha rate of N applied to the foliage of the vines. The p ...
Mistranslation and its control by tRNA synthetases
... Second, as shown in ageing bacteria, mistranslation is mutagenic, because of the DNA damage over many generations and the resulting errors of replication that come from the error-prone DNA repair system [11]. ...
... Second, as shown in ageing bacteria, mistranslation is mutagenic, because of the DNA damage over many generations and the resulting errors of replication that come from the error-prone DNA repair system [11]. ...
Proximate, Amino acid and Fatty acid profile of
... is considered benefit due to its involvement in the stabilization of the organisms during movements. Estimation of amino acids: The biological importance of protein is visibly reflected upon it essential amino acid content on the investigated species. The present study the twenty essential and non e ...
... is considered benefit due to its involvement in the stabilization of the organisms during movements. Estimation of amino acids: The biological importance of protein is visibly reflected upon it essential amino acid content on the investigated species. The present study the twenty essential and non e ...
Slide ()
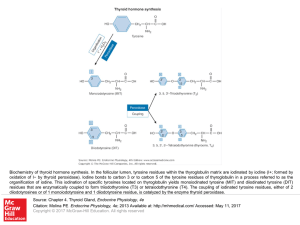
... Biochemistry of thyroid hormone synthesis. In the follicular lumen, tyrosine residues within the thyroglobulin matrix are iodinated by iodine (I+; formed by oxidation of I− by thyroid peroxidase). Iodine bonds to carbon 3 or to carbon 5 of the tyrosine residues of thyroglobulin in a process referred ...
... Biochemistry of thyroid hormone synthesis. In the follicular lumen, tyrosine residues within the thyroglobulin matrix are iodinated by iodine (I+; formed by oxidation of I− by thyroid peroxidase). Iodine bonds to carbon 3 or to carbon 5 of the tyrosine residues of thyroglobulin in a process referred ...