Bacterial methionine biosynthesis
... Methionine is a proteinogenic amino acid, best known for its role in the initiation of translation. It possesses an unbranched, hydrophobic side chain and it is the only amino acid that contains a thioether (i.e. C–S–C bonding). In general, methionine is assumed to play a simple structural role in t ...
... Methionine is a proteinogenic amino acid, best known for its role in the initiation of translation. It possesses an unbranched, hydrophobic side chain and it is the only amino acid that contains a thioether (i.e. C–S–C bonding). In general, methionine is assumed to play a simple structural role in t ...
answer key - chem.uwec.edu
... Chapter 14 – Metabolism: Basic Concepts and Design Be able to: • Classify organisms based on their source of energy. • Describe the energy requirements for living organisms. • Describe relationships between energy and metabolism. (Question 1) • Discuss phosphoryl transfer potentials and their import ...
... Chapter 14 – Metabolism: Basic Concepts and Design Be able to: • Classify organisms based on their source of energy. • Describe the energy requirements for living organisms. • Describe relationships between energy and metabolism. (Question 1) • Discuss phosphoryl transfer potentials and their import ...
proteins
... Whey • a by-product at (cottage) cheese production • yellowish liquid (the colour comes from riboflavin) • cca 12 % of high quality proteins (lactoalbumin, lactoglobulins) • rich in other B-complex vitamins and lactose • dried whey is available in shops (esp. fitness centres) ...
... Whey • a by-product at (cottage) cheese production • yellowish liquid (the colour comes from riboflavin) • cca 12 % of high quality proteins (lactoalbumin, lactoglobulins) • rich in other B-complex vitamins and lactose • dried whey is available in shops (esp. fitness centres) ...
Proteins of extracellular matrix
... 5. Secretion of procollagen molecules by exocytosis into the extracellular space. 6. Cleavage of registration peptides is catalysed by procollagen peptidases. The resulting molecule is called tropocollagen. 7. Oxidation – deamination of the hydroxylysine, the removal of (NH2) group has a net oxidat ...
... 5. Secretion of procollagen molecules by exocytosis into the extracellular space. 6. Cleavage of registration peptides is catalysed by procollagen peptidases. The resulting molecule is called tropocollagen. 7. Oxidation – deamination of the hydroxylysine, the removal of (NH2) group has a net oxidat ...
Energy Metabolism - Georgia Institute of Technology
... • More ADPfaster ATP – Discharge proton gradient – Lower ETC resitsance ...
... • More ADPfaster ATP – Discharge proton gradient – Lower ETC resitsance ...
Prelab Discussion
... Three pure slant cultures, one SIM tubes (3) each of: Proteus vulgaris Escherichia coli Klebsiella pneumoniae Work in a team of two students ...
... Three pure slant cultures, one SIM tubes (3) each of: Proteus vulgaris Escherichia coli Klebsiella pneumoniae Work in a team of two students ...
Chemistry 160:581 – Biochemistry - Syllabus for Fall 2014 Monday
... A strong prior preparation in organic chemistry and some preparation in physical chemistry are useful pre-requisites. This one-semester course introduces the structural aspects of the four major classes of biopolymers: nucleic acids, carbohydrates, proteins and lipids, with a significant emphasis on ...
... A strong prior preparation in organic chemistry and some preparation in physical chemistry are useful pre-requisites. This one-semester course introduces the structural aspects of the four major classes of biopolymers: nucleic acids, carbohydrates, proteins and lipids, with a significant emphasis on ...
344-352
... Although conventional hydrogen bonds that involve electronegative atoms like oxygen and nitrogen have been thoroughly studied over the decades since their first introduction into the literature and are presently well understood [19-21], but the CH…O interaction is thought to be crucial in a large of ...
... Although conventional hydrogen bonds that involve electronegative atoms like oxygen and nitrogen have been thoroughly studied over the decades since their first introduction into the literature and are presently well understood [19-21], but the CH…O interaction is thought to be crucial in a large of ...
Butyrate formation from glucose by the rumen protozoon Dasytricha
... that the glycolytic conversion of glucose into 3phosphoglyceric acid is associated with a microbody-like organelle termed the 'glycosome' (Opperdoes & Borst, 1977; Oduro, 1977; Taylor et al., 1980). The trypanosomes are completely dependent upon glycolysis for ATP synthesis (Bowman & Flynn, 1976), a ...
... that the glycolytic conversion of glucose into 3phosphoglyceric acid is associated with a microbody-like organelle termed the 'glycosome' (Opperdoes & Borst, 1977; Oduro, 1977; Taylor et al., 1980). The trypanosomes are completely dependent upon glycolysis for ATP synthesis (Bowman & Flynn, 1976), a ...
uptake of nutrients-2014
... concentration is higher on the outside of the cell, they cannot take up solutes that are already more concentrated within the cell (i.e., against a concentration gradient). Microorganisms often live in habitats characterized by very dilute nutrient sources, and, to flourish, they must be able to tra ...
... concentration is higher on the outside of the cell, they cannot take up solutes that are already more concentrated within the cell (i.e., against a concentration gradient). Microorganisms often live in habitats characterized by very dilute nutrient sources, and, to flourish, they must be able to tra ...
Sulfur Metabolism in Escherichia coli and Related Bacteria: Facts
... reaction is far from equilibrium. It cannot therefore be sufficient to pull the reaction toward synthesis of APS (Liu et al., 1998). This is why the synthesis of this latter molecule is also linked with hydrolysis of the ß,γ bond of GTP, which favors the reaction of sulfate incorporation (105-fold w ...
... reaction is far from equilibrium. It cannot therefore be sufficient to pull the reaction toward synthesis of APS (Liu et al., 1998). This is why the synthesis of this latter molecule is also linked with hydrolysis of the ß,γ bond of GTP, which favors the reaction of sulfate incorporation (105-fold w ...
exam1ans_2007 - algebra
... B is the correct answer– histidine, with a pKa of 6.0. The pKa at 2.0 is the carboxyl group, the pKa at 9.0 is the mainchain amino group. A (phenylalanine) is incorrect because it has no ionizable group on its sidechain. C (lysine) is incorrect because the pKa of its sidechain is 9.0. 2. (6 pts) The ...
... B is the correct answer– histidine, with a pKa of 6.0. The pKa at 2.0 is the carboxyl group, the pKa at 9.0 is the mainchain amino group. A (phenylalanine) is incorrect because it has no ionizable group on its sidechain. C (lysine) is incorrect because the pKa of its sidechain is 9.0. 2. (6 pts) The ...
8. Supplements
... BCAA's during training. Advocates of intra-workout supplements argue by supplying these critical constituents of muscle tissue during a time when blood flow to working muscles and muscle tissue breakdown is at a high level, trainees can have faster intra-set recovery as well as faster recovery and l ...
... BCAA's during training. Advocates of intra-workout supplements argue by supplying these critical constituents of muscle tissue during a time when blood flow to working muscles and muscle tissue breakdown is at a high level, trainees can have faster intra-set recovery as well as faster recovery and l ...
Doctorial Thesis Regulation of Branched
... Leucine is an essential branched-chain amino acid and plays a key role in protein synthesis through mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR). Recently, it has been reported that an oral administration of leucine has been revealed to influence the plasma concentrations of other amino acids not only isole ...
... Leucine is an essential branched-chain amino acid and plays a key role in protein synthesis through mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR). Recently, it has been reported that an oral administration of leucine has been revealed to influence the plasma concentrations of other amino acids not only isole ...
The Amino Acid Sequences of Cytochrome c from Four Plant Sources
... AMINO ACID SEQUENCES OF CYTOCHROME C since only three fragments remained to be ordered, one being blocked at the N-terminus and one having C-terminal serine or alanine, they may be ordered without recourse to homology. A total amino acid composition of the preparation used in this investigation is ...
... AMINO ACID SEQUENCES OF CYTOCHROME C since only three fragments remained to be ordered, one being blocked at the N-terminus and one having C-terminal serine or alanine, they may be ordered without recourse to homology. A total amino acid composition of the preparation used in this investigation is ...
Self-Referential Encoding on Modules of Anticodon Pairs—Roots of
... indication on the process. Dimers are considered mimics of the ribosomes—structures that hold tRNAs together and facilitate the transferase reaction, and of the translation process—anticodons are at the same time codons for each other. The primitive protein synthesis system gets stabilized when the ...
... indication on the process. Dimers are considered mimics of the ribosomes—structures that hold tRNAs together and facilitate the transferase reaction, and of the translation process—anticodons are at the same time codons for each other. The primitive protein synthesis system gets stabilized when the ...
Solution Worksheet Respiration
... 4 CO2 are released and the liberated energy is captured in the form of electrons/hydrogens and passed onto the co-enzymes NAD+ and FAD How many ATP are made in the electron transport part of cellular respiration? About 28 ATP via the process of chemiosmosis. NADH and FADH2 pass their Electrons to th ...
... 4 CO2 are released and the liberated energy is captured in the form of electrons/hydrogens and passed onto the co-enzymes NAD+ and FAD How many ATP are made in the electron transport part of cellular respiration? About 28 ATP via the process of chemiosmosis. NADH and FADH2 pass their Electrons to th ...
24,7 Loctic Fermentotion
... requires the expenditure of one of the sixAIP molecules invested in gluconeogenesis.Pyruvate carboxylase,the enzyme that catalyzes the reaction, requires the B-complex vitamin biotin as the coenzyrne.The biotin servesas a carrier of carbon dioxide in this and other biological carboxylation reactions ...
... requires the expenditure of one of the sixAIP molecules invested in gluconeogenesis.Pyruvate carboxylase,the enzyme that catalyzes the reaction, requires the B-complex vitamin biotin as the coenzyrne.The biotin servesas a carrier of carbon dioxide in this and other biological carboxylation reactions ...
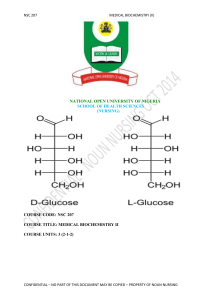
NSC 207 - National Open University of Nigeria
... laboratory. The interactive online activities will be available to you on the course link on the Website of NOUN. There are activities and assignments online for every unit every week. It is important that you visit the course sites weekly and do all assignments to meet deadlines and to contribute ...
... laboratory. The interactive online activities will be available to you on the course link on the Website of NOUN. There are activities and assignments online for every unit every week. It is important that you visit the course sites weekly and do all assignments to meet deadlines and to contribute ...
Building Triketide α-Pyrone-Producing Yeast Platform Using
... expression of heterologous genes. Using sets of dual expression vectors with different selectable makers on plasmids, it is possible to express various combinations of genes in a single stain. This system allows for the reconstruction of plant natural product biosynthetic pathways in yeast [14, 16]. ...
... expression of heterologous genes. Using sets of dual expression vectors with different selectable makers on plasmids, it is possible to express various combinations of genes in a single stain. This system allows for the reconstruction of plant natural product biosynthetic pathways in yeast [14, 16]. ...
3D Structures of Biological Macromolecules Jürgen Sühnel
... Entries listed by method of structure determination: Diffraction NMR Modeling ...
... Entries listed by method of structure determination: Diffraction NMR Modeling ...
PPT - FLI - Leibniz Institute for Age Research
... Entries listed by method of structure determination: Diffraction NMR Modeling ...
... Entries listed by method of structure determination: Diffraction NMR Modeling ...