Chemical synthesis of proteins
... is limited by the synthetic efficiency of each step. As discussed by Kent22, the synthesis of a 100-residue protein with 99.9% efficiency at each step provides a 90% overall yield of the desired product; 97% efficiency provides a 5% overall yield. The effective solvation of the peptide–resin complex ...
... is limited by the synthetic efficiency of each step. As discussed by Kent22, the synthesis of a 100-residue protein with 99.9% efficiency at each step provides a 90% overall yield of the desired product; 97% efficiency provides a 5% overall yield. The effective solvation of the peptide–resin complex ...
Functions of Ribosome-Associated Chaperones and their Interaction
... Crystallization of the N-terminal fragment of E. coli TF together with the 50S large ribosomal subunit from Haloarcula marismortui allowed the superposition of full-length TF with ribosomes and paved the way for understanding how this chaperone functions on ribosomes [9]. TF binds to the ribosomal p ...
... Crystallization of the N-terminal fragment of E. coli TF together with the 50S large ribosomal subunit from Haloarcula marismortui allowed the superposition of full-length TF with ribosomes and paved the way for understanding how this chaperone functions on ribosomes [9]. TF binds to the ribosomal p ...
ELEMENTARY STEPS IN ENZYME CATALYSIS AND REGULATION
... observed. The molecular weight dependence of the relaxation time is quite striking: the relaxation time increases with increasing molecular weight until a molecular weight of about 4000 is reached and then remains essentially constant (at 6 x 10" s) as the molecular weight is further increased34. Th ...
... observed. The molecular weight dependence of the relaxation time is quite striking: the relaxation time increases with increasing molecular weight until a molecular weight of about 4000 is reached and then remains essentially constant (at 6 x 10" s) as the molecular weight is further increased34. Th ...
nutrient composition of dandelions and its potential as human food
... the filtrate with acid and heat. The effects of pH, moisture content, pressure and temperature on the extractability and quality of protein were investigated. A mass balance was performed on dry matter and protein contents during the extraction steps. Proximate analysis was performed on the extracte ...
... the filtrate with acid and heat. The effects of pH, moisture content, pressure and temperature on the extractability and quality of protein were investigated. A mass balance was performed on dry matter and protein contents during the extraction steps. Proximate analysis was performed on the extracte ...
Ten remarks on peptide bond formation on the ribosome
... and shows deficiencies in PT activity and impaired binding of tRNA to the A site [15]. H. marismortui ribosomes do not have protein L27 or any homologous counterpart, indicating that L27 cannot be a part of an evolutionarily conserved PT mechanism which is expected to employ the same residues in all ...
... and shows deficiencies in PT activity and impaired binding of tRNA to the A site [15]. H. marismortui ribosomes do not have protein L27 or any homologous counterpart, indicating that L27 cannot be a part of an evolutionarily conserved PT mechanism which is expected to employ the same residues in all ...
1 ENZYME KINETICS [APPLICATION OF UV
... influenced by several factors such as substrate concentration, temperature, pH and the presence of inhibitors. The substrate concentration factor can be explained in terms of collision theory: the more substrate molecules available, the quicker the enzyme molecules collide and bind with them. The te ...
... influenced by several factors such as substrate concentration, temperature, pH and the presence of inhibitors. The substrate concentration factor can be explained in terms of collision theory: the more substrate molecules available, the quicker the enzyme molecules collide and bind with them. The te ...
Compound specific amino acid δ13C patterns in a deep
... consisting of phenylalanine (Phe), threonine (Thr), isoleucine (Ile), leucine (Leu), valine (Val), and lysine (Lys); and the non-essential amino acid (NEAA) group, consisting of aspartic acid + aspartate (Asx), glutamic acid + glutamate (Glx), proline (Pro), alanine (Ala), serine (Ser), and glycine ...
... consisting of phenylalanine (Phe), threonine (Thr), isoleucine (Ile), leucine (Leu), valine (Val), and lysine (Lys); and the non-essential amino acid (NEAA) group, consisting of aspartic acid + aspartate (Asx), glutamic acid + glutamate (Glx), proline (Pro), alanine (Ala), serine (Ser), and glycine ...
Document
... Entry of other carbohydrates into glycolysis Fructose Liver Cells They have another enzyme, fructokinase. • It has a stronger affinity for fructose. • It catalyzes phosphoryl group transfer from ATP to produce fructose-1phosphate. An aldolase-type cleavage and additional phosphorylation must also o ...
... Entry of other carbohydrates into glycolysis Fructose Liver Cells They have another enzyme, fructokinase. • It has a stronger affinity for fructose. • It catalyzes phosphoryl group transfer from ATP to produce fructose-1phosphate. An aldolase-type cleavage and additional phosphorylation must also o ...
Ch 5 Notes - Dublin Schools
... Amino Acid Monomers • Amino acids are organic molecules with carboxyl and amino groups • Amino acids differ in their properties due to differing side chains, called R groups ...
... Amino Acid Monomers • Amino acids are organic molecules with carboxyl and amino groups • Amino acids differ in their properties due to differing side chains, called R groups ...
Essentials of Glycobiology Lecture 13 April 25th. 2000
... single enzyme and amongst different enzymes explains evolution of two MPRs with complementary binding properties. Together with factors such as the number, compartmental localization, properties and availability of receptors, the endosomal pH, and concentration of divalent cations, there is much f ...
... single enzyme and amongst different enzymes explains evolution of two MPRs with complementary binding properties. Together with factors such as the number, compartmental localization, properties and availability of receptors, the endosomal pH, and concentration of divalent cations, there is much f ...
Cellular Respiration
... Both acetyl (C2) groups received from prep reaction: – Acetyl (C2) group transferred to oxaloacetate (C2) to make citrate (C6) – Each acetyl oxidized to two CO2 molecules – Remaining 4 carbons from oxaloacetate converted back to oxaloacetate (thus “cyclic”) ...
... Both acetyl (C2) groups received from prep reaction: – Acetyl (C2) group transferred to oxaloacetate (C2) to make citrate (C6) – Each acetyl oxidized to two CO2 molecules – Remaining 4 carbons from oxaloacetate converted back to oxaloacetate (thus “cyclic”) ...
Chemistry 1010 Plastics I
... Nylon-6 is made from monomers which have a carboxylic acid one one end and an amine on the other. ...
... Nylon-6 is made from monomers which have a carboxylic acid one one end and an amine on the other. ...
Test 5 Ch 2 - Kenton County Schools
... a difference in the activation energy of these reactions. c. Reactant A contains more energy at the beginning of the reaction than product C has at the end of the reaction. d. Product B contains more energy at the end of the reaction than reactant A has at the beginning of the reaction. ____ 12. Ref ...
... a difference in the activation energy of these reactions. c. Reactant A contains more energy at the beginning of the reaction than product C has at the end of the reaction. d. Product B contains more energy at the end of the reaction than reactant A has at the beginning of the reaction. ____ 12. Ref ...
Jeopardy
... groups: an acid group, a hydrogen atom, a side chain, and a/an _______ group. a. alcohol ...
... groups: an acid group, a hydrogen atom, a side chain, and a/an _______ group. a. alcohol ...
1 ENZYME KINETICS [APPLICATION OF UV
... influenced by several factors such as substrate concentration, temperature, pH and the presence of inhibitors. The substrate concentration factor can be explained in terms of collision theory: the more substrate molecules available, the quicker the enzyme molecules collide and bind with them. The te ...
... influenced by several factors such as substrate concentration, temperature, pH and the presence of inhibitors. The substrate concentration factor can be explained in terms of collision theory: the more substrate molecules available, the quicker the enzyme molecules collide and bind with them. The te ...
Organic Molecularly Imprinted Polymers As Mimics Of Hydrolytic
... approach, combinatorial chemistry was used to screen generated catalysts for enzyme-like activity. A third strategy was to generate a host that was capable of binding to a transition state analogue (TSA) of a reaction; upon removal of the template the host should behave as an artificial enzyme for t ...
... approach, combinatorial chemistry was used to screen generated catalysts for enzyme-like activity. A third strategy was to generate a host that was capable of binding to a transition state analogue (TSA) of a reaction; upon removal of the template the host should behave as an artificial enzyme for t ...
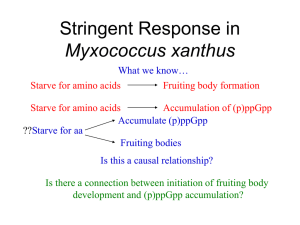
Stringent Response in Myxococcus xanthus
... Starve for amino acids Fruiting body formation Starve for amino acids Accumulation of (p)ppGpp Accumulate (p)ppGpp ??Starve for aa Fruiting bodies Is this a causal relationship? Is there a connection between initiation of fruiting body development and (p)ppGpp accumulation? ...
... Starve for amino acids Fruiting body formation Starve for amino acids Accumulation of (p)ppGpp Accumulate (p)ppGpp ??Starve for aa Fruiting bodies Is this a causal relationship? Is there a connection between initiation of fruiting body development and (p)ppGpp accumulation? ...
extraction of keratin protein from chicken feather
... also shows higher protein concentration. It was observed that the highest absorbance is in sodium sulfide reacted solution and lowest is in the thiglycolic acid reacted solution. The dissolving rate of feathers in thioglycolate solution and potassium cyanide solution is low because the reaction will ...
... also shows higher protein concentration. It was observed that the highest absorbance is in sodium sulfide reacted solution and lowest is in the thiglycolic acid reacted solution. The dissolving rate of feathers in thioglycolate solution and potassium cyanide solution is low because the reaction will ...
Isoprenoid metabolism: cholesterol and the others
... i.e. break them down into much smaller sizes so that digestive enzymes (mainly pancreatic lipase) can effectively hydrolyse them. Bile therefore acts in a similar way as washing up liquid or a detergent. In addition to essentially inert components such as water, inorganic ions and bile pigments (mos ...
... i.e. break them down into much smaller sizes so that digestive enzymes (mainly pancreatic lipase) can effectively hydrolyse them. Bile therefore acts in a similar way as washing up liquid or a detergent. In addition to essentially inert components such as water, inorganic ions and bile pigments (mos ...
Drug-Resistant Variants of Escherichia coli Thymidylate Synthase
... 14 mM 2-mercaptoethanol, and 1 mM EDTA, pH 7.5), centrifuged at 11,000g for 30 min, and applied to a DEAE Affi-Gel Blue (Sigma, St. Louis, MO) column (2.5 ⫻ 15-cm) pre-equilibrated in QA buffer. The column was washed with three column volumes of QA buffer, two column volumes of 100 mM KCl, then by t ...
... 14 mM 2-mercaptoethanol, and 1 mM EDTA, pH 7.5), centrifuged at 11,000g for 30 min, and applied to a DEAE Affi-Gel Blue (Sigma, St. Louis, MO) column (2.5 ⫻ 15-cm) pre-equilibrated in QA buffer. The column was washed with three column volumes of QA buffer, two column volumes of 100 mM KCl, then by t ...
Lipid metabolism in the fowl under normal and abnormal
... Large amounts of lipids (>IOO mg/g fresh weight) accumulate in the liver cells, disorganizing their internal structure and imparting a putty colour to the liver. The whole organ is very friable, probably owing to the degeneration of reticulin (Hall, 1974). The fat present has abnormally high content ...
... Large amounts of lipids (>IOO mg/g fresh weight) accumulate in the liver cells, disorganizing their internal structure and imparting a putty colour to the liver. The whole organ is very friable, probably owing to the degeneration of reticulin (Hall, 1974). The fat present has abnormally high content ...
acetyl CoA - LSU School of Medicine
... carbohydrate, low fat diet; inhibited by low carbohydrate, high fat diet. Same is true for fatty acid synthase (or synthetase) ...
... carbohydrate, low fat diet; inhibited by low carbohydrate, high fat diet. Same is true for fatty acid synthase (or synthetase) ...