Human Physiology - Maryville University
... Negative N balance: less N ingested than excreted In healthy adults amount of N excreted = amount ingested Excess amino acids can be converted into carbos & fat ...
... Negative N balance: less N ingested than excreted In healthy adults amount of N excreted = amount ingested Excess amino acids can be converted into carbos & fat ...
Document
... (from oxaloacetate), which crosses the membrane and gives them back to NAD to generate NADH (and oxaloacetate). Oxaloacetate is converted into aspartate, which crosses back to the cytosol and is metabolized to oxaloacetate to begin the process all over again. [Students may get this confused or mixed ...
... (from oxaloacetate), which crosses the membrane and gives them back to NAD to generate NADH (and oxaloacetate). Oxaloacetate is converted into aspartate, which crosses back to the cytosol and is metabolized to oxaloacetate to begin the process all over again. [Students may get this confused or mixed ...
Plant cell walls as targets for biotechnology
... comprising the complete cellulose synthase complex. The finding of a Zn2+-binding domain near the amino terminus of celA is consistent with the hypothesis that the synthase interacts with at least one other protein [21]. One candidate is a recently-discovered, extracellular, membrane-associated endo ...
... comprising the complete cellulose synthase complex. The finding of a Zn2+-binding domain near the amino terminus of celA is consistent with the hypothesis that the synthase interacts with at least one other protein [21]. One candidate is a recently-discovered, extracellular, membrane-associated endo ...
An Introduction to Energy, Enzymes, and Metabolism
... to the stomach. Only recently, however, have we learned how such drugs work. Aspirin and ibuprofen are examples of drugs that inhibit specific enzymes found in cells. In this case, these drugs inhibit an enzyme called cyclooxygenase. This enzyme is needed to synthesize molecules called prostaglandin ...
... to the stomach. Only recently, however, have we learned how such drugs work. Aspirin and ibuprofen are examples of drugs that inhibit specific enzymes found in cells. In this case, these drugs inhibit an enzyme called cyclooxygenase. This enzyme is needed to synthesize molecules called prostaglandin ...
Full Text
... closing during the threading process. The initial automatic alignment revealed three residues known to be involved in anesthetic binding at the same relative height along the core axis of the four-helix bundle. Refined SeqFold Search for Modeling Template. Using the CATH database (http://www.biochem ...
... closing during the threading process. The initial automatic alignment revealed three residues known to be involved in anesthetic binding at the same relative height along the core axis of the four-helix bundle. Refined SeqFold Search for Modeling Template. Using the CATH database (http://www.biochem ...
Biochemistry of Sulfur
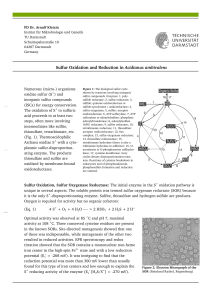
... a leader peptide with a twin-arginine translocation motif (TAT) not present in the mature protein suggesting a transport across the membrane (Fig. 7). Fe and Ni were present in membrane and in enriched hydrogenase fractions in accordance with the observed sequence similarity. The Ac. ambivalens SR g ...
... a leader peptide with a twin-arginine translocation motif (TAT) not present in the mature protein suggesting a transport across the membrane (Fig. 7). Fe and Ni were present in membrane and in enriched hydrogenase fractions in accordance with the observed sequence similarity. The Ac. ambivalens SR g ...
Strain TrpC TrpB TrpA
... is inactive. What does this indicate about the structure and function of the wild-type rII protein? ANSWER: The N-terminus and the C-terminus of the wild-type rII protein are essential for function. The region in the middle of the protein, between base 30 and 75, does not appear to be important, as ...
... is inactive. What does this indicate about the structure and function of the wild-type rII protein? ANSWER: The N-terminus and the C-terminus of the wild-type rII protein are essential for function. The region in the middle of the protein, between base 30 and 75, does not appear to be important, as ...
BI0 120 cell and tissues
... 28. The activation phase of the glycolysis consist of A. adding phosphates, modifying sugars and forming glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate. B. oxidative steps, proton pumping, and reaction with oxygen. C. oxidation of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate, and storage of energy. D. ATP synthesis by substrate-level ph ...
... 28. The activation phase of the glycolysis consist of A. adding phosphates, modifying sugars and forming glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate. B. oxidative steps, proton pumping, and reaction with oxygen. C. oxidation of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate, and storage of energy. D. ATP synthesis by substrate-level ph ...
NITROGEN METABOLISM
... In legumes, nitrogen fixation occurs in specialized bodies called root nodules. The nodules develop due to interaction between the bacteria Rhizobium and the legume roots (see diagram 6.4c). The biochemical steps for nitrogen fixation are same. Notes However, legume nodules possess special protein c ...
... In legumes, nitrogen fixation occurs in specialized bodies called root nodules. The nodules develop due to interaction between the bacteria Rhizobium and the legume roots (see diagram 6.4c). The biochemical steps for nitrogen fixation are same. Notes However, legume nodules possess special protein c ...
Review Evolution of the coordinate regulation of glycolytic enzyme
... Because substrate fluctuation was the principal selection pressure for evolving Archean microorganisms, modulons became the principal mechanism for the coordinated regulation of all genes involved in carbohydrate metabolism, including glycolytic enzymes. However even in early Moneras there is eviden ...
... Because substrate fluctuation was the principal selection pressure for evolving Archean microorganisms, modulons became the principal mechanism for the coordinated regulation of all genes involved in carbohydrate metabolism, including glycolytic enzymes. However even in early Moneras there is eviden ...
Origin of Life
... No organisms were actually made. Even if organisms were made in this way, this would not prove it to be how things actually happened, it only shows it to be one possible way. Accumulation of organic monomers is only the first step in chemical evolution. ©2000 Timothy G. Standish ...
... No organisms were actually made. Even if organisms were made in this way, this would not prove it to be how things actually happened, it only shows it to be one possible way. Accumulation of organic monomers is only the first step in chemical evolution. ©2000 Timothy G. Standish ...
Human Ig heavy chain CDR3 regions in adult
... diversity is illustrated by the fact that this region forms the center of the antigen binding site and provides essential residues for antigen binding (2,3,18–22). Given the central location of the HCDR3 within the antigen-binding pocket, major changes in HCDR3 length, sequence and/or bulk are thoug ...
... diversity is illustrated by the fact that this region forms the center of the antigen binding site and provides essential residues for antigen binding (2,3,18–22). Given the central location of the HCDR3 within the antigen-binding pocket, major changes in HCDR3 length, sequence and/or bulk are thoug ...
Direct and indirect cellular effects of aspartame on the brain
... an inhibitory neurotransmitter. However, if phenylalanine, as the main part of aspartame, competes with tyrosine for NAAT, a compromised dopamine production will result because phenylalanine will bind more frequently and freely than tyrosine owing to its higher concentration, and thus lead to lower ...
... an inhibitory neurotransmitter. However, if phenylalanine, as the main part of aspartame, competes with tyrosine for NAAT, a compromised dopamine production will result because phenylalanine will bind more frequently and freely than tyrosine owing to its higher concentration, and thus lead to lower ...
Lecture Fermentation
... • Grow very fast if sufficient glucose is present • Double numbers within 20 min (up to 109/ml) Produce lactic acid • Lactobacillus ruminis & L. vitulinus also produce some lactic acid Methanobacter ruminantium in rumen (2 x 108/ml) • Sensitive to pH below 6.0 • Have no capacity to utilize more H+ • ...
... • Grow very fast if sufficient glucose is present • Double numbers within 20 min (up to 109/ml) Produce lactic acid • Lactobacillus ruminis & L. vitulinus also produce some lactic acid Methanobacter ruminantium in rumen (2 x 108/ml) • Sensitive to pH below 6.0 • Have no capacity to utilize more H+ • ...
生物化學小考(一) 範圍ch1~ch4
... (B) In anaerobic muscle, pyruvate is converted to lactate. (C) In yeast growing anaerobically, pyruvate is converted to ethanol. (D) Reduction of pyruvate to lactate regenerates a cofactor essential for glycolysis. (E)Under anaerobic conditions pyruvate does not form because glycolysis does not occu ...
... (B) In anaerobic muscle, pyruvate is converted to lactate. (C) In yeast growing anaerobically, pyruvate is converted to ethanol. (D) Reduction of pyruvate to lactate regenerates a cofactor essential for glycolysis. (E)Under anaerobic conditions pyruvate does not form because glycolysis does not occu ...
Molecular analysis of an operon in Bacillus subtilis
... proteins (Fath & Kolter, 1993). The components of a bacterial transporter are often separate proteins encoded by one multicistronic operon, but may also be different domains of a single polypeptide, which is the structural arrangement found in eukaryotic ABC transporters (Higgins, 1992). We have pre ...
... proteins (Fath & Kolter, 1993). The components of a bacterial transporter are often separate proteins encoded by one multicistronic operon, but may also be different domains of a single polypeptide, which is the structural arrangement found in eukaryotic ABC transporters (Higgins, 1992). We have pre ...
File Ref.No.7054/GA - IV - J1/2013/CU UNIVERSITY OF CALICUT
... Enzyme catalysis and Mechanism of enzyme action-: Idea of enzyme specificity; Concept of active site and the ‘lock and key’ model of Emil Fischer; Koshland’s induced fit theory of enzyme catalysis. Standard free energy change in a reaction. Transition state, energy of activation of non-enzymatic and ...
... Enzyme catalysis and Mechanism of enzyme action-: Idea of enzyme specificity; Concept of active site and the ‘lock and key’ model of Emil Fischer; Koshland’s induced fit theory of enzyme catalysis. Standard free energy change in a reaction. Transition state, energy of activation of non-enzymatic and ...
First Title - Buckeye Valley
... The mRNA strand binds to the small ribosomal subunit and is joined at the start codon by the first tRNA, which carries the amino acid methionine. Binding occurs between complementary base pairs of the codon and anticodon. ...
... The mRNA strand binds to the small ribosomal subunit and is joined at the start codon by the first tRNA, which carries the amino acid methionine. Binding occurs between complementary base pairs of the codon and anticodon. ...
2_3 Slides - Lipids _ Carbs
... • In Amylopectin the chain is branched, so has a more globular shape. • Due it’s branched nature amylopectin can be much larger consisting of 2,000200,000 units ...
... • In Amylopectin the chain is branched, so has a more globular shape. • Due it’s branched nature amylopectin can be much larger consisting of 2,000200,000 units ...