Interaction of Urea with Amino Acids: Implications for Urea
... CUW between 1.44 (THR, SER) and 1.82 (CYS). For each amino acid the CUW of the backbone alone is higher than for the complete amino acid. The CUW of the backbone alone, averaged over all residues, is 1.78 ( 0.18. In summary, urea interacts mainly with aromatic and nonpolar residues, as well as with ...
... CUW between 1.44 (THR, SER) and 1.82 (CYS). For each amino acid the CUW of the backbone alone is higher than for the complete amino acid. The CUW of the backbone alone, averaged over all residues, is 1.78 ( 0.18. In summary, urea interacts mainly with aromatic and nonpolar residues, as well as with ...
LAB: (Day 1) Macromolecules/Enzymes
... down into smaller monomers to use them. Carbohydrates are broken down into simple sugars, such as glucose, that are used to create energy in cellular respiration. Proteins are broken down into amino acids that are then rearranged during translation to make proteins important to the body, such as ins ...
... down into smaller monomers to use them. Carbohydrates are broken down into simple sugars, such as glucose, that are used to create energy in cellular respiration. Proteins are broken down into amino acids that are then rearranged during translation to make proteins important to the body, such as ins ...
Principles of BIOCHEMISTRY - Illinois State University
... • Catalyzes a metabolically irreversible hydrolysis reaction ...
... • Catalyzes a metabolically irreversible hydrolysis reaction ...
Introduction
... Plant sterols and their saturated derivatives, stanols, are a group of cholesterol analogues with different side chain configurations. ...
... Plant sterols and their saturated derivatives, stanols, are a group of cholesterol analogues with different side chain configurations. ...
Structure of L‑Serine Dehydratase from Legionella
... defects in the phosphorylated pathway of L-serine production result in auxotrophy,4,5 whereas high levels of L-serine can be toxic.6 All organisms contain enzymes that specifically deaminate Lserine to produce pyruvate and ammonia. In eukaryotes, these enzymes utilize pyridoxal 5′-phosphate (PLP) for ...
... defects in the phosphorylated pathway of L-serine production result in auxotrophy,4,5 whereas high levels of L-serine can be toxic.6 All organisms contain enzymes that specifically deaminate Lserine to produce pyruvate and ammonia. In eukaryotes, these enzymes utilize pyridoxal 5′-phosphate (PLP) for ...
Ch 9 Cellular respiration
... Types of molecules that can be used for glycolysis: 1. carbohydrates: if dissaccharides, polysaccharides, first need to be hydrolyzed to glucose and other monosaccharides 2. proteins: must be hydrolyzed to amino acids, then converted by enzymes to intermediates in glycolysis and citric acid cycle ...
... Types of molecules that can be used for glycolysis: 1. carbohydrates: if dissaccharides, polysaccharides, first need to be hydrolyzed to glucose and other monosaccharides 2. proteins: must be hydrolyzed to amino acids, then converted by enzymes to intermediates in glycolysis and citric acid cycle ...
An acyltransferase-like gene obtained by differential gene
... Figure 4. A molecular phylogenetic tree of the deduced amino acid sequences of LaAT with other plant acyltransferases belonging to the BAHD family. The tree was constructed by the neighbor-joining method by using the MEGA4 program. The lengths of the lines indicate the relative distances between nod ...
... Figure 4. A molecular phylogenetic tree of the deduced amino acid sequences of LaAT with other plant acyltransferases belonging to the BAHD family. The tree was constructed by the neighbor-joining method by using the MEGA4 program. The lengths of the lines indicate the relative distances between nod ...
Biosynthesis of plant-derived flavor compounds
... saturated and unsaturated, straight-chain, branched-chain and cyclic structures bearing various functional groups (e.g. alcohols, aldehydes, ketones, esters and ethers) and also nitrogen and sulfur. They are commercially important for the food, pharmaceutical, agricultural and chemical industries as ...
... saturated and unsaturated, straight-chain, branched-chain and cyclic structures bearing various functional groups (e.g. alcohols, aldehydes, ketones, esters and ethers) and also nitrogen and sulfur. They are commercially important for the food, pharmaceutical, agricultural and chemical industries as ...
Nutrition 101
... have to ingest gobs of the stuff to see results. Exercise and what you eat post-workout are the best ways to do this. After a workout, have a whey protein shake and some fast carbs, such as honey mixed with the shake. This will boost insulin levels which will enhance muscle recovery and growth. The ...
... have to ingest gobs of the stuff to see results. Exercise and what you eat post-workout are the best ways to do this. After a workout, have a whey protein shake and some fast carbs, such as honey mixed with the shake. This will boost insulin levels which will enhance muscle recovery and growth. The ...
Acetyl-coenzyme A carboxylases: Versatile targets for
... Acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC) catalyzes the ATP-dependent carboxylation of acetyl-CoA to form malonyl-CoA [Kim, 1997; Harwood, 2005; Tong, 2005]. This reaction, which proceeds in two half-reactions, a biotin carboxylase (BC) reaction and a carboxyltransferase (CT) reaction (Fig. 1A), is the first com ...
... Acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC) catalyzes the ATP-dependent carboxylation of acetyl-CoA to form malonyl-CoA [Kim, 1997; Harwood, 2005; Tong, 2005]. This reaction, which proceeds in two half-reactions, a biotin carboxylase (BC) reaction and a carboxyltransferase (CT) reaction (Fig. 1A), is the first com ...
10.4 Factors That Affect Enzyme Activity, Continued
... that occur during a chemical reaction. • Activation energy is the energy required to start a reaction, and plays a role in the rate of reaction. • The lower the activation energy, the faster the rate of reaction. • Heat of reaction is a measure of the production or consumption of energy in a reactio ...
... that occur during a chemical reaction. • Activation energy is the energy required to start a reaction, and plays a role in the rate of reaction. • The lower the activation energy, the faster the rate of reaction. • Heat of reaction is a measure of the production or consumption of energy in a reactio ...
Enzyme
... Stored at high concentration, as lyophilized powders, or in a concentrated (NH4)2SO4 solution Some proteases may go through autolysis during storage. Some enzymes are easier to subject to denaturation at low concentrations. Stored at low temperatures Be careful: freeze-thaw cycles would inac ...
... Stored at high concentration, as lyophilized powders, or in a concentrated (NH4)2SO4 solution Some proteases may go through autolysis during storage. Some enzymes are easier to subject to denaturation at low concentrations. Stored at low temperatures Be careful: freeze-thaw cycles would inac ...
88. Merging photoredox with nickel catalysis: Coupling of -carboxyl sp 3 -carbons with aryl halides
... CH3CN and E1/2red [IrIII/IrII] = –1.37 V versus SCE in CH3CN} (22, 24). However, we recognize that an alternative pathway could be operable wherein the oxidative addition step occurs from the Ni(I) complex to form a Ni(III) aryl halide adduct. In this pathway, photocatalyst-mediated reduction of the ...
... CH3CN and E1/2red [IrIII/IrII] = –1.37 V versus SCE in CH3CN} (22, 24). However, we recognize that an alternative pathway could be operable wherein the oxidative addition step occurs from the Ni(I) complex to form a Ni(III) aryl halide adduct. In this pathway, photocatalyst-mediated reduction of the ...
Oxidative Phosphorylation in Homogenates of
... remains constant during phase II when inorganic phosphate is being removed from the reaction. This stationary phase of the ammonia curves in kidney homogenates is much more pronounced in individual experiments, e.g., as shown in Chart 6, than in Chart 5, which represents the average of five homogena ...
... remains constant during phase II when inorganic phosphate is being removed from the reaction. This stationary phase of the ammonia curves in kidney homogenates is much more pronounced in individual experiments, e.g., as shown in Chart 6, than in Chart 5, which represents the average of five homogena ...
Dosyayı İndir
... 1.The acceptor stem is a 7-base pair (bp) stem made by the base pairing of the 5'terminal nucleotide with the 3'-terminal nucleotide (which contains the CCA 3'terminal group used to attach the amino acid). The CCA tail This sequence is important for the recognition of tRNA by enzymes and critical ...
... 1.The acceptor stem is a 7-base pair (bp) stem made by the base pairing of the 5'terminal nucleotide with the 3'-terminal nucleotide (which contains the CCA 3'terminal group used to attach the amino acid). The CCA tail This sequence is important for the recognition of tRNA by enzymes and critical ...
Metabolic Adaptation and Protein Complexes in Prokaryotes
... factors and influences protein complexes and metabolic pathways, but also allows adaptation to the nutrient-poor, low-glucose environment of the cytoplasm of the host [27]. The metabolism of host and pathogen is intertwined and L. monocytogenes is well adapted to this nutrient-poor environment, not ...
... factors and influences protein complexes and metabolic pathways, but also allows adaptation to the nutrient-poor, low-glucose environment of the cytoplasm of the host [27]. The metabolism of host and pathogen is intertwined and L. monocytogenes is well adapted to this nutrient-poor environment, not ...
Chemical Inactivation of the Cinnamate 4
... The cinnamate (CA) 4-hydroxylase (C4H) is a cytochrome P450 that catalyzes the second step of the main phenylpropanoid pathway, leading to the synthesis of lignin, pigments, and many defense molecules. Salicylic acid (SA) is an essential trigger of plant disease resistance. Some plant species can sy ...
... The cinnamate (CA) 4-hydroxylase (C4H) is a cytochrome P450 that catalyzes the second step of the main phenylpropanoid pathway, leading to the synthesis of lignin, pigments, and many defense molecules. Salicylic acid (SA) is an essential trigger of plant disease resistance. Some plant species can sy ...
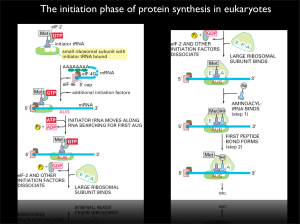
The initiation phase of protein synthesis in eukaryotes
... uORF1, ∼50% of the 40S ribosomes remain attached to the mRNA and resume scanning. Under nonstarvation conditions, the 40S subunit quickly rebinds the TC and reinitiates at uORF4 because the ...
... uORF1, ∼50% of the 40S ribosomes remain attached to the mRNA and resume scanning. Under nonstarvation conditions, the 40S subunit quickly rebinds the TC and reinitiates at uORF4 because the ...
Problem 5. Inorganic chains and rings
... Photosynthesis is believed to be an efficient way of light energy conversion. Let’s check this statement from various points of view. Consider the overall chemical equation of photosynthesis performed by green plants in the form: H2O + CO2 CH2O + O2 where CH2O denotes the formed carbohydrates. Tho ...
... Photosynthesis is believed to be an efficient way of light energy conversion. Let’s check this statement from various points of view. Consider the overall chemical equation of photosynthesis performed by green plants in the form: H2O + CO2 CH2O + O2 where CH2O denotes the formed carbohydrates. Tho ...
Saimaa University of Applied Sciences Faculty of Technology, Imatra, Finland ’s Degree Bachelor
... The molecular weight of monomer enzyme is between 13,000 and 35,000 Da. Monomer enzyme normally belongs to the primary structure of enzyme, as shown in figure 3.1. Primary structure refers to AA order in the protein connection, including the location of the disulfide bond. It is the actual sequence ...
... The molecular weight of monomer enzyme is between 13,000 and 35,000 Da. Monomer enzyme normally belongs to the primary structure of enzyme, as shown in figure 3.1. Primary structure refers to AA order in the protein connection, including the location of the disulfide bond. It is the actual sequence ...
Chapter 5 - Hale AP Biology
... Amino Acid Monomers • Amino acids are organic molecules with carboxyl and amino groups ...
... Amino Acid Monomers • Amino acids are organic molecules with carboxyl and amino groups ...
TQ bank Lab 4
... Some organisms produce an enzyme called caseinase? A. TRUE B. FALSE In the Citrate Test what does the medium turn out to be if it is a positive test? A. Black B. Blue C. Red D. No Color In the Casein Test, Negative is a clearing (halo) around the area of growth of the organism. A. TRUE B. FALSE In t ...
... Some organisms produce an enzyme called caseinase? A. TRUE B. FALSE In the Citrate Test what does the medium turn out to be if it is a positive test? A. Black B. Blue C. Red D. No Color In the Casein Test, Negative is a clearing (halo) around the area of growth of the organism. A. TRUE B. FALSE In t ...