Q1. The drawing shows part of a root hair cell. (a) Use words from
... Which arrow, A, B, C or D represents: (i) ...
... Which arrow, A, B, C or D represents: (i) ...
Biology EOC Review Answers
... 3. chemical messengers produced by the cells bind to receptors on the plasma membrane of other cells or enter other cells and alter the metabolic function of those cells. 4. regulate the endocrine system Diagram of proteins and molecules embedded in a cell membrane: 1. double layered sheet called a ...
... 3. chemical messengers produced by the cells bind to receptors on the plasma membrane of other cells or enter other cells and alter the metabolic function of those cells. 4. regulate the endocrine system Diagram of proteins and molecules embedded in a cell membrane: 1. double layered sheet called a ...
ch3 rev - Anatomy Corner
... 8. List and describe the stages in the life cycle of a cell. 9. List in order the phases of mitosis and tell the main events that occur in each phase. 10. What is cytosol? What is nucleoplasm? 11. A chromosome is made up of an identical pair of _________________________. 12. What cell structure play ...
... 8. List and describe the stages in the life cycle of a cell. 9. List in order the phases of mitosis and tell the main events that occur in each phase. 10. What is cytosol? What is nucleoplasm? 11. A chromosome is made up of an identical pair of _________________________. 12. What cell structure play ...
Honors Biology Midterm
... 26. Catalase, ligase, polymerase, etc. These are all examples of: 27. Is water a polar compound? 28. Is fructose a monosaccharide? 29. The bonding of water molecules on one another is called: 30. The _________________ of DNA is a nucleotide. 31. Does a decrease in hydrogen ions leads to a decrease i ...
... 26. Catalase, ligase, polymerase, etc. These are all examples of: 27. Is water a polar compound? 28. Is fructose a monosaccharide? 29. The bonding of water molecules on one another is called: 30. The _________________ of DNA is a nucleotide. 31. Does a decrease in hydrogen ions leads to a decrease i ...
Cell Review Notes
... Rough ER - have ribosomes attached to surface acts as transport of polypeptides (made at ribosomes) through cell. Smooth ER-does not have ribosomes attached - acts as transport (like rough ER) also, contains enzymes to detoxify drugs and alcohol (liver cells) and synthesize lipids like steroid hormo ...
... Rough ER - have ribosomes attached to surface acts as transport of polypeptides (made at ribosomes) through cell. Smooth ER-does not have ribosomes attached - acts as transport (like rough ER) also, contains enzymes to detoxify drugs and alcohol (liver cells) and synthesize lipids like steroid hormo ...
Lipids and Membranes, Fall 13--Worksheet Crowe
... Work in groups of two or three to complete this worksheet. Your understanding will be checked using clicker questions periodically throughout the activity. Membranes are some of the most important macrostructures of biological systems. Membranes define the organism and separate it from its environme ...
... Work in groups of two or three to complete this worksheet. Your understanding will be checked using clicker questions periodically throughout the activity. Membranes are some of the most important macrostructures of biological systems. Membranes define the organism and separate it from its environme ...
Rebel Academy – Khan Academy Review
... Eukaryotic cells are found in plants, _________________________, ____________________________ and also Protists. ( not mentioned in the video) mRNA is translated into ______________________ at the ribosome. Ribosomes are the sites where information is converted into ______________________________. T ...
... Eukaryotic cells are found in plants, _________________________, ____________________________ and also Protists. ( not mentioned in the video) mRNA is translated into ______________________ at the ribosome. Ribosomes are the sites where information is converted into ______________________________. T ...
Concept Review Question #2 Name: Biology Due Date: ______
... 3. Why is the cell membrane sometimes refer to as a fluid mosaic model? What part of the cell membrane acts like a fluid? What part acts like a mosaic? (3 points) ...
... 3. Why is the cell membrane sometimes refer to as a fluid mosaic model? What part of the cell membrane acts like a fluid? What part acts like a mosaic? (3 points) ...
Organelles of Plant and Animal Cells
... Takes in food and converts it to ATP, which is broken down for energy Some cells have more mitochondrion than others. ...
... Takes in food and converts it to ATP, which is broken down for energy Some cells have more mitochondrion than others. ...
The Cell Theory and Membrane Transport
... • Endocytosis = the process by which cells ingest external fluid, macromolecules, and large particles. – Pinocytosis = water – Phagocytosis = particles (solids) • Exocytosis = the process by which cells remove fluids, macromolecules, and large particles. ...
... • Endocytosis = the process by which cells ingest external fluid, macromolecules, and large particles. – Pinocytosis = water – Phagocytosis = particles (solids) • Exocytosis = the process by which cells remove fluids, macromolecules, and large particles. ...
Section: Passive Transport
... The movement of a substance into a cell by a vesicle is called endocytosis. During endocytosis, the cell membrane forms a pouch around a substance outside the cell. The pouch then closes up and pinches off from the membrane to form a vesicle. Vesicles formed by endocytosis may fuse with lysosomes or ...
... The movement of a substance into a cell by a vesicle is called endocytosis. During endocytosis, the cell membrane forms a pouch around a substance outside the cell. The pouch then closes up and pinches off from the membrane to form a vesicle. Vesicles formed by endocytosis may fuse with lysosomes or ...
Return to animal Cell
... concentration to regions of lower concentration. Diffusion Osmosis is the movement of water molecules through a selectively permeable membrane into a region of higher solute concentration, aiming to equalize the solute concentrations on the two sides Active and Passive Transport ...
... concentration to regions of lower concentration. Diffusion Osmosis is the movement of water molecules through a selectively permeable membrane into a region of higher solute concentration, aiming to equalize the solute concentrations on the two sides Active and Passive Transport ...
Slide 1 - Ommbid.com
... Relationship of integral and peripheral membrane proteins to the membrane phospholipid bilayer. Integral membrane proteins (a) have portions of their mass embedded in the membrane that interact directly with the hydrophobic tails of the phospholipids. Other portions of these proteins are exposed on ...
... Relationship of integral and peripheral membrane proteins to the membrane phospholipid bilayer. Integral membrane proteins (a) have portions of their mass embedded in the membrane that interact directly with the hydrophobic tails of the phospholipids. Other portions of these proteins are exposed on ...
3.1 - Investigating Structure of Cells
... • Chloroplasts are organelles surrounded by a double membrane. • The inner membrane is folded into thylakoid membranes, which are where PHOTOSYNTHESIS TAKES PLACE. • The chloroplasts contain a light-absorbing pigment called chlorophyll which give plants their green colour. ...
... • Chloroplasts are organelles surrounded by a double membrane. • The inner membrane is folded into thylakoid membranes, which are where PHOTOSYNTHESIS TAKES PLACE. • The chloroplasts contain a light-absorbing pigment called chlorophyll which give plants their green colour. ...
The Cell
... Cell Theory All things are made up of at least one cell Cells carry on life processes (RENT…) Come from “old” cells Exceptions? Where did the 1st one come from? Viruses aren’t cells ...
... Cell Theory All things are made up of at least one cell Cells carry on life processes (RENT…) Come from “old” cells Exceptions? Where did the 1st one come from? Viruses aren’t cells ...
AP Biology - ReicheltScience.com
... polysaccharides (pectins) glues cells together Plasmodesmatacommunicating channel between plant cells ...
... polysaccharides (pectins) glues cells together Plasmodesmatacommunicating channel between plant cells ...
H. Bio Cell Membrane
... pores that ions can pass through. Pore is the thickness of the membrane Ion does not have touch the nonpolar interior of the bilayer. ...
... pores that ions can pass through. Pore is the thickness of the membrane Ion does not have touch the nonpolar interior of the bilayer. ...
Cole Research RCST 4029B Offic
... A key property of lipids is that they have hydrophilic and hydrophobic properties. Lipids form barriers, called membranes, that allow compartmentalization. Lipids also function as fuel molecules and signal molecules. ...
... A key property of lipids is that they have hydrophilic and hydrophobic properties. Lipids form barriers, called membranes, that allow compartmentalization. Lipids also function as fuel molecules and signal molecules. ...
How do materials move across the cell membrane?
... until they are evenly mixed. Molecules move from areas of higher concentration to lower concentration. Small molecules diffuse through membranes during passive transport: materials move without using the cell’s energy. The diffusion of water through a membrane is called osmosis. ...
... until they are evenly mixed. Molecules move from areas of higher concentration to lower concentration. Small molecules diffuse through membranes during passive transport: materials move without using the cell’s energy. The diffusion of water through a membrane is called osmosis. ...
Homework: Respiration - Fall River Public Schools
... Cell Biologist’s Name: _________________________________ Class: 8__ Date: ______________ Mrs. Bouchard– 8th Grade Science ...
... Cell Biologist’s Name: _________________________________ Class: 8__ Date: ______________ Mrs. Bouchard– 8th Grade Science ...
Recognise structures as seen under the electron microscope, e.g.
... • Contains the DNA which carries the information for protein synthesis • The DNA is associated with histone protein to form ...
... • Contains the DNA which carries the information for protein synthesis • The DNA is associated with histone protein to form ...
provide support and protection for the cell.
... • Only glucose can pass through this channel, and it can move through in either direction. • 100’s of different protein channels have been found that allow particular substances to cross different membranes. ...
... • Only glucose can pass through this channel, and it can move through in either direction. • 100’s of different protein channels have been found that allow particular substances to cross different membranes. ...
Transport
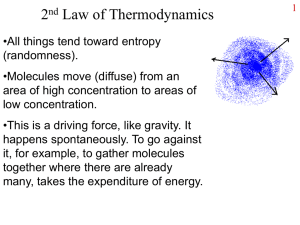
... •All things tend toward entropy (randomness). •Molecules move (diffuse) from an area of high concentration to areas of low concentration. •This is a driving force, like gravity. It happens spontaneously. To go against it, for example, to gather molecules together where there are already many, takes ...
... •All things tend toward entropy (randomness). •Molecules move (diffuse) from an area of high concentration to areas of low concentration. •This is a driving force, like gravity. It happens spontaneously. To go against it, for example, to gather molecules together where there are already many, takes ...
Cell membrane
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane or cytoplasmic membrane) is a biological membrane that separates the interior of all cells from the outside environment. The cell membrane is selectively permeable to ions and organic molecules and controls the movement of substances in and out of cells. The basic function of the cell membrane is to protect the cell from its surroundings. It consists of the phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins. Cell membranes are involved in a variety of cellular processes such as cell adhesion, ion conductivity and cell signalling and serve as the attachment surface for several extracellular structures, including the cell wall, glycocalyx, and intracellular cytoskeleton. Cell membranes can be artificially reassembled.