The Cell and Its Structures
... supplies for energy, making products and getting rid of wastes) - to carry out these functions, cells must have certain internal structures known as organelles A – Cell membrane – surrounds and protects the contents of the cell B – Cytoplasm – jellylike substance inside the cell that supports other ...
... supplies for energy, making products and getting rid of wastes) - to carry out these functions, cells must have certain internal structures known as organelles A – Cell membrane – surrounds and protects the contents of the cell B – Cytoplasm – jellylike substance inside the cell that supports other ...
chapter_4_2007
... through a selectivelypermeable membrane. Occurs when there is a difference in water concentration on opposite sides of the membrane. Water will move to the side where there is less water ...
... through a selectivelypermeable membrane. Occurs when there is a difference in water concentration on opposite sides of the membrane. Water will move to the side where there is less water ...
cytology answers
... In the center of the cell, it’s the largest structure other than a plant’s vacuole, it is usually round in shape 10. What do ribosomes look like? The smallest structure in the cell, small round circular structures 11. What does the mitochondria look like? A medium sized structure, shapes like a kidn ...
... In the center of the cell, it’s the largest structure other than a plant’s vacuole, it is usually round in shape 10. What do ribosomes look like? The smallest structure in the cell, small round circular structures 11. What does the mitochondria look like? A medium sized structure, shapes like a kidn ...
Cell Size
... Cell Types: Prokaryotic • Nucleoid: DNA concentration • No organelles with membranes • Ribosomes: protein synthesis • Plasma membrane (all cells); semi-permeable • Cytoplasm/cytosol (all cells) ...
... Cell Types: Prokaryotic • Nucleoid: DNA concentration • No organelles with membranes • Ribosomes: protein synthesis • Plasma membrane (all cells); semi-permeable • Cytoplasm/cytosol (all cells) ...
Structural view of bacteria (2)
... Gm+ organisms have cell walls that may contain as much as 90% peptidoglycan, with membrane associated proteins and Teichoic acids comprising the remaining components. ...
... Gm+ organisms have cell walls that may contain as much as 90% peptidoglycan, with membrane associated proteins and Teichoic acids comprising the remaining components. ...
plasma membrane
... • The cell membrane is a biological membrane that separates the interior of all cells from the outside environment. • The cell membrane is selectively-permeable to ions and organic molecules and controls the movement of substances in and out of cells. • It consists of the phospholipid bilayer with e ...
... • The cell membrane is a biological membrane that separates the interior of all cells from the outside environment. • The cell membrane is selectively-permeable to ions and organic molecules and controls the movement of substances in and out of cells. • It consists of the phospholipid bilayer with e ...
Biology 211 Anatomy & Physiology I
... You should also understand the Endoplasmic reticulum basic structure and function of Golgi complex cilia and flagella Mitochondria Lysosomes Peroxisomes You will be responsible Vesicles for these on exams Cytoskeleton ...
... You should also understand the Endoplasmic reticulum basic structure and function of Golgi complex cilia and flagella Mitochondria Lysosomes Peroxisomes You will be responsible Vesicles for these on exams Cytoskeleton ...
File
... • Tiny pockets form along cell membrane, and pinch off into vacuoles inside the cell. Sometimes called “Cell Drinking” ...
... • Tiny pockets form along cell membrane, and pinch off into vacuoles inside the cell. Sometimes called “Cell Drinking” ...
GCPS_05_SC_LS_T4 (_GCPS_05_SC_LS_T4)
... 7. Which group of animals has the MOST similar type of body coverings? A. humans, dogs, horses B. owls, beetles, chickens C. grasshoppers, bats, worms D. snails, whales, sunfish 8. Which object would best demonstrate how roots function in the soil? A. rock B. sponge C. mirror D. jar of water 9. Whic ...
... 7. Which group of animals has the MOST similar type of body coverings? A. humans, dogs, horses B. owls, beetles, chickens C. grasshoppers, bats, worms D. snails, whales, sunfish 8. Which object would best demonstrate how roots function in the soil? A. rock B. sponge C. mirror D. jar of water 9. Whic ...
CELLS-A STUDY GUIDE CHECKLIST
... CELLS-A STUDY GUIDE CHECKLIST In order to do well on the test the following is a list of what you will need to know: I. II. ...
... CELLS-A STUDY GUIDE CHECKLIST In order to do well on the test the following is a list of what you will need to know: I. II. ...
BI 112 VITAL VOCAB #2 Be sure to review the SCIENTIFIC
... 5. Surface area to Volume ratio (why is this important?) ...
... 5. Surface area to Volume ratio (why is this important?) ...
plasma membrane - Citrus College
... Boundary that separates the living cell from it’s non-living surroundings. Phospholipid bilayer Amphipathic - having both: hydrophilic heads hydrophobic tails Phospholipid ~8 nm thick ...
... Boundary that separates the living cell from it’s non-living surroundings. Phospholipid bilayer Amphipathic - having both: hydrophilic heads hydrophobic tails Phospholipid ~8 nm thick ...
Reading Cellular Boundaries Name Period All cells contain cell
... For example-The structure of the cell membrane. Once the first reading is complete go back and provide questions and examples along the left side. Include vocabulary you don’t understand. Place a + by the ideas you understand and – by the ideas you don’t understand. 10 Points Title of this Section: ...
... For example-The structure of the cell membrane. Once the first reading is complete go back and provide questions and examples along the left side. Include vocabulary you don’t understand. Place a + by the ideas you understand and – by the ideas you don’t understand. 10 Points Title of this Section: ...
topic 1.6 quiz - Peoria Public Schools
... Animal cells form a cleavage furrow as the cell membrane is pulled inwards whilst plant cells use vesicles, to form a cell plate, which eventually fuses with the existing plasma membrane to separate the cells. ...
... Animal cells form a cleavage furrow as the cell membrane is pulled inwards whilst plant cells use vesicles, to form a cell plate, which eventually fuses with the existing plasma membrane to separate the cells. ...
The Cell - Angelfire
... • The first name is always the Genus name • The second name is always the species name • The first letter of the first name is always in upper case & the first letter of the species name is always in the lower case • The name is written in italics or alternatively underlined • e.g. Amoeba proteus OR ...
... • The first name is always the Genus name • The second name is always the species name • The first letter of the first name is always in upper case & the first letter of the species name is always in the lower case • The name is written in italics or alternatively underlined • e.g. Amoeba proteus OR ...
Cells - Bonar Law Memorial
... Organism: General term used to refer to any living thing. Organelle: Specialized structures with specific functions found inside a cell. Cell Theory All living things are made of one or more cells Cells are the basic unit of structure and function Cells come only from living cells. Two Types ...
... Organism: General term used to refer to any living thing. Organelle: Specialized structures with specific functions found inside a cell. Cell Theory All living things are made of one or more cells Cells are the basic unit of structure and function Cells come only from living cells. Two Types ...
Chapter 6 Cells
... cell what proteins (enzymes) to make. • Uncoiled chromosomes are called chromatin ...
... cell what proteins (enzymes) to make. • Uncoiled chromosomes are called chromatin ...
Cell Organelle Worksheet
... microtubules that function in cell division in animal cells. They anchor the spindle fibers during cell division and allow chromosomes to be moved to the opposite ends of the cell. ...
... microtubules that function in cell division in animal cells. They anchor the spindle fibers during cell division and allow chromosomes to be moved to the opposite ends of the cell. ...
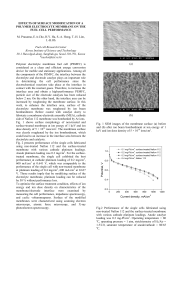
Effects of Surface Modification of a Polymer Electrolyte Membrane
... Polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cell (PEMFC) is considered as a clean and efficient energy conversion device for mobile and stationary applications. Among all the components of the PEMFC, the interface between the electrolyte and electrode catalyst plays an important role in determining the cell p ...
... Polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cell (PEMFC) is considered as a clean and efficient energy conversion device for mobile and stationary applications. Among all the components of the PEMFC, the interface between the electrolyte and electrode catalyst plays an important role in determining the cell p ...
Cell membrane
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane or cytoplasmic membrane) is a biological membrane that separates the interior of all cells from the outside environment. The cell membrane is selectively permeable to ions and organic molecules and controls the movement of substances in and out of cells. The basic function of the cell membrane is to protect the cell from its surroundings. It consists of the phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins. Cell membranes are involved in a variety of cellular processes such as cell adhesion, ion conductivity and cell signalling and serve as the attachment surface for several extracellular structures, including the cell wall, glycocalyx, and intracellular cytoskeleton. Cell membranes can be artificially reassembled.