Cells
... Eukaryotic Plant Cell • Has chloroplasts that use sunlight to make energy • Has a cell wall that protects and supports the plant cell. • Has a large vacuole which is used to store ...
... Eukaryotic Plant Cell • Has chloroplasts that use sunlight to make energy • Has a cell wall that protects and supports the plant cell. • Has a large vacuole which is used to store ...
AP Biology - gwbiology
... substances to cross into or out of the cell through the membrane more easily than others. This is important because it allows the cell to regulate transport across cellular boundaries, for example by allowing nutrients to enter and waste to exit the cell, while at the same time regulating the concen ...
... substances to cross into or out of the cell through the membrane more easily than others. This is important because it allows the cell to regulate transport across cellular boundaries, for example by allowing nutrients to enter and waste to exit the cell, while at the same time regulating the concen ...
Diffusion and Osmosis
... • Plant cells – rigid cell walls and contractile vacuoles • Animal cells – remove dissolved particles from cytoplasm – Increases free H2O molecules inside of cell ...
... • Plant cells – rigid cell walls and contractile vacuoles • Animal cells – remove dissolved particles from cytoplasm – Increases free H2O molecules inside of cell ...
Cells Questions - misslongscience
... provide energy for tail to work; large nucleus containing the genes to pass on 13. What is the job of a root hair cell and how is it adapted to do it? To absorb water. Adaptations: large surface area to move water into cell; large vacuole which affects movement of water from soil 14. List 3 ways in ...
... provide energy for tail to work; large nucleus containing the genes to pass on 13. What is the job of a root hair cell and how is it adapted to do it? To absorb water. Adaptations: large surface area to move water into cell; large vacuole which affects movement of water from soil 14. List 3 ways in ...
The Diversity of Cells Note-taking Guide (Chapter 3: Section 1
... Who was the first person to see and describe cells? How did he do it? Describe how he made his discovery. ...
... Who was the first person to see and describe cells? How did he do it? Describe how he made his discovery. ...
Cell Transport - Heritage High School
... substance across the cell membrane against its gradient Requires Energy ( usually ATP) ...
... substance across the cell membrane against its gradient Requires Energy ( usually ATP) ...
cell organelle webquest
... Objective: Upon completion of this activity, you should be able to describe the cell and identify its parts (organelles). You should be able to distinguish between plant and animal cells. PART I Go to: www.wisc-online.com/objects/index_tj.asp?objid=AP11604 Click “Next” to begin the activity. Answer ...
... Objective: Upon completion of this activity, you should be able to describe the cell and identify its parts (organelles). You should be able to distinguish between plant and animal cells. PART I Go to: www.wisc-online.com/objects/index_tj.asp?objid=AP11604 Click “Next” to begin the activity. Answer ...
B-3 Notes
... Nucleus and Mitochondria • The ‘brain’ of the cell. It controls the cell’s activities. It also contains all of the genetic material of the cell. The nucleus is responsible for growth and reproduction of cells. (Cell splitting). It is a large circular object in a cell that is easily seen in a compou ...
... Nucleus and Mitochondria • The ‘brain’ of the cell. It controls the cell’s activities. It also contains all of the genetic material of the cell. The nucleus is responsible for growth and reproduction of cells. (Cell splitting). It is a large circular object in a cell that is easily seen in a compou ...
Differences between prokaryotic and Eukaryotic
... prokaryotes is present fairly rigid, chemically complex ...
... prokaryotes is present fairly rigid, chemically complex ...
osb Week02 Organelles
... The chart below contains the organelles and structures common to all eukaryotic cells. There will be two charts that follow demonstrating the different organelles found in plant-like and animal-like cells. ORGANELLE OR STRUCTURE Plasma (Cell) Membrane ...
... The chart below contains the organelles and structures common to all eukaryotic cells. There will be two charts that follow demonstrating the different organelles found in plant-like and animal-like cells. ORGANELLE OR STRUCTURE Plasma (Cell) Membrane ...
Diffusion Lab
... 5. Small molecules that do not have an electrical charge can easily diffuse across the selectively permeable cell membrane, but larger molecules or charged atoms or molecules (ions) cannot. Sometimes a cell needs to transport molecules that are too big or have too much charge to diffuse through the ...
... 5. Small molecules that do not have an electrical charge can easily diffuse across the selectively permeable cell membrane, but larger molecules or charged atoms or molecules (ions) cannot. Sometimes a cell needs to transport molecules that are too big or have too much charge to diffuse through the ...
Cells are the basic
... • Found in plants in green algae • Contain the pigment Chlorophyll • Capture sunlight (solar energy) and store it in the bonds of glucose ...
... • Found in plants in green algae • Contain the pigment Chlorophyll • Capture sunlight (solar energy) and store it in the bonds of glucose ...
Modeling Cell Membranes
... Cell membranes are made of a variety of materials including lipids, proteins, carbohydrates, and cholesterol. The most abundant part of the cell’s membrane are phospholipids. They are special types of lipids, composed of the following parts: a glycerol molecule, two fatty acids, and one phosphate io ...
... Cell membranes are made of a variety of materials including lipids, proteins, carbohydrates, and cholesterol. The most abundant part of the cell’s membrane are phospholipids. They are special types of lipids, composed of the following parts: a glycerol molecule, two fatty acids, and one phosphate io ...
Unit1-KA1-Revision
... How do we improve the reliability of Repeat the experiment the results of an experiment? Why do we repeat experiments? To improve the reliability of the results How do we improve the validity of an By improving its design. For example, having experiment? all the reagents at the same temperature to s ...
... How do we improve the reliability of Repeat the experiment the results of an experiment? Why do we repeat experiments? To improve the reliability of the results How do we improve the validity of an By improving its design. For example, having experiment? all the reagents at the same temperature to s ...
major food source of the world
... “Some 3.4 billion years ago, a puddle of green slime kick-started a process that would terraform an inhospitable Earth into a planet with oxygen and ecosystems. Ancient cyanobacteria had stumbled onto something incredible: using photons of light to split water, and channeling the resultant burst of ...
... “Some 3.4 billion years ago, a puddle of green slime kick-started a process that would terraform an inhospitable Earth into a planet with oxygen and ecosystems. Ancient cyanobacteria had stumbled onto something incredible: using photons of light to split water, and channeling the resultant burst of ...
Active Transport
... but no energy must be used to move something down its concentration gradient. ...
... but no energy must be used to move something down its concentration gradient. ...
Cell Review!!
... ___________________________ Multiple small vacuoles. ___________________________ Smaller, simple structures ___________________________ Bacteria. ___________________________ Unicellular & Multicellular. ___________________________ Everything but bacteria cells. ___________________________ Contains c ...
... ___________________________ Multiple small vacuoles. ___________________________ Smaller, simple structures ___________________________ Bacteria. ___________________________ Unicellular & Multicellular. ___________________________ Everything but bacteria cells. ___________________________ Contains c ...
What to know Chap 11
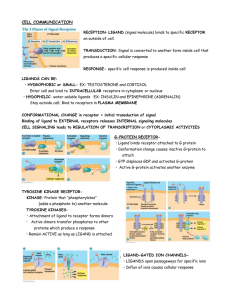
... • GTP displaces GDP and activates G-protein • Active G-protein activates another enzyme ...
... • GTP displaces GDP and activates G-protein • Active G-protein activates another enzyme ...
Cell Organelles Powerpoint 1
... • The cell membrane (and the membranes covering some organelles) are made of phospholipids. ...
... • The cell membrane (and the membranes covering some organelles) are made of phospholipids. ...
Cell Division
... Cell Growth • Organisms grow by producing more cells • Cell division occurs throughout an organisms life • Why do cells divide instead of just getting bigger? – Large cell = harder to move substances in and out – High Surface to Volume ratio ...
... Cell Growth • Organisms grow by producing more cells • Cell division occurs throughout an organisms life • Why do cells divide instead of just getting bigger? – Large cell = harder to move substances in and out – High Surface to Volume ratio ...
Lecture slides for 05 Cell Signallling
... • a cells have receptor sites for the α factor and also produce the a factor. • When mating factors are exchanged, it causes the two cells to fuse and meiosis to occur. ...
... • a cells have receptor sites for the α factor and also produce the a factor. • When mating factors are exchanged, it causes the two cells to fuse and meiosis to occur. ...
Honors Biology Unit 3 Ch.4,5 Cells & Membranes THINKING AHEAD:
... a. I can explain why cells are microscopic. b. I can explain why there is a limit to cell size. c. I can explain why prokaryotic cells are smaller than eukaryotic cells. 5. Membrane Structure - How are macromolecules arranged to form a membrane? a. I can identify the parts of the plasma membrane fro ...
... a. I can explain why cells are microscopic. b. I can explain why there is a limit to cell size. c. I can explain why prokaryotic cells are smaller than eukaryotic cells. 5. Membrane Structure - How are macromolecules arranged to form a membrane? a. I can identify the parts of the plasma membrane fro ...
Cell Organelle Notes A. Cell Wall
... L. Golgi Apparatus 1. Proteins move from ER to Golgi 2. Enzymes attach Carbohydrates and Lipids to the protein in the Golgi 3. Proteins are packaged and sent to their destination ...
... L. Golgi Apparatus 1. Proteins move from ER to Golgi 2. Enzymes attach Carbohydrates and Lipids to the protein in the Golgi 3. Proteins are packaged and sent to their destination ...
CHAPTER 15
... Unlike eukaryotic cells, prokaryotic cells do not possess membrane bound organelles, e.g. nucleus, endoplasmic reticulum, mitochondria etc. If a cell wall is present in eukaryotic cells it is composed of either cellulose (algae and plants) or chitin (fungi); in prokaryotic cells it is composed of mu ...
... Unlike eukaryotic cells, prokaryotic cells do not possess membrane bound organelles, e.g. nucleus, endoplasmic reticulum, mitochondria etc. If a cell wall is present in eukaryotic cells it is composed of either cellulose (algae and plants) or chitin (fungi); in prokaryotic cells it is composed of mu ...
Cell membrane
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane or cytoplasmic membrane) is a biological membrane that separates the interior of all cells from the outside environment. The cell membrane is selectively permeable to ions and organic molecules and controls the movement of substances in and out of cells. The basic function of the cell membrane is to protect the cell from its surroundings. It consists of the phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins. Cell membranes are involved in a variety of cellular processes such as cell adhesion, ion conductivity and cell signalling and serve as the attachment surface for several extracellular structures, including the cell wall, glycocalyx, and intracellular cytoskeleton. Cell membranes can be artificially reassembled.