8.2 Cell Growth and Reproduction
... DNA coils up into chromosomes just before cell divides Chromatin – uncoiled DNA ...
... DNA coils up into chromosomes just before cell divides Chromatin – uncoiled DNA ...
Bio 101 Cell Exam questions
... 2. How do cells get information? 3. What is involved with osmosis? 4. What are the three main shapes of prokaryotic cell? 5. What is the difference between heterotrophic and autotrophic? ...
... 2. How do cells get information? 3. What is involved with osmosis? 4. What are the three main shapes of prokaryotic cell? 5. What is the difference between heterotrophic and autotrophic? ...
Cell Structure Lab
... HONORS BIOLOGY I Cell Structure INTRODUCTION: Although there are great differences in the size, shape, color, and activities of living things, the basic building units of all life have much in common. In this investigation, you will see what some cells look like and compare the structure and organiz ...
... HONORS BIOLOGY I Cell Structure INTRODUCTION: Although there are great differences in the size, shape, color, and activities of living things, the basic building units of all life have much in common. In this investigation, you will see what some cells look like and compare the structure and organiz ...
CHAPTER SUMMARY
... C. Chemical attractions are the forces that hold membranes together D. Groupings of membrane molecules form rafts that float as a unit in the membrane (Figure 3-4) 1. Rafts may pinch inward to bring material into the cell or organelle 2. Primary structure of a cell membrane is a double layer of phos ...
... C. Chemical attractions are the forces that hold membranes together D. Groupings of membrane molecules form rafts that float as a unit in the membrane (Figure 3-4) 1. Rafts may pinch inward to bring material into the cell or organelle 2. Primary structure of a cell membrane is a double layer of phos ...
01 Physiology as the science. Bioelectrical phenomena in nerve
... Forces that determine ionic movement Electrostatic forces Opposite charges attract Identical charges repel Concentration forces Diffusion – movement of ions through semipermeable membrane Osmosis – movement of water from region of high concentration to low ...
... Forces that determine ionic movement Electrostatic forces Opposite charges attract Identical charges repel Concentration forces Diffusion – movement of ions through semipermeable membrane Osmosis – movement of water from region of high concentration to low ...
CellsandHeredityCh1S..
... a. All living things are made up of cells. b. The cell is the smallest unit of a living thing. c. The cell is the basic unit of function in an organism. ...
... a. All living things are made up of cells. b. The cell is the smallest unit of a living thing. c. The cell is the basic unit of function in an organism. ...
Cell Organelles Picture and Key Function Verbs and Analogy Key
... into useable energy(ATP) through cellular respiration. o Takes sugar and breaks it down into carbon dioxide and water. o Energy is taken out of the sugar and put into another form that is useable (ATP). o In order for sugar to be broken down, oxygen is needed. Without oxygen respiration would stop. ...
... into useable energy(ATP) through cellular respiration. o Takes sugar and breaks it down into carbon dioxide and water. o Energy is taken out of the sugar and put into another form that is useable (ATP). o In order for sugar to be broken down, oxygen is needed. Without oxygen respiration would stop. ...
cell wall - take2theweb
... •Explain what would happen if a plant cell was surrounded by a solution with a higher water concentration. Water molecules would move into the plant cell by osmosis from high concentration outside cell and it would become turgid as it has a cell wall to prevent it bursting •In both cases above whic ...
... •Explain what would happen if a plant cell was surrounded by a solution with a higher water concentration. Water molecules would move into the plant cell by osmosis from high concentration outside cell and it would become turgid as it has a cell wall to prevent it bursting •In both cases above whic ...
A1987K827900002
... lamina. This established that, unlike epidennis-fixed melanocytes, 1-cells can communicate between the dermis and epidermis. 1-cells in the middle stages of mitosis were observed in the epidermis. This proved that they can self-reproduce independently from melanocytes. The 1-cell periphery had numer ...
... lamina. This established that, unlike epidennis-fixed melanocytes, 1-cells can communicate between the dermis and epidermis. 1-cells in the middle stages of mitosis were observed in the epidermis. This proved that they can self-reproduce independently from melanocytes. The 1-cell periphery had numer ...
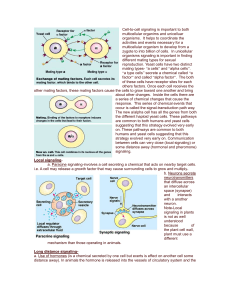
Cell-to-cell signaling is important to both multicellular organims and
... perception in vision and smell. NoteBacteria that often cause disease by secreting toxins. These toxins may interfere with G-protein functions. 60% of all medicines exert their effect by influencing G-protein pathways. b. Tyrosine-Kinase receptors-are receptors that when activated can activate more ...
... perception in vision and smell. NoteBacteria that often cause disease by secreting toxins. These toxins may interfere with G-protein functions. 60% of all medicines exert their effect by influencing G-protein pathways. b. Tyrosine-Kinase receptors-are receptors that when activated can activate more ...
Introduction to Biotechnology
... Other cell inclusions Golgi bodies- involved in modification, packaging, and secretion of materials Lysosomes- membrane-bound vesicles found in most eucaryotes involved in intracellular digestion ...
... Other cell inclusions Golgi bodies- involved in modification, packaging, and secretion of materials Lysosomes- membrane-bound vesicles found in most eucaryotes involved in intracellular digestion ...
Hongzhi Li School of Life Science
... classes distinguished by the intimacy of their relationship to the lipid bilayer (Figure 4.12). These are 1. Integral proteins that penetrate the lipid bilayer. Integral proteins are transmembrane proteins; that is, they pass entirely through the lipid bilayer and thus have domains that protrude fro ...
... classes distinguished by the intimacy of their relationship to the lipid bilayer (Figure 4.12). These are 1. Integral proteins that penetrate the lipid bilayer. Integral proteins are transmembrane proteins; that is, they pass entirely through the lipid bilayer and thus have domains that protrude fro ...
Cells Chp 7 BioA.1
... – Mitochondria – convert chemical energy stored in food (glucose) into more useful chemical energy (ATP), double membrane bound organelle, cell respiration – Chloroplasts – found in plant but not animal cells, convert light energy into chemical energy (glucose), double membrane bound organelle, phot ...
... – Mitochondria – convert chemical energy stored in food (glucose) into more useful chemical energy (ATP), double membrane bound organelle, cell respiration – Chloroplasts – found in plant but not animal cells, convert light energy into chemical energy (glucose), double membrane bound organelle, phot ...
Cell membrane - Holy Family Regional School
... acquire these substances and other times they must release them. •The methods of cell transport are classified by whether they require energy. •Active transport requires energy to conduct. •Passive transport does not require energy. ...
... acquire these substances and other times they must release them. •The methods of cell transport are classified by whether they require energy. •Active transport requires energy to conduct. •Passive transport does not require energy. ...
Doellman, Cell Structure and Function Unit Exam
... another way to regulate water uptake into the cell or they will need to develop a more rigid cell membrane.___________________________________________________ ...
... another way to regulate water uptake into the cell or they will need to develop a more rigid cell membrane.___________________________________________________ ...
THE PLANT BODY AND PLANT CELLS
... --"standard, non-specialized" plant cell; photosynthetic (in green shoots); for storage (in shoots and roots); grows, provides some structure (turgid, stiff) ...
... --"standard, non-specialized" plant cell; photosynthetic (in green shoots); for storage (in shoots and roots); grows, provides some structure (turgid, stiff) ...
Open questions: Missing pieces from the immunological jigsaw puzzle COMMENT Open Access
... cytosed by dendritic cells, released into the cytoplasm, and displayed to cytotoxic T lymphocytes through the proteasomal/MHC class I pathway that operates in the presentation of intracellular antigens (Figure 1). Although it has been clear for many years that proteins are released from endocytic co ...
... cytosed by dendritic cells, released into the cytoplasm, and displayed to cytotoxic T lymphocytes through the proteasomal/MHC class I pathway that operates in the presentation of intracellular antigens (Figure 1). Although it has been clear for many years that proteins are released from endocytic co ...
3.3 Cell Membrane (p. 81) 3.4 Diffusion and Osmosis
... ________________ - forms _______________ bonds with water o 2 ____________ ___________ tails Nonpolar ________________ – attracted to each other and repelled by water o Arranged as a ______________ polar _________________ on the outside nonpolar ______________ in the middle • Sketch figure ...
... ________________ - forms _______________ bonds with water o 2 ____________ ___________ tails Nonpolar ________________ – attracted to each other and repelled by water o Arranged as a ______________ polar _________________ on the outside nonpolar ______________ in the middle • Sketch figure ...
Looking Inside Cells
... Endoplasmic Reticulum • Organelle in the ________________ that moves materials around in a cell, is made up of folded ________________; can be _________________ or _________________ Golgi Bodies • Golgi body is the cell’s _________________ room • Organelles that _________________ cellular material ( ...
... Endoplasmic Reticulum • Organelle in the ________________ that moves materials around in a cell, is made up of folded ________________; can be _________________ or _________________ Golgi Bodies • Golgi body is the cell’s _________________ room • Organelles that _________________ cellular material ( ...
organelle function ws. - Old Saybrook Public Schools
... 15. Another name for the DNA material located within the nucleus of the cell is ...
... 15. Another name for the DNA material located within the nucleus of the cell is ...
View PDF
... a. thin protein fibers that provide support in cell cytoskeleton b. short projections involved in movement cilia c. longer projections involved in movement flagella d. hollow protein fibers that make up cytoskeleton microtubules e. solid protein fibers that make up cytoskeleton microfilaments f. jel ...
... a. thin protein fibers that provide support in cell cytoskeleton b. short projections involved in movement cilia c. longer projections involved in movement flagella d. hollow protein fibers that make up cytoskeleton microtubules e. solid protein fibers that make up cytoskeleton microfilaments f. jel ...
221 exam 1
... Describe the process of peptidoglycan synthesis beginning with the first precursor molecule inside the cell. (It is OK to use abbreviations for the monomeric components of the cell wall) ...
... Describe the process of peptidoglycan synthesis beginning with the first precursor molecule inside the cell. (It is OK to use abbreviations for the monomeric components of the cell wall) ...
Cell membrane
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane or cytoplasmic membrane) is a biological membrane that separates the interior of all cells from the outside environment. The cell membrane is selectively permeable to ions and organic molecules and controls the movement of substances in and out of cells. The basic function of the cell membrane is to protect the cell from its surroundings. It consists of the phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins. Cell membranes are involved in a variety of cellular processes such as cell adhesion, ion conductivity and cell signalling and serve as the attachment surface for several extracellular structures, including the cell wall, glycocalyx, and intracellular cytoskeleton. Cell membranes can be artificially reassembled.