Cumulative Vocabulary List Organism: A living thing Cell: The basic
... Cumulative Vocabulary List Organism: A living thing Cell: The basic unit of structure and function in all living things Cell Membrane: Holds a cell together and controls what goes into or out of the cell Cell Wall: Supports and protects a plant cell Cytoplasm: A jelly-like substance containing chemi ...
... Cumulative Vocabulary List Organism: A living thing Cell: The basic unit of structure and function in all living things Cell Membrane: Holds a cell together and controls what goes into or out of the cell Cell Wall: Supports and protects a plant cell Cytoplasm: A jelly-like substance containing chemi ...
Bacterial Morphology
... • Spores produced by bacteria in the genera Bacillus and Clostrridium enable them to survive hard environment conditions. • Spores are developed within of vegetative cells. • Spores are resistant to heat, desiccation and disinfectants. ...
... • Spores produced by bacteria in the genera Bacillus and Clostrridium enable them to survive hard environment conditions. • Spores are developed within of vegetative cells. • Spores are resistant to heat, desiccation and disinfectants. ...
Cell Communication
... • A receptor protein on or near the target cell allows the cell to detect and react to messages • The signaling molecule is complimentary in shape and site specific on the receptor molecule • Ligand (molecule that specifically binds to another) binding generally causes a receptor protein to change s ...
... • A receptor protein on or near the target cell allows the cell to detect and react to messages • The signaling molecule is complimentary in shape and site specific on the receptor molecule • Ligand (molecule that specifically binds to another) binding generally causes a receptor protein to change s ...
Biology: Assignment #4 Cell Membrane
... Passive transport is easiest for the cells because they don’t need to use any energy to make it happen. Diffusion is the simplest and most common form of passive transport. During the diffusion process, tiny particles of the materials that need to be delivered to the cells are spread through either ...
... Passive transport is easiest for the cells because they don’t need to use any energy to make it happen. Diffusion is the simplest and most common form of passive transport. During the diffusion process, tiny particles of the materials that need to be delivered to the cells are spread through either ...
P T ASSIVE RANSPORT
... linked such that the product of one reaction is consumed in the next reaction. 2. Chloroplasts have an inner membrane system consisting of thylakoids. The pumping of protons into the thylakoids builds up a proton concentration gradient across the thylakoid membrane. 3. The energy-carrying products a ...
... linked such that the product of one reaction is consumed in the next reaction. 2. Chloroplasts have an inner membrane system consisting of thylakoids. The pumping of protons into the thylakoids builds up a proton concentration gradient across the thylakoid membrane. 3. The energy-carrying products a ...
Cell Transport Review - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... _______________ 9. In passive transport, the movement of particles across a membrane requires energy. _______________ 10. Endocytosis is a process by which a cell membrane surrounds and takes in material from the environment. _______________ 11. The passive transport of material across a membrane by ...
... _______________ 9. In passive transport, the movement of particles across a membrane requires energy. _______________ 10. Endocytosis is a process by which a cell membrane surrounds and takes in material from the environment. _______________ 11. The passive transport of material across a membrane by ...
Vocabulary from the 1 st 6 weeks
... Cellulose: Cellulose is the chemical that makes the cell wall. We call it “wood”. Cellulose is made of fibers that cross over each other to make a mat. Structure: Plant cells have a cell wall that surrounds the cell. This gives the plant the strength and support that it needs. To help cell wall is ...
... Cellulose: Cellulose is the chemical that makes the cell wall. We call it “wood”. Cellulose is made of fibers that cross over each other to make a mat. Structure: Plant cells have a cell wall that surrounds the cell. This gives the plant the strength and support that it needs. To help cell wall is ...
The Cell Membrane
... • Saturated faEy acid tails decrease fluidity (more viscous) – allows for close packing ...
... • Saturated faEy acid tails decrease fluidity (more viscous) – allows for close packing ...
CELL STRUCTURE_2012_crossing the
... expelled into the intercellular space (which may be into the bloodstream). ...
... expelled into the intercellular space (which may be into the bloodstream). ...
Chapter 5 - Dr. Wilson`s Site
... Genetic material – single circular molecule in prokaryotes – double helix located in nucleus in eukaryotes Cytoplasm fills cell interior Plasma membrane encloses the cell ...
... Genetic material – single circular molecule in prokaryotes – double helix located in nucleus in eukaryotes Cytoplasm fills cell interior Plasma membrane encloses the cell ...
Animal Cell - MindMeister
... • Cell Membrane - the semipermeable membrane that encloses the cytoplasm of a cell • Cytoskeleton - the cytoskeleton is a network of fibers throughout the cell's cytoplasm that helps the cell maintain its shape and gives support to the cell • Starch Grains - energy storage in plant cells • Vacuole - ...
... • Cell Membrane - the semipermeable membrane that encloses the cytoplasm of a cell • Cytoskeleton - the cytoskeleton is a network of fibers throughout the cell's cytoplasm that helps the cell maintain its shape and gives support to the cell • Starch Grains - energy storage in plant cells • Vacuole - ...
Prokaryote vs Eukaryote Worksheet
... cells does not float freely in the cytoplasm. Instead, it is found in the nucleus, an internal compartment bound by a cell membrane. The nucleus is one kind of organelle found in eukaryotic cells. Organelles are structures that perform specific functions. Most organelles are surrounded by a membrane ...
... cells does not float freely in the cytoplasm. Instead, it is found in the nucleus, an internal compartment bound by a cell membrane. The nucleus is one kind of organelle found in eukaryotic cells. Organelles are structures that perform specific functions. Most organelles are surrounded by a membrane ...
Cell analogy project
... labels. You must include these structures in your cell: Cell membrane Nucleus Nuclear membrane (envelope) Endoplasmic reticulum (rough & smooth) Ribosomes Cytoplasm Lysosome Golgi bodies Vacuole Chloroplast Mitochondrion Centrioles Chromatin Cell wall Remember that not all of these parts are in both ...
... labels. You must include these structures in your cell: Cell membrane Nucleus Nuclear membrane (envelope) Endoplasmic reticulum (rough & smooth) Ribosomes Cytoplasm Lysosome Golgi bodies Vacuole Chloroplast Mitochondrion Centrioles Chromatin Cell wall Remember that not all of these parts are in both ...
Cells: The Basic Units of Life
... • Perhaps inspired by Hooke, Anton van Leeuwenhoek took up microscopy and built more than 500 microscopes, grinding the lenses himself. ...
... • Perhaps inspired by Hooke, Anton van Leeuwenhoek took up microscopy and built more than 500 microscopes, grinding the lenses himself. ...
Plasma Membrane and Cell Transport Clicker Questions
... A.The nonpolar (hydrophobic) ends of the molecules faces inwards B.The polar (hydrophilic) ends of the molecules faces inwards C.The fatty acid tails of the molecules ...
... A.The nonpolar (hydrophobic) ends of the molecules faces inwards B.The polar (hydrophilic) ends of the molecules faces inwards C.The fatty acid tails of the molecules ...
cell wall - HCC Learning Web
... Extracellular components and connections between cells help coordinate cellular activities • Most cells synthesize and secrete materials that are external to the plasma membrane • These extracellular structures include – Cell walls of plants – The extracellular matrix (ECM) of animal cells – Interc ...
... Extracellular components and connections between cells help coordinate cellular activities • Most cells synthesize and secrete materials that are external to the plasma membrane • These extracellular structures include – Cell walls of plants – The extracellular matrix (ECM) of animal cells – Interc ...
printer-friendly sample test questions
... 1st Item Specification: Identify major cell structures and their functions. Depth of Knowledge Level 1 1. Which organelles are most directly involved in transporting materials out of the cell? A. Nucleus and Ribosomes B. Chloroplast and Mitochondria C. Cell Membrane and Cell wall D. Golgi apparatus ...
... 1st Item Specification: Identify major cell structures and their functions. Depth of Knowledge Level 1 1. Which organelles are most directly involved in transporting materials out of the cell? A. Nucleus and Ribosomes B. Chloroplast and Mitochondria C. Cell Membrane and Cell wall D. Golgi apparatus ...
Transport in cells - Durrington High School
... Key words and definitions Diffusion – the spreading out of the particles of any substance in a solution or gas resulting in the net movement of particles from an area of high concentration to an area of lower concentration down a concentration gradient. Osmosis – the diffusion of water through a par ...
... Key words and definitions Diffusion – the spreading out of the particles of any substance in a solution or gas resulting in the net movement of particles from an area of high concentration to an area of lower concentration down a concentration gradient. Osmosis – the diffusion of water through a par ...
2.4 cell membrane transport
... They bond and drag molecules through the bilipid layer and release them on the opposite side. ...
... They bond and drag molecules through the bilipid layer and release them on the opposite side. ...
The Cell
... ____ 1. Provides energy for the cell by breaking down glucose molecules. ____ 2. Converts light energy to chemical energy for the plant cell through photosynthesis. ____ 3. This organelle controls all cell activities. ____ 4. Is selectively permeable. ____ 5. A gelatin-like substance that is the sit ...
... ____ 1. Provides energy for the cell by breaking down glucose molecules. ____ 2. Converts light energy to chemical energy for the plant cell through photosynthesis. ____ 3. This organelle controls all cell activities. ____ 4. Is selectively permeable. ____ 5. A gelatin-like substance that is the sit ...
No Slide Title
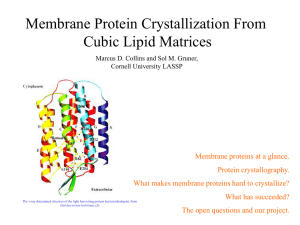
... cell membranes. They can serve as structural supports, as both passive and active channels for ions and chemicals, or serve more specialized functions such as light reception. Fully one quarter of the human genome encodes membrane protein sequences. ...
... cell membranes. They can serve as structural supports, as both passive and active channels for ions and chemicals, or serve more specialized functions such as light reception. Fully one quarter of the human genome encodes membrane protein sequences. ...
Cell membrane
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane or cytoplasmic membrane) is a biological membrane that separates the interior of all cells from the outside environment. The cell membrane is selectively permeable to ions and organic molecules and controls the movement of substances in and out of cells. The basic function of the cell membrane is to protect the cell from its surroundings. It consists of the phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins. Cell membranes are involved in a variety of cellular processes such as cell adhesion, ion conductivity and cell signalling and serve as the attachment surface for several extracellular structures, including the cell wall, glycocalyx, and intracellular cytoskeleton. Cell membranes can be artificially reassembled.