1. Cell Structure - NCEA Level 2 Biology
... Label organelles in a plant and animal cell Describe the functions of organelles ...
... Label organelles in a plant and animal cell Describe the functions of organelles ...
Cells - A world of biology
... 28. Osmosis is the passive movement of water across a partially permeable membrane along a concentration gradient. 29. Cells expend energy (ATP) during active transport. Passive transport does not involve the expenditure of ATP by the cell. 30. Endocytosis and exocytosis are examples of active tran ...
... 28. Osmosis is the passive movement of water across a partially permeable membrane along a concentration gradient. 29. Cells expend energy (ATP) during active transport. Passive transport does not involve the expenditure of ATP by the cell. 30. Endocytosis and exocytosis are examples of active tran ...
Ενδοκυττάρια ∆ιαµερίσµατα, ∆ιαλογή και µεταφορά πρωτεινών
... synthesis of most lipids (Chapter 11); synthesis of proteins for distribution to many organelles and to the plasma membrane (this chapter) ...
... synthesis of most lipids (Chapter 11); synthesis of proteins for distribution to many organelles and to the plasma membrane (this chapter) ...
Cells
... – Cells are the fundamental units of life. – All organisms are composed of cells. – All cells come from preexisting cells. • each cell possesses the different molecules necessary for sustaining life & specializations ...
... – Cells are the fundamental units of life. – All organisms are composed of cells. – All cells come from preexisting cells. • each cell possesses the different molecules necessary for sustaining life & specializations ...
Cellular Structures I
... f. Peripheral membranes are loosely associated with the membrane, usually via attaches by other proteins or lipids g. Many membrane proteins are glycosylated (this process occurs in the ER), h. Their glycosylations will always end up on the external side of the membrane VIII. EM of Cell Membrane a. ...
... f. Peripheral membranes are loosely associated with the membrane, usually via attaches by other proteins or lipids g. Many membrane proteins are glycosylated (this process occurs in the ER), h. Their glycosylations will always end up on the external side of the membrane VIII. EM of Cell Membrane a. ...
Acc_Bio_4_1and4_2_ws
... Read the passage below. Notice that the sentences are numbered. Then answer the questions that follow. 1 The diffusion of water through a selectively permeable membrane is called osmosis. 2Like other forms of diffusion, osmosis involves the movement of a substance—water—down its concentration gradie ...
... Read the passage below. Notice that the sentences are numbered. Then answer the questions that follow. 1 The diffusion of water through a selectively permeable membrane is called osmosis. 2Like other forms of diffusion, osmosis involves the movement of a substance—water—down its concentration gradie ...
Chapter 7: Cell Structure and Function
... The observations and conclusions of many scientists helped to develop the current understanding of the cell Robert Hooke (1665) __________________________________________ __________________________________________ __________________________________________ _______________________________________ ...
... The observations and conclusions of many scientists helped to develop the current understanding of the cell Robert Hooke (1665) __________________________________________ __________________________________________ __________________________________________ _______________________________________ ...
The Cell Membrane
... specific channels allow specific material across cell membrane Thus control is also maintained. Not just anybody can get in. ...
... specific channels allow specific material across cell membrane Thus control is also maintained. Not just anybody can get in. ...
Goal 2.03 Quiz 1
... B. The pituitary gland releases a hormone to the liver, which causes less water to be absorbed from the nephrons. C. The pituitary gland releases a hormone to the kidneys, which causes more water to be reabsorbed from the nephrons. D. The hypothalamus increases water available to the body, and the p ...
... B. The pituitary gland releases a hormone to the liver, which causes less water to be absorbed from the nephrons. C. The pituitary gland releases a hormone to the kidneys, which causes more water to be reabsorbed from the nephrons. D. The hypothalamus increases water available to the body, and the p ...
Bacterial morphology, metabolism and growth
... • Bacterial 70S chromosome (30+50S) • Proteins and RNA of the ribosome are significantly different • Major targets for antibacterial drugs ...
... • Bacterial 70S chromosome (30+50S) • Proteins and RNA of the ribosome are significantly different • Major targets for antibacterial drugs ...
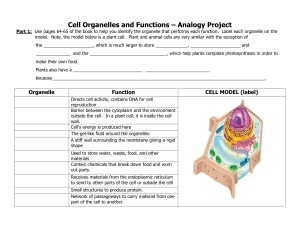
Cell Organelles and Functions – Analogy Project
... Barrier between the cytoplasm and the environment outside the cell. In a plant cell, it is inside the cell wall. Cell’s energy is produced here The gel-like fluid around the organelles A stiff wall surrounding the membrane giving a rigid shape Used to store water, waste, food, and other materials Co ...
... Barrier between the cytoplasm and the environment outside the cell. In a plant cell, it is inside the cell wall. Cell’s energy is produced here The gel-like fluid around the organelles A stiff wall surrounding the membrane giving a rigid shape Used to store water, waste, food, and other materials Co ...
2-Inside-a-cell
... 1.All living things are made of cells. 2. Cells are the basic unit of all living things. 3. Cells can only be produced by other living cells. ...
... 1.All living things are made of cells. 2. Cells are the basic unit of all living things. 3. Cells can only be produced by other living cells. ...
LB145-lecture3
... DdeI (a) DdeI restriction sites in normal and sickle-cell alleles of -globin gene ...
... DdeI (a) DdeI restriction sites in normal and sickle-cell alleles of -globin gene ...
Cell Membrane Transport Notes
... • Definition: The amount of matter in a given amount of space (area). • High Concentration = More matter in a given amount of space. • Low Concentration = Less matter in a given amount of space. • “Concentration Gradient”: A difference in concentrations. ...
... • Definition: The amount of matter in a given amount of space (area). • High Concentration = More matter in a given amount of space. • Low Concentration = Less matter in a given amount of space. • “Concentration Gradient”: A difference in concentrations. ...
Final Review
... plant has 3 corn seeds and uses the same soil from the same bag. The pots are set in the sun where they all receive the same amount of sun. The student waters the plants every day using the same amount of water at the same time. Two of the plants get 2 different fertilizers in their water. Use the p ...
... plant has 3 corn seeds and uses the same soil from the same bag. The pots are set in the sun where they all receive the same amount of sun. The student waters the plants every day using the same amount of water at the same time. Two of the plants get 2 different fertilizers in their water. Use the p ...
Chapter 4-Structure and function of Cell
... could use them to examine cells. (2) The presence of organelles and more membranes in eukaryotic cells makes possible a greater specialization of function. (3) A red blood cell is specialized to perform one main function. Without a nucleus or mitochondria, it can carry more hemoglobin and therefore, ...
... could use them to examine cells. (2) The presence of organelles and more membranes in eukaryotic cells makes possible a greater specialization of function. (3) A red blood cell is specialized to perform one main function. Without a nucleus or mitochondria, it can carry more hemoglobin and therefore, ...
Chapter 8-1: Cellular Transport
... Water is equal on both sides of the cell No water movement Cells remains circular ...
... Water is equal on both sides of the cell No water movement Cells remains circular ...
Cellular Structure - Austin Community College
... Have a nucleus Have internal membrane-bound organelles Are larger, 10-100 µm in diameter Have more complex structure Composed of algae, protozoa, fungi, animals, and plants ...
... Have a nucleus Have internal membrane-bound organelles Are larger, 10-100 µm in diameter Have more complex structure Composed of algae, protozoa, fungi, animals, and plants ...
Endocytosis and Exocytosis
... material, are brought into a cell from the outside environment is called endocytosis. This process is used to transport solids or liquids that the cell can use as nutrients into the cytoplasm. Phagocytosis is one type of endocytosis that occurs when a cell uses its membrane to bring non-dissolved so ...
... material, are brought into a cell from the outside environment is called endocytosis. This process is used to transport solids or liquids that the cell can use as nutrients into the cytoplasm. Phagocytosis is one type of endocytosis that occurs when a cell uses its membrane to bring non-dissolved so ...
Ch. 7.3 Notes, Parts 2-4
... Diffusion of specific particles through transport proteins found in the cell membrane Example:Glucose a.Transport Proteins are specific – they “select” only certain molecules to cross the membrane b.Transports molecules that are large or insoluble in lipids. ...
... Diffusion of specific particles through transport proteins found in the cell membrane Example:Glucose a.Transport Proteins are specific – they “select” only certain molecules to cross the membrane b.Transports molecules that are large or insoluble in lipids. ...
MTC25 - Intracellular Processing
... Once inside the rough ER, new proteins undergo a series of post-translational modifications depending on their ultimate destination and function, including glycosylation of 14 N-linked sugars and formation of tertiary structure under the supervision of chaperones (a large class of ATP-hydrolysing pr ...
... Once inside the rough ER, new proteins undergo a series of post-translational modifications depending on their ultimate destination and function, including glycosylation of 14 N-linked sugars and formation of tertiary structure under the supervision of chaperones (a large class of ATP-hydrolysing pr ...
Cells Name: Date: 1. Which organelle is primarily concerned with
... The process of osmosis is best illustrated by the movement of A. ...
... The process of osmosis is best illustrated by the movement of A. ...
CSP_7-16-01_outline.rtf
... Distance from the surface to center Can you figure out how many cells you have in your little finger? Group activity on page 109 How many cells? 1.3 times 10 to the 12 th B. All cells are essentially organized in the following way: 1. The plasma membrane surrounds the outside of the cell. (overhead) ...
... Distance from the surface to center Can you figure out how many cells you have in your little finger? Group activity on page 109 How many cells? 1.3 times 10 to the 12 th B. All cells are essentially organized in the following way: 1. The plasma membrane surrounds the outside of the cell. (overhead) ...
Cell membrane
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane or cytoplasmic membrane) is a biological membrane that separates the interior of all cells from the outside environment. The cell membrane is selectively permeable to ions and organic molecules and controls the movement of substances in and out of cells. The basic function of the cell membrane is to protect the cell from its surroundings. It consists of the phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins. Cell membranes are involved in a variety of cellular processes such as cell adhesion, ion conductivity and cell signalling and serve as the attachment surface for several extracellular structures, including the cell wall, glycocalyx, and intracellular cytoskeleton. Cell membranes can be artificially reassembled.