Looking Inside Cells
... The cell wall is a rigid layer of nonliving material that surrounds the cells of plants and some other organisms. It helps protect and support a cell. Although the cell wall is stiff, many materials can pass through it. In cells that do not have cell walls, the cell membrane is the outside boundary ...
... The cell wall is a rigid layer of nonliving material that surrounds the cells of plants and some other organisms. It helps protect and support a cell. Although the cell wall is stiff, many materials can pass through it. In cells that do not have cell walls, the cell membrane is the outside boundary ...
The Cell
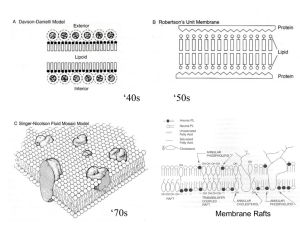
... the fluid mosaic model. This model was first proposed by biochemists S.J. Singer and Garth L. Nicolson. The model retains the basic lipid bilayer structure, however, proteins are thought to be globular and to float within the lipid bilayer. As in the other models, the hydrophobic tails of the phosph ...
... the fluid mosaic model. This model was first proposed by biochemists S.J. Singer and Garth L. Nicolson. The model retains the basic lipid bilayer structure, however, proteins are thought to be globular and to float within the lipid bilayer. As in the other models, the hydrophobic tails of the phosph ...
TOPIC: Cells AIM: What are the parts of a cell?
... When a protein is made in the ER, something called a vesicle is made. This vesicle or sac floats through the cytoplasm to the Golgi apparatus and is absorbed. After the Golgi does its work on the molecules inside the sac, a secretory vesicle is created and released into the cytoplasm. From there, ...
... When a protein is made in the ER, something called a vesicle is made. This vesicle or sac floats through the cytoplasm to the Golgi apparatus and is absorbed. After the Golgi does its work on the molecules inside the sac, a secretory vesicle is created and released into the cytoplasm. From there, ...
I. Bacteria
... a. convert nitrogen into a usable form on the roots of plants Recycling of nutrients ...
... a. convert nitrogen into a usable form on the roots of plants Recycling of nutrients ...
Chapter 3 - Palm Beach State College
... Development of the Cell Theory • Cell theory – All organisms composed of cells and cell products – Cell is the simplest structural and functional unit of life – An organism’s structure and functions are due to activities of cells – Cells come only from preexisting cells – Cells of all species exhib ...
... Development of the Cell Theory • Cell theory – All organisms composed of cells and cell products – Cell is the simplest structural and functional unit of life – An organism’s structure and functions are due to activities of cells – Cells come only from preexisting cells – Cells of all species exhib ...
Lesson 1 - Mrs. Parsiola`s Homepage
... a. Cell membrane – flexible structure that protects the inside of the cell from the environment outside the cell (animal cell #2, plant cell #9) b. Cell wall – stiff structure that protects a cell from attack by harmful organisms (plant cell #2) c. Cell appendages – often used for movement, ex. cili ...
... a. Cell membrane – flexible structure that protects the inside of the cell from the environment outside the cell (animal cell #2, plant cell #9) b. Cell wall – stiff structure that protects a cell from attack by harmful organisms (plant cell #2) c. Cell appendages – often used for movement, ex. cili ...
Lecture 1
... Pseudopodia (which translates to "false feet") are temporary cytoplasmfilled projections of the cell wall that certain eukaryotic cells use for motion or for ingesting nutrients. Pseudopodia are formed by microtubule and filament structures. The cell surface projects a membrane process called the la ...
... Pseudopodia (which translates to "false feet") are temporary cytoplasmfilled projections of the cell wall that certain eukaryotic cells use for motion or for ingesting nutrients. Pseudopodia are formed by microtubule and filament structures. The cell surface projects a membrane process called the la ...
RAD 7.3 - Mayfield City Schools
... Passive Transport Active Transport Bulk Transport Molecular Transport Endocytosis Exocytosis ...
... Passive Transport Active Transport Bulk Transport Molecular Transport Endocytosis Exocytosis ...
CK12 Passive Transport - Diffusion, Osmosis, and Facilitated Diffusion
... One example of passive transport is diffusion, when molecules move from an area of high concentration (large amount) to an area of low concentration (low amount). The amount of a substance in relation to the total volume is the concentration. They will continue to move in this way until equilibrium ...
... One example of passive transport is diffusion, when molecules move from an area of high concentration (large amount) to an area of low concentration (low amount). The amount of a substance in relation to the total volume is the concentration. They will continue to move in this way until equilibrium ...
Protist Kingdom
... Microscope and Protist Test Review • Be able to identify the stage, coarse adjustment, base, tube and eyepiece on a microscope. • Cells can be many shapes and sizes. • Be able to identify the following cell parts: Nucleus Cell membrane Cell wall Cytoplasm • Living things are part of the protist kin ...
... Microscope and Protist Test Review • Be able to identify the stage, coarse adjustment, base, tube and eyepiece on a microscope. • Cells can be many shapes and sizes. • Be able to identify the following cell parts: Nucleus Cell membrane Cell wall Cytoplasm • Living things are part of the protist kin ...
Mrs. Kaplan`s Science Page!
... 4. True or False: There are living things smaller than cells. False 5. True or False: All living things are made of cells. True 6. True or False: Cells must come from other cells. True 7. These statements are part of what theory? Cell Theory 8. Which scientist said all animals are composed of cells? ...
... 4. True or False: There are living things smaller than cells. False 5. True or False: All living things are made of cells. True 6. True or False: Cells must come from other cells. True 7. These statements are part of what theory? Cell Theory 8. Which scientist said all animals are composed of cells? ...
lecture 11
... 4 reviews on domain formation in model membranes and physical properties that underlie raft formation 2 reviews to describe techniques used for studying rafts (FRET) – and uncertainty for detecting rafts in cell membranes Raft Function in Cells: 4 on signal transduction(IgE receptor signaling, Growt ...
... 4 reviews on domain formation in model membranes and physical properties that underlie raft formation 2 reviews to describe techniques used for studying rafts (FRET) – and uncertainty for detecting rafts in cell membranes Raft Function in Cells: 4 on signal transduction(IgE receptor signaling, Growt ...
Science
... Justify why some unicellular organisms like Euglena cannot be classified as plant cells. Justify why alveoli are one cell thick and how this links to gas exchange and increasing the rate of diffusion. ...
... Justify why some unicellular organisms like Euglena cannot be classified as plant cells. Justify why alveoli are one cell thick and how this links to gas exchange and increasing the rate of diffusion. ...
1. Why is it that small lipids are soluble across the plasma
... 9. Which substance is correctly paired to the way it crosses the plasma membrane? a) water: always diffuses directly through the phospholipid bilayer without the use of channels b) carbon dioxide: passes through gaps formed as phospholipids move c) glucose: binds to carrier proteins then moves acro ...
... 9. Which substance is correctly paired to the way it crosses the plasma membrane? a) water: always diffuses directly through the phospholipid bilayer without the use of channels b) carbon dioxide: passes through gaps formed as phospholipids move c) glucose: binds to carrier proteins then moves acro ...
Molecules of Life - CCRI Faculty Web
... acids, which can be unhealthy Example: butter Most plant oils tend to be low in saturated fatty acids Example: corn oil ...
... acids, which can be unhealthy Example: butter Most plant oils tend to be low in saturated fatty acids Example: corn oil ...
Course Outline - Purdue University
... “Energy Transduction in Biological Membranes” (2 credits) Fall, 2014 9:30-10:20 Tuesday and Thursday, in LILY G458 I. COURSE SUMMARY This course provides an introduction to (1) the biophysical and biochemical basis for energy transduction in biological membranes; and (2) the structure and functions ...
... “Energy Transduction in Biological Membranes” (2 credits) Fall, 2014 9:30-10:20 Tuesday and Thursday, in LILY G458 I. COURSE SUMMARY This course provides an introduction to (1) the biophysical and biochemical basis for energy transduction in biological membranes; and (2) the structure and functions ...
Cells - Deer Creek Schools
... • Consists of a double layer membrane surrounding “sausage-like” structures which can move and wriggle about • Functions to carry out the reactions which use O2 to break down food into cellular energy (ATP) • Found most in metabolically busy cells such as the liver & muscle cells ...
... • Consists of a double layer membrane surrounding “sausage-like” structures which can move and wriggle about • Functions to carry out the reactions which use O2 to break down food into cellular energy (ATP) • Found most in metabolically busy cells such as the liver & muscle cells ...
Membrane peptidase activity of a human endothelial cell line (EA.hy
... resulted in equal soluhilisation of ECE by all the detergents. E-24.11.a Vansmemhrane anchored protein. exhibited a similar profile (Table I). Incubation of EA.hy 926 cell membranes with bacterial PI-PLC a l 3 W failed to solubilise either E-24. I I or ECE. In conclusion, EA.by 926 cells exhibit lim ...
... resulted in equal soluhilisation of ECE by all the detergents. E-24.11.a Vansmemhrane anchored protein. exhibited a similar profile (Table I). Incubation of EA.hy 926 cell membranes with bacterial PI-PLC a l 3 W failed to solubilise either E-24. I I or ECE. In conclusion, EA.by 926 cells exhibit lim ...
Cell Organelles Worksheet
... Stores material within the cell Closely stacked, flattened sacs (plants only) The sites of protein synthesis Transports materials within the cell The region inside the cell except for the nucleus Organelle that manages or controls all the cell functions in a eukaryotic cell Contains chlorophyll, a g ...
... Stores material within the cell Closely stacked, flattened sacs (plants only) The sites of protein synthesis Transports materials within the cell The region inside the cell except for the nucleus Organelle that manages or controls all the cell functions in a eukaryotic cell Contains chlorophyll, a g ...
Cell Organelle Quiz
... 1. This organelle is considered the “control center” of the cell. 2. This organelle provides energy for the cell through a process known as cellular respiration. 3. If water content in this organelle is low the plant will wilt. 4. Chlorophyll, the green pigment necessary for photosynthesis is found ...
... 1. This organelle is considered the “control center” of the cell. 2. This organelle provides energy for the cell through a process known as cellular respiration. 3. If water content in this organelle is low the plant will wilt. 4. Chlorophyll, the green pigment necessary for photosynthesis is found ...
I. The Cell Membrane: II. Three Functions of the Cell Membrane
... 3. Isotonic: solution outside of the cell has the same concentration of particles and the same concentration of water ...
... 3. Isotonic: solution outside of the cell has the same concentration of particles and the same concentration of water ...
Cell membrane
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane or cytoplasmic membrane) is a biological membrane that separates the interior of all cells from the outside environment. The cell membrane is selectively permeable to ions and organic molecules and controls the movement of substances in and out of cells. The basic function of the cell membrane is to protect the cell from its surroundings. It consists of the phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins. Cell membranes are involved in a variety of cellular processes such as cell adhesion, ion conductivity and cell signalling and serve as the attachment surface for several extracellular structures, including the cell wall, glycocalyx, and intracellular cytoskeleton. Cell membranes can be artificially reassembled.