Cell City Project – You are the Designer!
... Floating around in the cytoplasm of a cell are small structures called organelles. Like the organs in your own body, each one carries out a specific function necessary for the cell to survive. In order to survive, the cell must be able to interact with its surroundings, use energy, produce materi ...
... Floating around in the cytoplasm of a cell are small structures called organelles. Like the organs in your own body, each one carries out a specific function necessary for the cell to survive. In order to survive, the cell must be able to interact with its surroundings, use energy, produce materi ...
The Cell
... Eukaryotic cells contain a nucleus in which their genetic material is separated from the rest of the cell. Plants, animals, fungi, and protists are eukaryotes. ...
... Eukaryotic cells contain a nucleus in which their genetic material is separated from the rest of the cell. Plants, animals, fungi, and protists are eukaryotes. ...
Anti-KCNMB3 antibody [S40B-18] ab94590 Product datasheet 1 Image Overview
... Replacement or refund for products not performing as stated on the datasheet Valid for 12 months from date of delivery Response to your inquiry within 24 hours We provide support in Chinese, English, French, German, Japanese and Spanish Extensive multi-media technical resources to help you We invest ...
... Replacement or refund for products not performing as stated on the datasheet Valid for 12 months from date of delivery Response to your inquiry within 24 hours We provide support in Chinese, English, French, German, Japanese and Spanish Extensive multi-media technical resources to help you We invest ...
File
... a. Where in the plant cell would you expect to find this reaction occurring? b. Name another organelle in all plant cells that it needs for structure & support. c. How many carbon dioxide molecules are in the reactant? d. If you start with 12 oz. of carbon dioxide & 16 oz. of water, and you end up w ...
... a. Where in the plant cell would you expect to find this reaction occurring? b. Name another organelle in all plant cells that it needs for structure & support. c. How many carbon dioxide molecules are in the reactant? d. If you start with 12 oz. of carbon dioxide & 16 oz. of water, and you end up w ...
Mt. SAC
... “cream of potato soup” contain 16s ribosomes usually have a cell wall bacteria unicellular bacteria & archaea ...
... “cream of potato soup” contain 16s ribosomes usually have a cell wall bacteria unicellular bacteria & archaea ...
Movement of Substances
... molecules from a region of their higher concentration to a region of their lower concentration through a partially permeable membrane • Describe the importance of water potential gradient in the uptake of water by plants and its effect on plant and animals tissues ...
... molecules from a region of their higher concentration to a region of their lower concentration through a partially permeable membrane • Describe the importance of water potential gradient in the uptake of water by plants and its effect on plant and animals tissues ...
Cell Project Choice Board - Oxford Preparatory Academy
... and all of its organelles. animal or plant cell. Your poem, rap, or song should Your book must show creativity, include information about all the cell pictures, and a developed story line organelles and structures and what with characters. they do in a cell. The story must tell about a cell’s ...
... and all of its organelles. animal or plant cell. Your poem, rap, or song should Your book must show creativity, include information about all the cell pictures, and a developed story line organelles and structures and what with characters. they do in a cell. The story must tell about a cell’s ...
The Ear - RVC Learn
... blood or for the injection of drugs- particularly in the pig and in wild animals- elephant, rhinotranquilisation. The outer ear directs sound waves to the ear canal which is boot shaped in animals unlike the human. It is this boot shape that predispose the animal to wax accumulation or retention of ...
... blood or for the injection of drugs- particularly in the pig and in wild animals- elephant, rhinotranquilisation. The outer ear directs sound waves to the ear canal which is boot shaped in animals unlike the human. It is this boot shape that predispose the animal to wax accumulation or retention of ...
Viruses and Bacteria
... – responsible for many animal diseases like mad cow disease and the human equivalent Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. – ex. Kuru—occurred in many tribal ...
... – responsible for many animal diseases like mad cow disease and the human equivalent Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. – ex. Kuru—occurred in many tribal ...
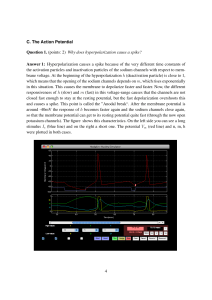
C. The Action Potential
... answer in terms of gates and voltages. Consider the plot (yellow, green, and cyan lines) of m, h and n below the voltage. Recall that the fast sodium channel conductance is proportional to m3 h, and potassium channel conductance is proportional to n4 . Answer 2: Directly after a spike occurs, the Na ...
... answer in terms of gates and voltages. Consider the plot (yellow, green, and cyan lines) of m, h and n below the voltage. Recall that the fast sodium channel conductance is proportional to m3 h, and potassium channel conductance is proportional to n4 . Answer 2: Directly after a spike occurs, the Na ...
Prentice Hall Science Explorer Cells and Heredity
... • cell wall - a rigid layer of nonliving material that surrounds the cells of plants and some other organisms. – Helps to protect and support the cell – Made mostly of cellulose (a strong material) – Allows some materials (such as water and oxygen) to pass through ...
... • cell wall - a rigid layer of nonliving material that surrounds the cells of plants and some other organisms. – Helps to protect and support the cell – Made mostly of cellulose (a strong material) – Allows some materials (such as water and oxygen) to pass through ...
Prentice Hall Science Explorer Cells and Heredity
... • cell wall - a rigid layer of nonliving material that surrounds the cells of plants and some other organisms. – Helps to protect and support the cell – Made mostly of cellulose (a strong material) – Allows some materials (such as water and oxygen) to pass through ...
... • cell wall - a rigid layer of nonliving material that surrounds the cells of plants and some other organisms. – Helps to protect and support the cell – Made mostly of cellulose (a strong material) – Allows some materials (such as water and oxygen) to pass through ...
Trask Zool 3200: Cell Biology Exam 4—Part II
... The lab you work in has discovered a previously unidentified extracellular signal molecule called X, a 75,000-dalton protein. You add purified protein X to different types of cells to determine its effect(s). When you add protein X to heart muscle cells, you observe an increase in cell contraction. ...
... The lab you work in has discovered a previously unidentified extracellular signal molecule called X, a 75,000-dalton protein. You add purified protein X to different types of cells to determine its effect(s). When you add protein X to heart muscle cells, you observe an increase in cell contraction. ...
Cell Unit Practice Test #1 Name - Mr-Paullers-wiki
... Primitive cells did not need to synthesize proteins. ...
... Primitive cells did not need to synthesize proteins. ...
Standard Biology Test Cell Unit
... bacteria and is the source of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) in these bacteria. Cell wall Composed of peptidoglycan (polysaccharides + protein), the cell wall maintains the overall shape of a bacterial cell. The three primary shapes in bacteria are coccus ...
... bacteria and is the source of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) in these bacteria. Cell wall Composed of peptidoglycan (polysaccharides + protein), the cell wall maintains the overall shape of a bacterial cell. The three primary shapes in bacteria are coccus ...
Key Area 2 Transport across membranes
... Cells and diffusion • Many substances can enter or leave cells by diffusion. • This happens across the cell membrane. • Animal cells take in glucose, oxygen and amino acids by diffusion. • Carbon dioxide and waste materials leave animal cells by diffusion. ...
... Cells and diffusion • Many substances can enter or leave cells by diffusion. • This happens across the cell membrane. • Animal cells take in glucose, oxygen and amino acids by diffusion. • Carbon dioxide and waste materials leave animal cells by diffusion. ...
Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells
... If we take a closer look at the comparison of these cells, we see the following differences: 1. Eukaryotic cells have a true nucleus, bound by a double membrane. Prokaryotic cells have no nucleus. The purpose of the nucleus is to sequester the DNA-related functions of the big eukaryotic cell into a ...
... If we take a closer look at the comparison of these cells, we see the following differences: 1. Eukaryotic cells have a true nucleus, bound by a double membrane. Prokaryotic cells have no nucleus. The purpose of the nucleus is to sequester the DNA-related functions of the big eukaryotic cell into a ...
File - Portfolio - Kelly Nicole Boden
... the ACh has been broken down, the gated receptors close again. The sodium-potassium pumps then work to restore the equilibrium of the postsynaptic neuron. This process is the stimulus that continues the signal from the brain to the destination site. The signal goes from neuron to neuron this way. At ...
... the ACh has been broken down, the gated receptors close again. The sodium-potassium pumps then work to restore the equilibrium of the postsynaptic neuron. This process is the stimulus that continues the signal from the brain to the destination site. The signal goes from neuron to neuron this way. At ...
Life`s structure and classification
... Cell Structure Cytoskeleton a framework found throughout the • _____________maintain or change its ___________ cytoplasm which helps the cell __________ ________ shape and enables some cells to _______ move • One substance that takes part in nearly every cell activity is _________ protein ...
... Cell Structure Cytoskeleton a framework found throughout the • _____________maintain or change its ___________ cytoplasm which helps the cell __________ ________ shape and enables some cells to _______ move • One substance that takes part in nearly every cell activity is _________ protein ...
Erratum to: Minimization of extracellular space as a driving force in
... the ‘syntrophy hypothesis’ only (e.g. their comment on page 13). Syntrophy means ‘feeding together’ and I applied that term generically to metabolic symbioses, including the hydrogen hypothesis which, from a metabolic point of view, is very similar to the syntrophy hypothesis. The two models involve ...
... the ‘syntrophy hypothesis’ only (e.g. their comment on page 13). Syntrophy means ‘feeding together’ and I applied that term generically to metabolic symbioses, including the hydrogen hypothesis which, from a metabolic point of view, is very similar to the syntrophy hypothesis. The two models involve ...
Plant Cell Structures - cK-12
... Most organelles are common to both animal and plant cells. However, plant cells also have features that animal cells do not have: a cell wall, a large central vacuole, and plastids such as chloroplasts. Plants have very different lifestyles from animals, and these differences are apparent when you e ...
... Most organelles are common to both animal and plant cells. However, plant cells also have features that animal cells do not have: a cell wall, a large central vacuole, and plastids such as chloroplasts. Plants have very different lifestyles from animals, and these differences are apparent when you e ...
Cell membrane
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane or cytoplasmic membrane) is a biological membrane that separates the interior of all cells from the outside environment. The cell membrane is selectively permeable to ions and organic molecules and controls the movement of substances in and out of cells. The basic function of the cell membrane is to protect the cell from its surroundings. It consists of the phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins. Cell membranes are involved in a variety of cellular processes such as cell adhesion, ion conductivity and cell signalling and serve as the attachment surface for several extracellular structures, including the cell wall, glycocalyx, and intracellular cytoskeleton. Cell membranes can be artificially reassembled.

![Anti-KCNMB3 antibody [S40B-18] ab94590 Product datasheet 1 Image Overview](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008296195_1-8866c58dd265986a1d042cbf807044a8-300x300.png)