3-D Cell Model
... B.) Your cell must be 3- dimensional with front, back and sides. C.) The model may be made out of any materials that are non-perishable D.) All parts of your cell must be labeled clearly. This can be accomplished in 2 ways: 1) Use toothpicks or straight pins and pieces of paper to make “flag” labels ...
... B.) Your cell must be 3- dimensional with front, back and sides. C.) The model may be made out of any materials that are non-perishable D.) All parts of your cell must be labeled clearly. This can be accomplished in 2 ways: 1) Use toothpicks or straight pins and pieces of paper to make “flag” labels ...
lecture30.pps
... Dependent on proteins and phagocytic cells that recognize conserved features of pathogens that are absent in the host. Found in vertebrates, invertebrates and plants. ...
... Dependent on proteins and phagocytic cells that recognize conserved features of pathogens that are absent in the host. Found in vertebrates, invertebrates and plants. ...
PureCube Rho1D4 Agarose
... One advantage of the system is the high specificity of the antibody-epitope interaction. Epitope sequence and chain length are critical for binding. For example, replacing the third alanine with glycine which removes a single methyl group, eliminates binding. Likewise, the full 9-amino acid tag bind ...
... One advantage of the system is the high specificity of the antibody-epitope interaction. Epitope sequence and chain length are critical for binding. For example, replacing the third alanine with glycine which removes a single methyl group, eliminates binding. Likewise, the full 9-amino acid tag bind ...
Jeopardy
... The statement says that “Cells only arise from existing cells” Is part of the ______________. ...
... The statement says that “Cells only arise from existing cells” Is part of the ______________. ...
Osmosis Experimental Design Lab
... Objective: Design an experiment to determine if starch and/or water can cross a simulated cell membrane. Background: Recall from discussions in class that cells use transport methods such as diffusion, osmosis, and active transport to allow substances to cross their cell membrane. Some transport met ...
... Objective: Design an experiment to determine if starch and/or water can cross a simulated cell membrane. Background: Recall from discussions in class that cells use transport methods such as diffusion, osmosis, and active transport to allow substances to cross their cell membrane. Some transport met ...
Summary Cells respond to extracellular cues via receptor signaling
... not only elicits GEF activity by Epac1 [6], but also releases an affinity for the plasma membrane. As a consequence, Epac1 becomes uniformly distributed along the plasma membrane upon elevated cAMP levels. In contrast, recruitment of Epac1 by ERM proteins is regulated by ERM phosphorylation. When ph ...
... not only elicits GEF activity by Epac1 [6], but also releases an affinity for the plasma membrane. As a consequence, Epac1 becomes uniformly distributed along the plasma membrane upon elevated cAMP levels. In contrast, recruitment of Epac1 by ERM proteins is regulated by ERM phosphorylation. When ph ...
Document
... Cell Signaling and Chemotaxis Read Chapter 15 of “Molecular Biology of the Cell” Example for cell signaling in unicellular organisms: chemotaxis in bacteria (move cell optimally in environment), sexual mating in yeast (coordinate conjugation into cell with new assortment of genes) ...
... Cell Signaling and Chemotaxis Read Chapter 15 of “Molecular Biology of the Cell” Example for cell signaling in unicellular organisms: chemotaxis in bacteria (move cell optimally in environment), sexual mating in yeast (coordinate conjugation into cell with new assortment of genes) ...
Claire, Christine
... The cell wall is found on the outside of most prokaryotic cells, including plants and fungi, but not animal cells. ...
... The cell wall is found on the outside of most prokaryotic cells, including plants and fungi, but not animal cells. ...
(C)of the plant cell.
... molecules. It then takes those big molecules, packages them in vesicles, and either stores them for later use or sends them out of the cell. It is also the organelle that builds lysosomes. Golgi complexes in the plant may also secrete complex sugars and send them off in secretory vesicles by pinchin ...
... molecules. It then takes those big molecules, packages them in vesicles, and either stores them for later use or sends them out of the cell. It is also the organelle that builds lysosomes. Golgi complexes in the plant may also secrete complex sugars and send them off in secretory vesicles by pinchin ...
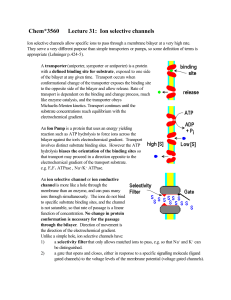
Chem*3560 Lecture 31: Ion selective channels
... function of concentration. No change in protein conformation is necessary for the passage through the bilayer. Direction of movement is the direction of the electrochemical gradient. Unlike a simple hole, ion selective channels have: ...
... function of concentration. No change in protein conformation is necessary for the passage through the bilayer. Direction of movement is the direction of the electrochemical gradient. Unlike a simple hole, ion selective channels have: ...
CH 3 Notes - Haiku Learning
... 3. Phospholipids align to form a bilayer when water is present a) large number of phospholipid molecules b) the fatty acids tails are not attract to each other very strongly so the membrane tends to be fluid or flexible i) allows animals cells to have a ...
... 3. Phospholipids align to form a bilayer when water is present a) large number of phospholipid molecules b) the fatty acids tails are not attract to each other very strongly so the membrane tends to be fluid or flexible i) allows animals cells to have a ...
The Cell - BotsRule
... merely the smallest functional units. Cells themselves contain smaller units called organelles. Organelles are tiny cell structures that carry out specific functions with a cell. Produce ...
... merely the smallest functional units. Cells themselves contain smaller units called organelles. Organelles are tiny cell structures that carry out specific functions with a cell. Produce ...
Cell Cycle-Dependent Targeting of a Kinesin at the Plasma
... fused N-terminally to RFP (ABD2-RFP) and stably transformed in GFP-KCA1 BY-2 cells. ABD2-RFP associated with the fine meshwork of actin filaments at the cell cortex except at the division site. Dual emission imaging showed that the ADZ and the KDZ colocalize (Figure 3A). Cells challenged with actin- ...
... fused N-terminally to RFP (ABD2-RFP) and stably transformed in GFP-KCA1 BY-2 cells. ABD2-RFP associated with the fine meshwork of actin filaments at the cell cortex except at the division site. Dual emission imaging showed that the ADZ and the KDZ colocalize (Figure 3A). Cells challenged with actin- ...
Create a Cell Project
... You have to create a cell using all the organelles discussed in class. You may choose to create a plant cell or an animal. Make sure that you include the correct organelles for the cell you chose to create. The cell may be made of any materials as long as it is in 3-D. You may choose to create an en ...
... You have to create a cell using all the organelles discussed in class. You may choose to create a plant cell or an animal. Make sure that you include the correct organelles for the cell you chose to create. The cell may be made of any materials as long as it is in 3-D. You may choose to create an en ...
Antifungal Agents
... 1. The same resistance mechanisms seen in bacteria except enzymatic inactivation of antifungals by fungi is unknown 2. The powerful means for gene transfer like conjugation and transposition are also absent ...
... 1. The same resistance mechanisms seen in bacteria except enzymatic inactivation of antifungals by fungi is unknown 2. The powerful means for gene transfer like conjugation and transposition are also absent ...
Meiosis II
... Meiosis is a specialized type of cell division that occurs in the formation of gametes such as egg and sperm. Although meiosis appears much more complicated than mitosis, it is really just two divisions in sequence, each one of which has strong similarities to mitosis. The illustrations used in the ...
... Meiosis is a specialized type of cell division that occurs in the formation of gametes such as egg and sperm. Although meiosis appears much more complicated than mitosis, it is really just two divisions in sequence, each one of which has strong similarities to mitosis. The illustrations used in the ...
LIFEPAC® 5th Grade Science Unit 1 Worktext - HomeSchool
... prokaryote (prō kar’ ē ot). The type of cell that contains only two basic parts: the cell membrane and protoplasm. It does not have a nucleus. Bacteria are an example of this cell. protoplasm (pro’ t\ plaz’ \m). The inner fluid material within the cell membrane. protozoan (pro’ t\ zo’ un). One-cel ...
... prokaryote (prō kar’ ē ot). The type of cell that contains only two basic parts: the cell membrane and protoplasm. It does not have a nucleus. Bacteria are an example of this cell. protoplasm (pro’ t\ plaz’ \m). The inner fluid material within the cell membrane. protozoan (pro’ t\ zo’ un). One-cel ...
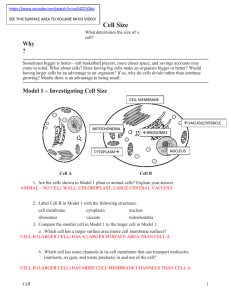
Model 1 – Investigating Cell Size
... a. Which cell has more mitochondria? CELL B (LARGER CELL) HAS MORE MITOCHONDRIA THAN CELL A. b. Propose an explanation for why the cell in part a would need more mitochondria for proper functioning of the cell. SINCE THE CELL IS LARGER, IT WILL NEED MORE ATP TO RUN CELL PROCESSES. 5. What would be t ...
... a. Which cell has more mitochondria? CELL B (LARGER CELL) HAS MORE MITOCHONDRIA THAN CELL A. b. Propose an explanation for why the cell in part a would need more mitochondria for proper functioning of the cell. SINCE THE CELL IS LARGER, IT WILL NEED MORE ATP TO RUN CELL PROCESSES. 5. What would be t ...
Neuronal cell biology, polarity, subcellular specializatio…
... filters. A, Representative Western blots from a cell surface biotinylation assay. This assay assessed the stable expression level of each EAAT at each cell surface by the application of membrane-impermeant biotinylating agent at the apical or basolateral surfaces. The control blots show that Na +/K+ ...
... filters. A, Representative Western blots from a cell surface biotinylation assay. This assay assessed the stable expression level of each EAAT at each cell surface by the application of membrane-impermeant biotinylating agent at the apical or basolateral surfaces. The control blots show that Na +/K+ ...
Nervous Tissue
... • Voltage-gated Na+ channels open & Na+ rushes into cell – in resting membrane, inactivation gate of sodium channel is open & activation gate is closed (Na+ can not get in) – when threshold (-55mV) is reached, both open & Na+ enters – inactivation gate closes again in few ten-thousandths of second – ...
... • Voltage-gated Na+ channels open & Na+ rushes into cell – in resting membrane, inactivation gate of sodium channel is open & activation gate is closed (Na+ can not get in) – when threshold (-55mV) is reached, both open & Na+ enters – inactivation gate closes again in few ten-thousandths of second – ...
Active transport
... (a) The NBD closed dimer viewed from above, as if looking down through the membrane and TMDs (which are hidden for clarity). As no complete transporter with bound ATP has been crystallized, a consensus structure based on structures of several NBDs and modeled for P-gp17 is shown. The two ATP molecul ...
... (a) The NBD closed dimer viewed from above, as if looking down through the membrane and TMDs (which are hidden for clarity). As no complete transporter with bound ATP has been crystallized, a consensus structure based on structures of several NBDs and modeled for P-gp17 is shown. The two ATP molecul ...
What is the “MOI”? - Lentiviral Gene Ontology Vectors
... The multiplicity of infection is a common term which indicates the number of vector particles per cell used in a transduction. For example, a MOI of 1 means the addition 104 vector particles to 104 cells. That’s easy, but: The term MOI is used in two slightly different ways which may make a great di ...
... The multiplicity of infection is a common term which indicates the number of vector particles per cell used in a transduction. For example, a MOI of 1 means the addition 104 vector particles to 104 cells. That’s easy, but: The term MOI is used in two slightly different ways which may make a great di ...
Non-enzymatic access to the plasma membrane of Medicago root
... The dynamics of the formation of a protoplast from a previously plasmolysed root hair perforated at its tip with a UV laser microbeam is reported in Fig. 1 (A-D). A few seconds after the opening of the hair tip, the protoplasm swells and tends to fill the apical plasmolytic space, which had been for ...
... The dynamics of the formation of a protoplast from a previously plasmolysed root hair perforated at its tip with a UV laser microbeam is reported in Fig. 1 (A-D). A few seconds after the opening of the hair tip, the protoplasm swells and tends to fill the apical plasmolytic space, which had been for ...
Chromosomes and Cell Reproduction Human Reproduction
... METAPHASE Chromosomes line up in single file at the center of the cell. The chromosomes (at the centromere) are held in place by the mitotic spindle. ...
... METAPHASE Chromosomes line up in single file at the center of the cell. The chromosomes (at the centromere) are held in place by the mitotic spindle. ...
Cell membrane
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane or cytoplasmic membrane) is a biological membrane that separates the interior of all cells from the outside environment. The cell membrane is selectively permeable to ions and organic molecules and controls the movement of substances in and out of cells. The basic function of the cell membrane is to protect the cell from its surroundings. It consists of the phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins. Cell membranes are involved in a variety of cellular processes such as cell adhesion, ion conductivity and cell signalling and serve as the attachment surface for several extracellular structures, including the cell wall, glycocalyx, and intracellular cytoskeleton. Cell membranes can be artificially reassembled.