Schwann cells - MsPhilip1234
... • What is the charge inside the neuron at rest? • Why is the cell negative inside and positive outside? (be specific) ...
... • What is the charge inside the neuron at rest? • Why is the cell negative inside and positive outside? (be specific) ...
How Does Alpha-L-Polylactate™ in Cytomax® Work Faster than
... the cell called the mitochondria, also referred to as the “powerhouse of the cell.” The mitochondria within cells are where oxygen is utilized (Lehninger). Mitochondria form a vast energy production and distribution network, in which the products of food digestion and enzymatic breakdown are burned ...
... the cell called the mitochondria, also referred to as the “powerhouse of the cell.” The mitochondria within cells are where oxygen is utilized (Lehninger). Mitochondria form a vast energy production and distribution network, in which the products of food digestion and enzymatic breakdown are burned ...
Vacuole Biogenesis in Living Soybean Root Tip
... cells the vacuole is derived de novo from other membrane systems. Currently there is not a widely accepted model of vacuole biogenesis in plants [1]. Electron micrographs show that developing vacuoles (provacuoles) in root tip meristem cells comprise complex membrane structures, including large numb ...
... cells the vacuole is derived de novo from other membrane systems. Currently there is not a widely accepted model of vacuole biogenesis in plants [1]. Electron micrographs show that developing vacuoles (provacuoles) in root tip meristem cells comprise complex membrane structures, including large numb ...
Biology 112 Exam Review - holyoke
... Review your plant study table ie. Land plants = nonvascular vs. vascular. Vascular = seedless vs. seed. Seed plants = gymnosperms vs. angiosperms. Angiosperms = monocots vs. dicots. Parts of a flower Life cycle of a conifer ...
... Review your plant study table ie. Land plants = nonvascular vs. vascular. Vascular = seedless vs. seed. Seed plants = gymnosperms vs. angiosperms. Angiosperms = monocots vs. dicots. Parts of a flower Life cycle of a conifer ...
eukaryotic
... Cytokinesis “from the greek cyto- (cell) and kinesis (motion, movement)” Cytokinesis is final part of telophase; however, cytokinesis is a separate process that begins at the same time as telophase. Cytokinesis is a separate process, necessary for completing cell division. In both animal and plant ...
... Cytokinesis “from the greek cyto- (cell) and kinesis (motion, movement)” Cytokinesis is final part of telophase; however, cytokinesis is a separate process that begins at the same time as telophase. Cytokinesis is a separate process, necessary for completing cell division. In both animal and plant ...
Biology 11 - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... Describe how cells are arranged into increasingly complex levels of cellular organization in multicellular organisms - tissues; organs; organ systems Explain why it is necessary for cells to have a high surface area to volume ratio. Use changes in SA:V ratios to explain why cells must be small. Desc ...
... Describe how cells are arranged into increasingly complex levels of cellular organization in multicellular organisms - tissues; organs; organ systems Explain why it is necessary for cells to have a high surface area to volume ratio. Use changes in SA:V ratios to explain why cells must be small. Desc ...
What happens after cells grow?
... of the cell can? 3. What is cellular respiration? 4. Which organelle is mostly responsible for cellular respiration? 5. What is protein synthesis? 6. Which organelles are responsible for protein synthesis? 7. Name and briefly describe the four phases of mitosis. 8. Create a t-chart or Venn diagram a ...
... of the cell can? 3. What is cellular respiration? 4. Which organelle is mostly responsible for cellular respiration? 5. What is protein synthesis? 6. Which organelles are responsible for protein synthesis? 7. Name and briefly describe the four phases of mitosis. 8. Create a t-chart or Venn diagram a ...
Ch 4 Notes
... • List three structures that are present in plant cells but not in animal cells. • Compare the plasma membrane,the primary cell wall, and the secondary cell wall. • Explain the role of the central vacuole. • Describe the roles of plastids in the life of a plant. • Identify features that distinguish ...
... • List three structures that are present in plant cells but not in animal cells. • Compare the plasma membrane,the primary cell wall, and the secondary cell wall. • Explain the role of the central vacuole. • Describe the roles of plastids in the life of a plant. • Identify features that distinguish ...
Diffusion vs. Bulk Flow
... • A major compartment in most mature plant cells is the vacuole, a large organelle that can occupy as much as 90% of more of the protoplast’s volume • The vacuolar membrane – Regulates transport between the cytosol and the vacuole Cell wall Transport proteins in the plasma membrane regulate traffic ...
... • A major compartment in most mature plant cells is the vacuole, a large organelle that can occupy as much as 90% of more of the protoplast’s volume • The vacuolar membrane – Regulates transport between the cytosol and the vacuole Cell wall Transport proteins in the plasma membrane regulate traffic ...
Transport Across Cell Membrane - Bioenergetics and Cell Metabolism
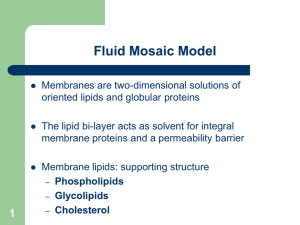
... Membranes are two-dimensional solutions of oriented lipids and globular proteins ...
... Membranes are two-dimensional solutions of oriented lipids and globular proteins ...
Introduction 1.1 The Importance of Homeostasis in Maintaining
... fission, and that form sexual states which are not enclosed in a fruiting body." (Boekhout and Kurtzman, 1996). Yeast cell membranes acts as impermeable barriers against hydrophilic molecules to prevent the mixing of the cytoplasm and external environment. Around 7.5 n thick, the cell membrane is co ...
... fission, and that form sexual states which are not enclosed in a fruiting body." (Boekhout and Kurtzman, 1996). Yeast cell membranes acts as impermeable barriers against hydrophilic molecules to prevent the mixing of the cytoplasm and external environment. Around 7.5 n thick, the cell membrane is co ...
Variations in Surface Protein Composition Associated
... that gonococcal resistance to serum killing is multifactorial, the use of isogenic variants has shown that one outer membrane protein (Ha*) is associated with considerable resistance. The data presented in Table 2 indicate that protein IIa* offers no protection against water-soluble, low molecular w ...
... that gonococcal resistance to serum killing is multifactorial, the use of isogenic variants has shown that one outer membrane protein (Ha*) is associated with considerable resistance. The data presented in Table 2 indicate that protein IIa* offers no protection against water-soluble, low molecular w ...
Lesson 1 - Wsimg.com
... • The inside of a cell is mainly water. • This makes it easier for the substances to move around inside a cell, gives cells their shapes, and helps keep the structures inside a cell organized. • The liquid part of a cell inside the cell membrane is called the cytoplasm. ...
... • The inside of a cell is mainly water. • This makes it easier for the substances to move around inside a cell, gives cells their shapes, and helps keep the structures inside a cell organized. • The liquid part of a cell inside the cell membrane is called the cytoplasm. ...
I--Prokaryotes 138-156 incl Chart
... environment necessary for biochemistry of life. Second, the membrane is involved in energy transduction (e.g., in the chemiosmotic synthesis of ATP in the mitochondrion, the chloroplast, and the bacterial membrane). Third, membranes are involved in recognition. ...
... environment necessary for biochemistry of life. Second, the membrane is involved in energy transduction (e.g., in the chemiosmotic synthesis of ATP in the mitochondrion, the chloroplast, and the bacterial membrane). Third, membranes are involved in recognition. ...
Mycobacterium tuberculosis evades macrophage defenses by
... Avirulent mycobacteria, including mutant forms of MTb that have lost their ability to cause disease, stimulate the macrophage to undergo apoptosis, which results in a 'cellular corpse' with an impermeable envelope that prevents bacteria from escaping. This process leads to containment and killing of ...
... Avirulent mycobacteria, including mutant forms of MTb that have lost their ability to cause disease, stimulate the macrophage to undergo apoptosis, which results in a 'cellular corpse' with an impermeable envelope that prevents bacteria from escaping. This process leads to containment and killing of ...
202_cpt - Christopher`s World Grille
... • The inside of a cell is mainly water. • This makes it easier for the substances to move around inside a cell, gives cells their shapes, and helps keep the structures inside a cell organized. • The liquid part of a cell inside the cell membrane is called the cytoplasm. ...
... • The inside of a cell is mainly water. • This makes it easier for the substances to move around inside a cell, gives cells their shapes, and helps keep the structures inside a cell organized. • The liquid part of a cell inside the cell membrane is called the cytoplasm. ...
BIO 218 F 2012 CH 02 Martini Lecture Outline
... Membrane permeability of the plasmalemma Active processes Endocytosis Phagocytosis Pinocytosis Receptor-mediated endocytosis ...
... Membrane permeability of the plasmalemma Active processes Endocytosis Phagocytosis Pinocytosis Receptor-mediated endocytosis ...
BIO 218 F 2012 CH 02 Martini Lecture Outline
... Membrane permeability of the plasmalemma Active processes Endocytosis Phagocytosis Pinocytosis Receptor-mediated endocytosis ...
... Membrane permeability of the plasmalemma Active processes Endocytosis Phagocytosis Pinocytosis Receptor-mediated endocytosis ...
Interaction between Cell Wall and Plasma Membrane via RGD Motif
... Our previous reports suggested that the plant cell wall plays crucial roles in the recognition of pathogens and in determination of plant-pathogen specificity (Kiba et al. 1995, 1996, 1997, Shiraishi et al. 1997, 1998). However, the mechanism of signal transmission from the cell wall to plasma membr ...
... Our previous reports suggested that the plant cell wall plays crucial roles in the recognition of pathogens and in determination of plant-pathogen specificity (Kiba et al. 1995, 1996, 1997, Shiraishi et al. 1997, 1998). However, the mechanism of signal transmission from the cell wall to plasma membr ...
AP Biology - Cell Structure and Function
... O Protein synthesis O Free or on ER (structurally identical) O Free make proteins that function in ...
... O Protein synthesis O Free or on ER (structurally identical) O Free make proteins that function in ...
Cell Structure Lesson: Vacuole
... special Cytoskeleton type of vacuole known as a contractile vacuole. ...
... special Cytoskeleton type of vacuole known as a contractile vacuole. ...
plant carbohydrates
... - as cells increase in volume, H-bonds that link cellulose and hemicellulose loosen, allowing the internal osmotic pressure of the cell to push apart the cellulose microfibers; this process is critical for plant cell growth and is helped by enzymatic cleavage of xyloglucan chains ...
... - as cells increase in volume, H-bonds that link cellulose and hemicellulose loosen, allowing the internal osmotic pressure of the cell to push apart the cellulose microfibers; this process is critical for plant cell growth and is helped by enzymatic cleavage of xyloglucan chains ...
The Role of MET in the Proliferation of Papillary Renal...
... After inhibiting the function of MET in two ...
... After inhibiting the function of MET in two ...
Section 3.1 Cell Theory and Comparison of Prokaryotic and
... Prokaryotic Cell Structures and their Functions A. Plasma Membrane – Protective coating surrounding the cytoplasm that regulates(controls) what enters/leaves cell. Archaea have special lipids in their membranes not found in any other type of organism on Earth. B. Cell Wall – Covering outside the cel ...
... Prokaryotic Cell Structures and their Functions A. Plasma Membrane – Protective coating surrounding the cytoplasm that regulates(controls) what enters/leaves cell. Archaea have special lipids in their membranes not found in any other type of organism on Earth. B. Cell Wall – Covering outside the cel ...
Cell membrane
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane or cytoplasmic membrane) is a biological membrane that separates the interior of all cells from the outside environment. The cell membrane is selectively permeable to ions and organic molecules and controls the movement of substances in and out of cells. The basic function of the cell membrane is to protect the cell from its surroundings. It consists of the phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins. Cell membranes are involved in a variety of cellular processes such as cell adhesion, ion conductivity and cell signalling and serve as the attachment surface for several extracellular structures, including the cell wall, glycocalyx, and intracellular cytoskeleton. Cell membranes can be artificially reassembled.