Biological membranes - Essays in Biochemistry
... the lipid bilayer surrounding cells is fluid in nature and allows lateral diffusion of both lipids and membrane proteins. Despite all this movement of lipids and proteins in the bilayer, vertical movement, or ‘flipflop’, of lipids and proteins from one leaflet to another occurs at an extremely low r ...
... the lipid bilayer surrounding cells is fluid in nature and allows lateral diffusion of both lipids and membrane proteins. Despite all this movement of lipids and proteins in the bilayer, vertical movement, or ‘flipflop’, of lipids and proteins from one leaflet to another occurs at an extremely low r ...
Chapter One
... What makes carbon such an abundant element in biomolecules? a. It can form up to five bonds by sharing its electrons. b. It forms only single bonds. c. It provides low bond energy. d. It forms stable covalent bonds by electron pair sharing. e. It does not usually bond to other carbons, allowing a mo ...
... What makes carbon such an abundant element in biomolecules? a. It can form up to five bonds by sharing its electrons. b. It forms only single bonds. c. It provides low bond energy. d. It forms stable covalent bonds by electron pair sharing. e. It does not usually bond to other carbons, allowing a mo ...
Cell Line Development Market by Product (Equipment
... U.S. We publish strategically analyzed market research reports and serve as a business intelligence partner to Fortune 500 companies across the world. M&M’s flagship competitive intelligence and market research platform, "RT" connects over 200,000 markets and entire value chains for deeper understan ...
... U.S. We publish strategically analyzed market research reports and serve as a business intelligence partner to Fortune 500 companies across the world. M&M’s flagship competitive intelligence and market research platform, "RT" connects over 200,000 markets and entire value chains for deeper understan ...
biomolecular_STRUCTURES
... Organs and cells communicate through molecules circulating in the blood stream—hormones ...
... Organs and cells communicate through molecules circulating in the blood stream—hormones ...
Chapter 4 - 4.2PowerPoint
... • The nucleus stores genetic information. • Many processes occur in the endoplasmic reticulum. • There are two types of endoplasmic reticulum. – rough endoplasmic reticulum – smooth endoplasmic reticulum ...
... • The nucleus stores genetic information. • Many processes occur in the endoplasmic reticulum. • There are two types of endoplasmic reticulum. – rough endoplasmic reticulum – smooth endoplasmic reticulum ...
CELL-STRUCTURE AND FUNCTIIONS
... are enclosed in a membrane. This membrane provides shape to the cells of plants and animals. Cell wall is an additional covering over the cell membrane in plant cells. It gives shape and rigidity to these cells (Fig. 8.7). Bacterial cell also has a cell wall. Size of Cells The size of cells in livin ...
... are enclosed in a membrane. This membrane provides shape to the cells of plants and animals. Cell wall is an additional covering over the cell membrane in plant cells. It gives shape and rigidity to these cells (Fig. 8.7). Bacterial cell also has a cell wall. Size of Cells The size of cells in livin ...
cell — structure and functions cell — structure and
... membrane provides shape to the cells of plants and animals. Cell wall is an additional covering over the cell membrane in plant cells. It gives shape and rigidity to these cells (Fig. 8.7). Bacterial cell also has a cell wall. Size of Cells The size of cells in living organisms may be as small as a ...
... membrane provides shape to the cells of plants and animals. Cell wall is an additional covering over the cell membrane in plant cells. It gives shape and rigidity to these cells (Fig. 8.7). Bacterial cell also has a cell wall. Size of Cells The size of cells in living organisms may be as small as a ...
3D Cell City Guidelines and Rubric
... How does a cell function like a city? Think about the sites and sounds of a city. You see people and cars moving about, buildings, restaurants, and lights everywhere. What a flurry of activity! Cells, the basic units of life, can be compared to a city. Cells are building and breaking down material. ...
... How does a cell function like a city? Think about the sites and sounds of a city. You see people and cars moving about, buildings, restaurants, and lights everywhere. What a flurry of activity! Cells, the basic units of life, can be compared to a city. Cells are building and breaking down material. ...
Triton X-100 promotes a cholesterol
... We analysed the lipid structure of the cell surface of COS cells by means of two-photon microscopy. The fluorescent probe Laurdan has been used to characterize phase separation in model membranes [24,25] and visualize ordered domains on the surface of living cells [21]. Laurdan does not partition pr ...
... We analysed the lipid structure of the cell surface of COS cells by means of two-photon microscopy. The fluorescent probe Laurdan has been used to characterize phase separation in model membranes [24,25] and visualize ordered domains on the surface of living cells [21]. Laurdan does not partition pr ...
Is host lipidation of pathogen effector proteins a general virulence
... The involvement of lipidation in some and modified by N-myristoylation and severe human diseases (cancer, genetic S-palmitoylation (Dowen et al., 2009). In blindness, premature aging, or osteo- 2003, we showed that the Salmonella effecpetrosis; Perez-Sala, 2007) underlies the tor protein SifA has a ...
... The involvement of lipidation in some and modified by N-myristoylation and severe human diseases (cancer, genetic S-palmitoylation (Dowen et al., 2009). In blindness, premature aging, or osteo- 2003, we showed that the Salmonella effecpetrosis; Perez-Sala, 2007) underlies the tor protein SifA has a ...
Slide 1 - Elsevier Store
... FIGURE 3-10: Structure of a glutamate transporter. This bacterial glutamate transporter provides the first high-resolution model of a glutamate transporter (Yernool, et al., 2004). The X-ray data indicate a trimeric structure. (A) A view of the trimer extracellularly and perpendicular to the bilaye ...
... FIGURE 3-10: Structure of a glutamate transporter. This bacterial glutamate transporter provides the first high-resolution model of a glutamate transporter (Yernool, et al., 2004). The X-ray data indicate a trimeric structure. (A) A view of the trimer extracellularly and perpendicular to the bilaye ...
Cells, Mitosis-Meiosis, Photosynthesis
... You consist of a great many cells, but like all other organisms, you started life as a single cell. How did you develop from a single cell into an organism with trillions of cells? The answer is cell division. After cells grow to their maximum size, they divide into two new cells. These new cells ar ...
... You consist of a great many cells, but like all other organisms, you started life as a single cell. How did you develop from a single cell into an organism with trillions of cells? The answer is cell division. After cells grow to their maximum size, they divide into two new cells. These new cells ar ...
Gene Section BLNK (B-cell linker) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics
... plays a critical role in B cell development in human and mice. ...
... plays a critical role in B cell development in human and mice. ...
1.2 Ultrastructure of Cells 2016
... • Lots of mitochondria – the synthesis of protein requires enegy – this a metabolically active cell • Lots of secretory granules/vesicles near the inside border • Likely to be a cell that specializes in secreting a protein product, possibly a hormone or enzyme ...
... • Lots of mitochondria – the synthesis of protein requires enegy – this a metabolically active cell • Lots of secretory granules/vesicles near the inside border • Likely to be a cell that specializes in secreting a protein product, possibly a hormone or enzyme ...
Plant cell walls - Faculty of Biological Sciences
... • Plant cells have fixed neighbours for life • Cell separation is a more active & highly regulated process in all tissues – intercellular space – leaf and fruit abscission – pod dehiscence to release seed ...
... • Plant cells have fixed neighbours for life • Cell separation is a more active & highly regulated process in all tissues – intercellular space – leaf and fruit abscission – pod dehiscence to release seed ...
Terms to know - Northern Highlands
... 9. What is the organization of cells in multicellular organisms? Which parts are hydrophobic and hydrophilic? 10. Know the parts of the cell, their functions, and what type of cell they are found in (animal, plant, prokaryotic)? ...
... 9. What is the organization of cells in multicellular organisms? Which parts are hydrophobic and hydrophilic? 10. Know the parts of the cell, their functions, and what type of cell they are found in (animal, plant, prokaryotic)? ...
File
... • Lots of mitochondria – the synthesis of protein requires enegy – this a metabolically active cell • Lots of secretory granules/vesicles near the inside border • Likely to be a cell that specializes in secreting a protein product, possibly a hormone or enzyme ...
... • Lots of mitochondria – the synthesis of protein requires enegy – this a metabolically active cell • Lots of secretory granules/vesicles near the inside border • Likely to be a cell that specializes in secreting a protein product, possibly a hormone or enzyme ...
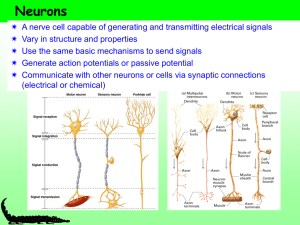
action potential
... than either input would produce separately. • If one input is excitatory and the other is inhibitory, they will cancel each other out Temporal Summation Temporal summation occurs when two presynaptic inputs arrive at the postsynaptic cell in rapid succession. Because the inputs overlap in time, they ...
... than either input would produce separately. • If one input is excitatory and the other is inhibitory, they will cancel each other out Temporal Summation Temporal summation occurs when two presynaptic inputs arrive at the postsynaptic cell in rapid succession. Because the inputs overlap in time, they ...
S-layer and cytoplasmic membrane – exceptions from the typical
... to them: high temperature, high acidity, high pressure, anoxic, no organic substrates. In those habitats, various species of hyperthermophilic or more generally extremophilic archaea were found and described. Therefore, the general cell plan of the majority of these extremophilic archaea and especia ...
... to them: high temperature, high acidity, high pressure, anoxic, no organic substrates. In those habitats, various species of hyperthermophilic or more generally extremophilic archaea were found and described. Therefore, the general cell plan of the majority of these extremophilic archaea and especia ...
Alex, Adnan
... Diffusion and Osmosis • Another method of transportation is called diffusion. In diffusion, molecules move from areas of high concentration to areas of low concentration. This makes sense since particles in general usually move to where there is more space. • The diffusion of water is given the spe ...
... Diffusion and Osmosis • Another method of transportation is called diffusion. In diffusion, molecules move from areas of high concentration to areas of low concentration. This makes sense since particles in general usually move to where there is more space. • The diffusion of water is given the spe ...
Neuron Structure and Function
... i) Na+ channels move into an inactive state ii) delayed K+ channels open Inactivating Na+ channels - Na+ channels go to an inactivated state after 1-2 msec after first opening - inactivated = can NOT be reopened - Membrane potential now determined mostly by K+ (same as for resting potential) and m ...
... i) Na+ channels move into an inactive state ii) delayed K+ channels open Inactivating Na+ channels - Na+ channels go to an inactivated state after 1-2 msec after first opening - inactivated = can NOT be reopened - Membrane potential now determined mostly by K+ (same as for resting potential) and m ...
Cells 3
... Bi means two Scientists use the fluid mosaic model to describe the the cell membrane. The lipid bilayer behaves more like a fluid than a solid. ...
... Bi means two Scientists use the fluid mosaic model to describe the the cell membrane. The lipid bilayer behaves more like a fluid than a solid. ...
7.5 Proteins - HS Biology IB
... tertiary structure refers to overall 3-D shape; conformation can determine function; tertiary structure determined by R-group interactions / ionic interactions / hydrophobic interactions / disulfide bridges / H-bonds; quaternary structure is only found in proteins formed from more than one polypepti ...
... tertiary structure refers to overall 3-D shape; conformation can determine function; tertiary structure determined by R-group interactions / ionic interactions / hydrophobic interactions / disulfide bridges / H-bonds; quaternary structure is only found in proteins formed from more than one polypepti ...
What is a Cell?
... 1. Fold your “Cell Structures: Cell Organelle Graphic Organizer” like a hamburger. It should flip open like a book with the title on the front and “Glue Here” on the back. 2. Apply glue to the “Glue Here” box. The best way to get the sheet to stick is to trace over the “Glue Here” box and then make ...
... 1. Fold your “Cell Structures: Cell Organelle Graphic Organizer” like a hamburger. It should flip open like a book with the title on the front and “Glue Here” on the back. 2. Apply glue to the “Glue Here” box. The best way to get the sheet to stick is to trace over the “Glue Here” box and then make ...
Chapter 3: Movement Of Substances Across the Substances
... (c) Explain the effect of the following solution to plant cell/ Explain what will happen to this cellular component/ Explain what happen on the red blood cells in solution M/Explain the phenomena(state the phenomena) P1-the solution is hypertonic to the red blood cell P2-Osmosis occur P3-Water molec ...
... (c) Explain the effect of the following solution to plant cell/ Explain what will happen to this cellular component/ Explain what happen on the red blood cells in solution M/Explain the phenomena(state the phenomena) P1-the solution is hypertonic to the red blood cell P2-Osmosis occur P3-Water molec ...
Cell membrane
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane or cytoplasmic membrane) is a biological membrane that separates the interior of all cells from the outside environment. The cell membrane is selectively permeable to ions and organic molecules and controls the movement of substances in and out of cells. The basic function of the cell membrane is to protect the cell from its surroundings. It consists of the phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins. Cell membranes are involved in a variety of cellular processes such as cell adhesion, ion conductivity and cell signalling and serve as the attachment surface for several extracellular structures, including the cell wall, glycocalyx, and intracellular cytoskeleton. Cell membranes can be artificially reassembled.