
11_Lecture_Presentation
... chemical messengers • Animal and plant cells have cell junctions that directly connect the cytoplasm of adjacent cells • In local signaling, animal cells may communicate by direct contact, or cell-cell recognition ...
... chemical messengers • Animal and plant cells have cell junctions that directly connect the cytoplasm of adjacent cells • In local signaling, animal cells may communicate by direct contact, or cell-cell recognition ...
Solubilization of Membrane Proteins into Functional Lipid‐Bilayer
... the rim of the nanodiscs. In sharp contrast with the situation encountered in SMALPs, the transition temperature was not downshifted upon solubilization by moderate DIBMA concentrations (Figure 3 d). This suggests much less perturbation of lipid packing by DIBMA compared with SMA(3:1), the stronger ...
... the rim of the nanodiscs. In sharp contrast with the situation encountered in SMALPs, the transition temperature was not downshifted upon solubilization by moderate DIBMA concentrations (Figure 3 d). This suggests much less perturbation of lipid packing by DIBMA compared with SMA(3:1), the stronger ...
File
... Oxidation and reduction are paired chemical reactions in which electrons are transferred from one substance to another in a predictable way. The control and applications of oxidation and reduction reactions have significant implications for industry, health and safety, and the environment. ...
... Oxidation and reduction are paired chemical reactions in which electrons are transferred from one substance to another in a predictable way. The control and applications of oxidation and reduction reactions have significant implications for industry, health and safety, and the environment. ...
Eukaryotic cells
... • Basic features of all cells: – Plasma membrane – Semifluid substance called cytosol – Chromosomes (carry genes) – Ribosomes (make proteins) ...
... • Basic features of all cells: – Plasma membrane – Semifluid substance called cytosol – Chromosomes (carry genes) – Ribosomes (make proteins) ...
cell: the basic unit of structure in living things
... lasm of a plant cell. Chloroplasts contain a green substance called chlorophyll {KLOR uh fillJ. Chlorophyll is needed by green plants for food- making, The food-making process of green plants is called photosynthesis [fo tuh SIN thuh sis . Most chlorophyll is found in the leaf cells of green plants. ...
... lasm of a plant cell. Chloroplasts contain a green substance called chlorophyll {KLOR uh fillJ. Chlorophyll is needed by green plants for food- making, The food-making process of green plants is called photosynthesis [fo tuh SIN thuh sis . Most chlorophyll is found in the leaf cells of green plants. ...
Document
... 1. The specific transport of a species down its concentration gradient is referred to as_............................... 2. Membrane pums are energy …………………………….. 3. In ……………………………………………. a phosphoryl group is transferred from ATP to a specific aspartate residue. 4. Cardiac steroids such as digitoxi ...
... 1. The specific transport of a species down its concentration gradient is referred to as_............................... 2. Membrane pums are energy …………………………….. 3. In ……………………………………………. a phosphoryl group is transferred from ATP to a specific aspartate residue. 4. Cardiac steroids such as digitoxi ...
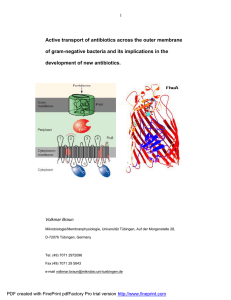
Active transport of antibiotics across the outer membrane of gram
... the cytoplasmic membrane. After transport into the cytoplasm, iron is released from albomycin, and the thioribosyl pyrimidine group has to be cleaved from the carrier to be inhibitory; in E. coli, this is mainly achieved by peptidase N. Mutants devoid of peptidase N activity are resistant to albomyc ...
... the cytoplasmic membrane. After transport into the cytoplasm, iron is released from albomycin, and the thioribosyl pyrimidine group has to be cleaved from the carrier to be inhibitory; in E. coli, this is mainly achieved by peptidase N. Mutants devoid of peptidase N activity are resistant to albomyc ...
Ch 7 Crossword Assignment Create a crossword puzzle using the
... 5 more words from the list, including: nucleus, organelle, plasma membrane, fluid mosaic model, phospholipid bilayer, chloroplast, or golgi apparatus. ...
... 5 more words from the list, including: nucleus, organelle, plasma membrane, fluid mosaic model, phospholipid bilayer, chloroplast, or golgi apparatus. ...
Chemical Change and Electrical Work
... To draw an atomic-scale diagram that illustrates the electrochemical processes involved in the corrosion of iron. To describe why metals such as aluminum and copper corrode more slowly than iron. To describe galvanizing, alloying and cathodic protection and how these methods are used to prevent corr ...
... To draw an atomic-scale diagram that illustrates the electrochemical processes involved in the corrosion of iron. To describe why metals such as aluminum and copper corrode more slowly than iron. To describe galvanizing, alloying and cathodic protection and how these methods are used to prevent corr ...
bop8e_chapter03 REVISED W16 Part 2
... Microtubule Arrays and the Cell Cycle • Changes in the distribution of microtubules during the cell cycle and cell wall formation during cytokinesis • (a) During interphase, and in enlarging and differentiating cells, the microtubules lie just inside the plasma membrane • (b) Just before prophase, ...
... Microtubule Arrays and the Cell Cycle • Changes in the distribution of microtubules during the cell cycle and cell wall formation during cytokinesis • (a) During interphase, and in enlarging and differentiating cells, the microtubules lie just inside the plasma membrane • (b) Just before prophase, ...
ears: the vestibuloauditory system
... angles to one another; their receptor areas are present in their ampullae and are called cristae ampullaris. Cristae are histologically similar to maculae, with hair cells, supporting cells, and nerve endings, with proteoglycan layer called the cupula. The cupula here is thick, and attached to the s ...
... angles to one another; their receptor areas are present in their ampullae and are called cristae ampullaris. Cristae are histologically similar to maculae, with hair cells, supporting cells, and nerve endings, with proteoglycan layer called the cupula. The cupula here is thick, and attached to the s ...
Document
... • Lamina may organize chromatin into functional domains, provide structure to nucleus; • breaks down in mitosis so that mitotic spindle microtubules can associate with kinetochores. • NEBD is initiated with one to three holes which expand over the entire envelope; • holes occur opposite of invaginat ...
... • Lamina may organize chromatin into functional domains, provide structure to nucleus; • breaks down in mitosis so that mitotic spindle microtubules can associate with kinetochores. • NEBD is initiated with one to three holes which expand over the entire envelope; • holes occur opposite of invaginat ...
Anti-GABA antibody [5A9] ab86186 Product datasheet 1 Abreviews 1 Image
... Use at an assay dependent concentration. (if perfusion fixed) ...
... Use at an assay dependent concentration. (if perfusion fixed) ...
Muscle Model Activities
... together, they form a fibrous bundle that is held together by a tough membrane. Several bundles are gathered together and wrapped in another membrane to form the muscle tissue. Tendons make-up the wrapping membrane. Now, we are going to make a model of a muscle. 1. Take 6 straws from your stack. Eac ...
... together, they form a fibrous bundle that is held together by a tough membrane. Several bundles are gathered together and wrapped in another membrane to form the muscle tissue. Tendons make-up the wrapping membrane. Now, we are going to make a model of a muscle. 1. Take 6 straws from your stack. Eac ...
7-2 Eukaryotic Cell Structure
... Cell biologists divide the eukaryotic cell into two major parts: the nucleus and the cytoplasm. The Cytoplasm is the jelly-like substance of the cell outside the nucleus that supports the ...
... Cell biologists divide the eukaryotic cell into two major parts: the nucleus and the cytoplasm. The Cytoplasm is the jelly-like substance of the cell outside the nucleus that supports the ...
Lipid Domain Theory of General Anesthesia - Deep Blue
... Using this model, previous work has shown that the actin skeleton acts as ‘pinning sites’ on the plasma membrane to disrupt larger fluctuations and instead localizes one phase to form a network of channels, segregating the membrane.7 This work has led to the hypothesis that the plasma membranes of ...
... Using this model, previous work has shown that the actin skeleton acts as ‘pinning sites’ on the plasma membrane to disrupt larger fluctuations and instead localizes one phase to form a network of channels, segregating the membrane.7 This work has led to the hypothesis that the plasma membranes of ...
cell cycle1
... 1. Interphase a. Interphase can be divided into 3 phases: i. G1 phase At the beginning of interphase, the cells are brand new. They are very small and do not have very much chemical energy (ATP). During this phase, the cell grows rapidly and makes ATP. Many metabolic activities are occuring. For e ...
... 1. Interphase a. Interphase can be divided into 3 phases: i. G1 phase At the beginning of interphase, the cells are brand new. They are very small and do not have very much chemical energy (ATP). During this phase, the cell grows rapidly and makes ATP. Many metabolic activities are occuring. For e ...
Remember what qualifies as *alive*?
... • When can I retest? ▫ As soon as the test autopsy has been completed. ▫ Turn in with your test autopsy. ▫ Earn up to an 80% with a score of 100% on the retest. ...
... • When can I retest? ▫ As soon as the test autopsy has been completed. ▫ Turn in with your test autopsy. ▫ Earn up to an 80% with a score of 100% on the retest. ...
Active transport - Teachit Science
... 6. The absorption of mineral ions is done by active transport. The energy for active transport comes from respiration which uses glucose and oxygen to produce energy. If there is insufficient oxygen the active transport of mineral ions can not take place. 7. The size of the concentration gradient; t ...
... 6. The absorption of mineral ions is done by active transport. The energy for active transport comes from respiration which uses glucose and oxygen to produce energy. If there is insufficient oxygen the active transport of mineral ions can not take place. 7. The size of the concentration gradient; t ...
Lesson 2
... • All cells (and all matter) are made up of atoms and molecules. • An element is a substance that cannot be broken down into a simpler substance. • The smallest unit of an element that maintains the properties of that element is called an atom. ...
... • All cells (and all matter) are made up of atoms and molecules. • An element is a substance that cannot be broken down into a simpler substance. • The smallest unit of an element that maintains the properties of that element is called an atom. ...
The syndapin protein family: linking membrane trafficking with the
... what is known about the functions of these proteins in vivo, we refer to them as such here – avoiding use of other names (e.g. FAP52, SH3p14 and PACSIN) to keep the nomenclature as simple as possible. Dynamin is an important player in endocytosis, a process that comprises several distinct steps. Fir ...
... what is known about the functions of these proteins in vivo, we refer to them as such here – avoiding use of other names (e.g. FAP52, SH3p14 and PACSIN) to keep the nomenclature as simple as possible. Dynamin is an important player in endocytosis, a process that comprises several distinct steps. Fir ...
Lecture 10: Introduction to Bacteria (Structure, Growth
... cytoplasmic mass where the nucleic acid, ribosomes, storage granules, and other cellular components are found and a protective cell envelope of variable complexity. ...
... cytoplasmic mass where the nucleic acid, ribosomes, storage granules, and other cellular components are found and a protective cell envelope of variable complexity. ...
Chapter # PLASMA MEMBRANE PHOSPHOLIPID ASYMMETRY
... oil. Because of this liquid-like character the polar lipids are able to rotate freely about their axis perpendicular to the plane of the membrane and to diffuse readily in the lateral plane. Movement from one leaflet of the bilayer to the other, however, is severely constrained and measured in half ...
... oil. Because of this liquid-like character the polar lipids are able to rotate freely about their axis perpendicular to the plane of the membrane and to diffuse readily in the lateral plane. Movement from one leaflet of the bilayer to the other, however, is severely constrained and measured in half ...
2010_Clement_BiolMed
... The observed increase in membrane fluidity in HT22H2O2 and HT22Glu cells suggests that the actual localization and/or distribution of lipids and membrane-associated proteins might be altered compared to HT22WT cells. We therefore analyzed the composition of different membrane regions, DRMs and non-DR ...
... The observed increase in membrane fluidity in HT22H2O2 and HT22Glu cells suggests that the actual localization and/or distribution of lipids and membrane-associated proteins might be altered compared to HT22WT cells. We therefore analyzed the composition of different membrane regions, DRMs and non-DR ...
Cell membrane
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane or cytoplasmic membrane) is a biological membrane that separates the interior of all cells from the outside environment. The cell membrane is selectively permeable to ions and organic molecules and controls the movement of substances in and out of cells. The basic function of the cell membrane is to protect the cell from its surroundings. It consists of the phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins. Cell membranes are involved in a variety of cellular processes such as cell adhesion, ion conductivity and cell signalling and serve as the attachment surface for several extracellular structures, including the cell wall, glycocalyx, and intracellular cytoskeleton. Cell membranes can be artificially reassembled.











![Anti-GABA antibody [5A9] ab86186 Product datasheet 1 Abreviews 1 Image](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008296205_1-9b8206993c446f240db0ef9ab99a7030-300x300.png)










