Radiation Protection Of Medical Staff
... For the reasons noted previously, it is crucial that programmes for radiation protection training in hospital settings include those medical personnel who are outside the radiology department but who are involved in X-ray imaging procedures. 4.2. Monitoring of occupational exposure in X-ray imaging ...
... For the reasons noted previously, it is crucial that programmes for radiation protection training in hospital settings include those medical personnel who are outside the radiology department but who are involved in X-ray imaging procedures. 4.2. Monitoring of occupational exposure in X-ray imaging ...
Proc. Intl. Soc. Mag. Reson. Med. 21 (2013)
... has been used successfully in evaluating stroke in the pediatric and neonatal populations [3,4] and more recently, even for quantitative evaluation of blood oxygenation [5]. SWI is a high resolution magnetic resonance (MR) imaging technique, which is much more sensitive than the typical T2* based bl ...
... has been used successfully in evaluating stroke in the pediatric and neonatal populations [3,4] and more recently, even for quantitative evaluation of blood oxygenation [5]. SWI is a high resolution magnetic resonance (MR) imaging technique, which is much more sensitive than the typical T2* based bl ...
BMSc Medical Imaging Core Courses
... Fall. Credit, two hours. This course introduces the student to the principles and practices of medical imaging. The function of radiographer and their relationship with the health care team is stressed. The student is also oriented to the hospital environment and health care systems. MI 203. Medical ...
... Fall. Credit, two hours. This course introduces the student to the principles and practices of medical imaging. The function of radiographer and their relationship with the health care team is stressed. The student is also oriented to the hospital environment and health care systems. MI 203. Medical ...
Distinguishing Tumefactive Demyelinating Lesions from Glioma or
... T2-weighted hyperintense lesion had no typical feature of vasogenic edema, it was considered an unenhanced tumor or TDL. CT imaging.—Two raters (D.G.N. and J.H.K.), blinded to the final diagnoses, independently evaluated the CT images at separate sessions more than 1 month after assessing MR images. ...
... T2-weighted hyperintense lesion had no typical feature of vasogenic edema, it was considered an unenhanced tumor or TDL. CT imaging.—Two raters (D.G.N. and J.H.K.), blinded to the final diagnoses, independently evaluated the CT images at separate sessions more than 1 month after assessing MR images. ...
INTRODUCTION TO CHEST IMAGING
... PLAIN RADIOGRAPHY OF THE CHEST (CXR) • CRITERIA OF A GOOD X-RAY OF THE CHEST • Patient central – a-Sterno-clavincular junction equidistant from midline (spinous process). – b-Mediasternum 2/3 to left and 1/3 to right • Lung apices appear and lower 3 cervical vertebrae. • The diaphragm should be fou ...
... PLAIN RADIOGRAPHY OF THE CHEST (CXR) • CRITERIA OF A GOOD X-RAY OF THE CHEST • Patient central – a-Sterno-clavincular junction equidistant from midline (spinous process). – b-Mediasternum 2/3 to left and 1/3 to right • Lung apices appear and lower 3 cervical vertebrae. • The diaphragm should be fou ...
associate of science in medical imaging course
... stressing the assessment process, differences between many types of medications, patient trust and health promotion. The course continues by focusing on mathematics and calculations, and outlines the essential information for various drug groups. MI 308 Overview of Medical Imaging Three semester hou ...
... stressing the assessment process, differences between many types of medications, patient trust and health promotion. The course continues by focusing on mathematics and calculations, and outlines the essential information for various drug groups. MI 308 Overview of Medical Imaging Three semester hou ...
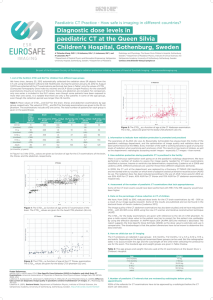
Diagnostic dose levels in paediatric CT at the
... levels of radiation when examining each and every child. This results in low levels of retakes, as well as the department’s radiologists accepting nosier images – especially CT images - than normal. 3. How radiation protection during paediatric CT is practised in the facility There is continuous opt ...
... levels of radiation when examining each and every child. This results in low levels of retakes, as well as the department’s radiologists accepting nosier images – especially CT images - than normal. 3. How radiation protection during paediatric CT is practised in the facility There is continuous opt ...
Time-resolved contrast-enhanced 3D MR angiography
... example, in Time frame 5 (see Fig. 2) if the contrast agent were not present during the acquisition of section A,, but arrived before the acquisition of section D q q . (Other interpolation methods can be employed to reduce or eliminate this effect.) Figures 4a-4c show MIP projections of three of 27 ...
... example, in Time frame 5 (see Fig. 2) if the contrast agent were not present during the acquisition of section A,, but arrived before the acquisition of section D q q . (Other interpolation methods can be employed to reduce or eliminate this effect.) Figures 4a-4c show MIP projections of three of 27 ...
Innovation, in reach 3D Panoramic Cephalometric Would you like to
... also be easy to understand and operate. Consequently, our design philosophy has always emphasized a commitment to practical ingenuity. In other words, we make sure innovation remains simple, while staying focused on the evolving needs of modern dentistry. Today’s practitioner requires diagnostic too ...
... also be easy to understand and operate. Consequently, our design philosophy has always emphasized a commitment to practical ingenuity. In other words, we make sure innovation remains simple, while staying focused on the evolving needs of modern dentistry. Today’s practitioner requires diagnostic too ...
Routine Shoulder MRI for Evaluating Glenoid Labrum Pathology as
... magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to determine the type and extent of their underlying shoulder pathology. When a glenoid labrum tear is suspected clinically and there are no contraindications, the patient will receive an intraarticular injection of gadolinium contrast prior to undergoing the MRI (MR ...
... magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to determine the type and extent of their underlying shoulder pathology. When a glenoid labrum tear is suspected clinically and there are no contraindications, the patient will receive an intraarticular injection of gadolinium contrast prior to undergoing the MRI (MR ...
Physics of CT
... MSCT can be used for: • Fast imaging for larger tissue volume • Fewer motion artifact ...
... MSCT can be used for: • Fast imaging for larger tissue volume • Fewer motion artifact ...
view brochure
... With the increasing demands on departments for improved clinical outcomes and faster workflows, iViewGT helps achieve this with: n excellent clearance and superior field-of-view n low patient dose, as small as 1MU n on- and off-line enhancement and registration of the images n on-line images for pat ...
... With the increasing demands on departments for improved clinical outcomes and faster workflows, iViewGT helps achieve this with: n excellent clearance and superior field-of-view n low patient dose, as small as 1MU n on- and off-line enhancement and registration of the images n on-line images for pat ...
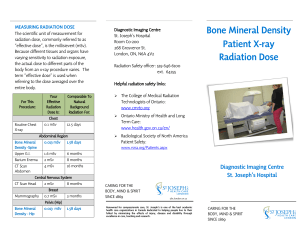
Bone Mineral Density Patient X
... greatly outweigh the risk of harm. X-rays are produced only when the exposure switch is momentarily turned on. As with visible light, no radiation remains after the switch is turned off. ...
... greatly outweigh the risk of harm. X-rays are produced only when the exposure switch is momentarily turned on. As with visible light, no radiation remains after the switch is turned off. ...
MODULE TITLE Imaging with IR (IIR) 3
... Attend reporting sessions, Attend staff meetings Find out how data is archived, Undertake contamination monitoring at the end of the day – or if there has been a spill under the direction of the RPS ...
... Attend reporting sessions, Attend staff meetings Find out how data is archived, Undertake contamination monitoring at the end of the day – or if there has been a spill under the direction of the RPS ...
TREMR: Table-resonance elastography with MR
... strong resonance in this low-frequency range, but the patient table is the hardware responsible for transmitting the vibrations to the subject. For multislice acquisitions, each slice needs to be acquired following its own vibration-inducing gradient lobe. It is also important that the TR per slice ...
... strong resonance in this low-frequency range, but the patient table is the hardware responsible for transmitting the vibrations to the subject. For multislice acquisitions, each slice needs to be acquired following its own vibration-inducing gradient lobe. It is also important that the TR per slice ...
ACR–SPR Practice Parameter for the Performance of Chest
... not intended, nor should they be used, to establish a legal standard of care1. For these reasons and those set forth below, the American College of Radiology and our collaborating medical specialty societies caution against the use of these documents in litigation in which the clinical decisions of ...
... not intended, nor should they be used, to establish a legal standard of care1. For these reasons and those set forth below, the American College of Radiology and our collaborating medical specialty societies caution against the use of these documents in litigation in which the clinical decisions of ...
Electronic Posters: Pulse Sequences, Reconstruction
... Total Variation was recently introduced in many different MRI applications. The assumption of TV is that images consist of areas which are piecewise constant. However, in many practical MRI situations, this assumption is not valid due to the existence of smooth signal inhomogeneities originating fro ...
... Total Variation was recently introduced in many different MRI applications. The assumption of TV is that images consist of areas which are piecewise constant. However, in many practical MRI situations, this assumption is not valid due to the existence of smooth signal inhomogeneities originating fro ...
RLA Inaugural Class Graduates
... in a research scan? Suppose the principle investigator is not an expert in the area. Does this change the situation? Should every Two ethical principles guide the discussion. 1) research study be clinically interpreted by a Respect for autonomy – the right of a person qualified physician? This could ...
... in a research scan? Suppose the principle investigator is not an expert in the area. Does this change the situation? Should every Two ethical principles guide the discussion. 1) research study be clinically interpreted by a Respect for autonomy – the right of a person qualified physician? This could ...
ACR–SPR–STR Practice Parameter for the Performance of Pulmonary
... pretest likelihood of pulmonary embolism and the results of any previously performed imaging studies, laboratory tests, or other clinical evaluations. For patients being studied for acute pulmonary embolic disease, current chest radiographic images, preferably posteroanterior and lateral, should be ...
... pretest likelihood of pulmonary embolism and the results of any previously performed imaging studies, laboratory tests, or other clinical evaluations. For patients being studied for acute pulmonary embolic disease, current chest radiographic images, preferably posteroanterior and lateral, should be ...
September - RadMD.com
... Request for a follow-up study - A follow-up study may be needed to help evaluate a patient’s progress after treatment, procedure, intervention or surgery. Documentation requires a medical reason that clearly indicates why additional imaging is needed for the type and area(s) requested. Conductive He ...
... Request for a follow-up study - A follow-up study may be needed to help evaluate a patient’s progress after treatment, procedure, intervention or surgery. Documentation requires a medical reason that clearly indicates why additional imaging is needed for the type and area(s) requested. Conductive He ...
Accelerator integrated cone beam systems for verification imaging
... CT, kV-CBCT uses a cone shaped x ray beam and acquires an entire volume (14–26 cm in length) in a single gantry rotation lasting ~2 mins. To acquire the kV-CBCT projection data, flat-panel detectors are used in fluoroscopy mode, obtaining multiple projections per second; these projections are used t ...
... CT, kV-CBCT uses a cone shaped x ray beam and acquires an entire volume (14–26 cm in length) in a single gantry rotation lasting ~2 mins. To acquire the kV-CBCT projection data, flat-panel detectors are used in fluoroscopy mode, obtaining multiple projections per second; these projections are used t ...
Localization II: Volume Imaging Techniques and Accuracy for
... limitations Know your applicators and their expected ...
... limitations Know your applicators and their expected ...
Fetal Magnetic Resonance Imaging at 3.0 T
... chemical constitution, flow, and action. In confirmation of the significance of these achievements, Paul Lauterbur and Peter Mansfield received the Nobel Prize in Medicine in 2003 for their discoveries concerning magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Magnetic resonance imaging is among the most notable ...
... chemical constitution, flow, and action. In confirmation of the significance of these achievements, Paul Lauterbur and Peter Mansfield received the Nobel Prize in Medicine in 2003 for their discoveries concerning magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Magnetic resonance imaging is among the most notable ...
Full Prescribing Information.
... DaTscan (Ioflupane I 123 Injection) is a radiopharmaceutical indicated for striatal dopamine transporter visualization using single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) brain imaging to assist in the evaluation of adult patients with suspected Parkinsonian syndromes (PS). In these patients, D ...
... DaTscan (Ioflupane I 123 Injection) is a radiopharmaceutical indicated for striatal dopamine transporter visualization using single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) brain imaging to assist in the evaluation of adult patients with suspected Parkinsonian syndromes (PS). In these patients, D ...
a study of topographic and phenotypic characteristics of normal skin
... 2- or 3-dimensional, crosssectional visualization of microstructural morphology of tissues5. It measures the intensity of reflection/backscatter of infrared light from the skin. As optical echoes cannot be measured directly because of the high velocity of light, OCT is therefore based on low-coheren ...
... 2- or 3-dimensional, crosssectional visualization of microstructural morphology of tissues5. It measures the intensity of reflection/backscatter of infrared light from the skin. As optical echoes cannot be measured directly because of the high velocity of light, OCT is therefore based on low-coheren ...
Medical imaging

Medical imaging is the technique and process of creating visual representations of the interior of a body for clinical analysis and medical intervention. Medical imaging seeks to reveal internal structures hidden by the skin and bones, as well as to diagnose and treat disease. Medical imaging also establishes a database of normal anatomy and physiology to make it possible to identify abnormalities. Although imaging of removed organs and tissues can be performed for medical reasons, such procedures are usually considered part of pathology instead of medical imaging.As a discipline and in its widest sense, it is part of biological imaging and incorporates radiology which uses the imaging technologies of X-ray radiography, magnetic resonance imaging, medical ultrasonography or ultrasound, endoscopy, elastography, tactile imaging, thermography, medical photography and nuclear medicine functional imaging techniques as positron emission tomography.Measurement and recording techniques which are not primarily designed to produce images, such as electroencephalography (EEG), magnetoencephalography (MEG), electrocardiography (ECG), and others represent other technologies which produce data susceptible to representation as a parameter graph vs. time or maps which contain information about the measurement locations. In a limited comparison these technologies can be considered as forms of medical imaging in another discipline.Up until 2010, 5 billion medical imaging studies had been conducted worldwide. Radiation exposure from medical imaging in 2006 made up about 50% of total ionizing radiation exposure in the United States.In the clinical context, ""invisible light"" medical imaging is generally equated to radiology or ""clinical imaging"" and the medical practitioner responsible for interpreting (and sometimes acquiring) the images is a radiologist. ""Visible light"" medical imaging involves digital video or still pictures that can be seen without special equipment. Dermatology and wound care are two modalities that use visible light imagery. Diagnostic radiography designates the technical aspects of medical imaging and in particular the acquisition of medical images. The radiographer or radiologic technologist is usually responsible for acquiring medical images of diagnostic quality, although some radiological interventions are performed by radiologists.As a field of scientific investigation, medical imaging constitutes a sub-discipline of biomedical engineering, medical physics or medicine depending on the context: Research and development in the area of instrumentation, image acquisition (e.g. radiography), modeling and quantification are usually the preserve of biomedical engineering, medical physics, and computer science; Research into the application and interpretation of medical images is usually the preserve of radiology and the medical sub-discipline relevant to medical condition or area of medical science (neuroscience, cardiology, psychiatry, psychology, etc.) under investigation. Many of the techniques developed for medical imaging also have scientific and industrial applications.Medical imaging is often perceived to designate the set of techniques that noninvasively produce images of the internal aspect of the body. In this restricted sense, medical imaging can be seen as the solution of mathematical inverse problems. This means that cause (the properties of living tissue) is inferred from effect (the observed signal). In the case of medical ultrasonography, the probe consists of ultrasonic pressure waves and echoes that go inside the tissue to show the internal structure. In the case of projectional radiography, the probe uses X-ray radiation, which is absorbed at different rates by different tissue types such as bone, muscle and fat.The term noninvasive is used to denote a procedure where no instrument is introduced into a patient's body which is the case for most imaging techniques used.