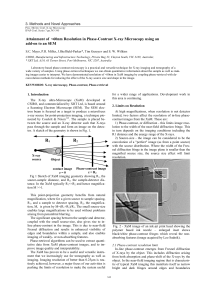
Attainment of 60nm Resolution in Phase-Contrast X
... For a given wavelength, and a fixed source to detector distance the fringe width decreases with decreasing R', and hence R1. This implies that for high resolution it is necessary to work at high magnification. However since contrast (e.g. phase contrast) tends to reduce with increasing magnification ...
... For a given wavelength, and a fixed source to detector distance the fringe width decreases with decreasing R', and hence R1. This implies that for high resolution it is necessary to work at high magnification. However since contrast (e.g. phase contrast) tends to reduce with increasing magnification ...
Real-Time Ultrasound Elastographic Imaging of Ocular and
... ous tissues, other than ocular and periocular structures, imply that the technique can accurately assess the mechanical properties of tissues, differentiate normal from abnormal tissues, and provide indications for the nature of tumors.4-10 The eye differs from other organs in which elastography has ...
... ous tissues, other than ocular and periocular structures, imply that the technique can accurately assess the mechanical properties of tissues, differentiate normal from abnormal tissues, and provide indications for the nature of tumors.4-10 The eye differs from other organs in which elastography has ...
Webb, Ch.2s5
... to the photons that interact in the patient and deliver dose. If the spectrum is too soft, then the lower-energy photons will only contribute to patient dose and not to image contrast, and it is important that they be removed from the x-ray beam before it reaches the patient. This can be achieved by ...
... to the photons that interact in the patient and deliver dose. If the spectrum is too soft, then the lower-energy photons will only contribute to patient dose and not to image contrast, and it is important that they be removed from the x-ray beam before it reaches the patient. This can be achieved by ...
Article (Published version)
... rithm. Another interest of this combination is that both modalities allow a two-dimensional image reconstruction from any scattered radiation collected by a one-dimensional collimated nonmoving camera. This involves a new concept of detector with high-energy resolution able to collect the scattered ...
... rithm. Another interest of this combination is that both modalities allow a two-dimensional image reconstruction from any scattered radiation collected by a one-dimensional collimated nonmoving camera. This involves a new concept of detector with high-energy resolution able to collect the scattered ...
Detection of Brain Metastases by 3
... by mutual consensus. Determination as metastases was based on the appearance of the lesions {e.g., ring enhancing lesions, lesions with peritumoral edema, and lesions which were hyperintense without continuity as vascular structure on all three sequences or one sequence of interest (i.e., T1-VISTA o ...
... by mutual consensus. Determination as metastases was based on the appearance of the lesions {e.g., ring enhancing lesions, lesions with peritumoral edema, and lesions which were hyperintense without continuity as vascular structure on all three sequences or one sequence of interest (i.e., T1-VISTA o ...
MI 001 - Specific Criteria for Medical Imaging, Oct 2014
... 3.15.2 Cassette/ screen must be uniquely identified on screen to identify screens with artifacts or defects. 3.15.3 With the exception of the markers indicating laterally and view, all labels must be placed as far from the breast as possible. ...
... 3.15.2 Cassette/ screen must be uniquely identified on screen to identify screens with artifacts or defects. 3.15.3 With the exception of the markers indicating laterally and view, all labels must be placed as far from the breast as possible. ...
Image-guided Radiation Therapy (IGRT)
... position and/or radiation beams in order to more precisely target radiation at the tumor and avoid healthy surrounding tissue. ...
... position and/or radiation beams in order to more precisely target radiation at the tumor and avoid healthy surrounding tissue. ...
The potential role of 3D x-ray spectroscopy in the imaging of breast
... The examination involves lying prone within the magnetic, with both breasts suspended into a dedicated radiofrequency coil. The examination can take over an hour as various pulse sequences are acquired. Contrast enhancement is achieved by the injection of gadolinium based media through a cannula, du ...
... The examination involves lying prone within the magnetic, with both breasts suspended into a dedicated radiofrequency coil. The examination can take over an hour as various pulse sequences are acquired. Contrast enhancement is achieved by the injection of gadolinium based media through a cannula, du ...
Ionizing Radiation * X-Ray Imaging
... • Differential contrast between bone and soft tissues • Differential contrast between soft tissues and air • Little difference between various tissue types i.e. fat, muscle, solid organs, blood…. ...
... • Differential contrast between bone and soft tissues • Differential contrast between soft tissues and air • Little difference between various tissue types i.e. fat, muscle, solid organs, blood…. ...
RT204 - Mohawk Valley Community College
... Explain the purpose of a diagnostic-type protective tube housing, differentiate between a primary and secondary protective barrier, and list examples of each. Describe the construction of protective structural shielding, and list the factors that govern the selection of appropriate construction mate ...
... Explain the purpose of a diagnostic-type protective tube housing, differentiate between a primary and secondary protective barrier, and list examples of each. Describe the construction of protective structural shielding, and list the factors that govern the selection of appropriate construction mate ...
Ionizing Radiation – X-Ray Imaging
... • Differential contrast between bone and soft tissues • Differential contrast between soft tissues and air • Little difference between various tissue types i.e. fat, muscle, solid organs, blood…. ...
... • Differential contrast between bone and soft tissues • Differential contrast between soft tissues and air • Little difference between various tissue types i.e. fat, muscle, solid organs, blood…. ...
Finding the Great Mimicker: Pheochromocytoma
... appearance of adrenal masses found on CT. These imaging characteristics often dictate appropriate subsequent biochemistry/surgical work up. From Young, WF. The Incidentally Discovered Adrenal Mass. New England Journal of Medicine 2007; 356:601610 ...
... appearance of adrenal masses found on CT. These imaging characteristics often dictate appropriate subsequent biochemistry/surgical work up. From Young, WF. The Incidentally Discovered Adrenal Mass. New England Journal of Medicine 2007; 356:601610 ...
Low cost digital detector technology for emerging economies
... • Amplified pixels have higher SNR for lower X-ray dose and reduce off -panel circuit complexity (by MUXing) when compared to PPS pixels • When both innovations are put together, the question arises: • Are higher quality and lower cost possible right now? • “Yes!” ...
... • Amplified pixels have higher SNR for lower X-ray dose and reduce off -panel circuit complexity (by MUXing) when compared to PPS pixels • When both innovations are put together, the question arises: • Are higher quality and lower cost possible right now? • “Yes!” ...
Optimization of Bolus Tracking Technique in Abdominal Dual
... The evaluation of arterial blood supply (i.e. vascularity or vascular pattern) in tumor is an essential step for diagnosis of various abdominal malignancies such as hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and pancreatic cancer (PC), and it is usually performed by multi-phasic contrast-enhanced CT. Recent dev ...
... The evaluation of arterial blood supply (i.e. vascularity or vascular pattern) in tumor is an essential step for diagnosis of various abdominal malignancies such as hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and pancreatic cancer (PC), and it is usually performed by multi-phasic contrast-enhanced CT. Recent dev ...
Athens Euroclinic - Breast Centres Network
... comprehensive and quality healthcare services to women in the area of prevention, diagnosis and treatment of breast conditions. Staffed by specialized scientists from all related medical specialties and equipped with state-of-the-art diagnostic and imaging devices, it ensures very efficient diagnosi ...
... comprehensive and quality healthcare services to women in the area of prevention, diagnosis and treatment of breast conditions. Staffed by specialized scientists from all related medical specialties and equipped with state-of-the-art diagnostic and imaging devices, it ensures very efficient diagnosi ...
6668 Form Completion Guidelines
... to registration to determine and confirm study eligibility. It includes general demographic characteristics (including age, gender, and race), inclusion/exclusion criteria checks, and receipt of written informed consent. At the time of enrollment, the participant is to review, sign and date the cons ...
... to registration to determine and confirm study eligibility. It includes general demographic characteristics (including age, gender, and race), inclusion/exclusion criteria checks, and receipt of written informed consent. At the time of enrollment, the participant is to review, sign and date the cons ...
Complete right cerebral hemispheric diffusion restriction and its
... the disease.4 These features were demonstrated in our case. However, complete right cerebral hemispheric diffusion restriction seen in the acute phase in our patient has not been previously reported, to the best of our knowledge. We aim to highlight this finding and offer an explanation for it. DWI i ...
... the disease.4 These features were demonstrated in our case. However, complete right cerebral hemispheric diffusion restriction seen in the acute phase in our patient has not been previously reported, to the best of our knowledge. We aim to highlight this finding and offer an explanation for it. DWI i ...
Overview of Focused Ultrasound (aka `all the fuss over FUS)
... T1W+C MRI => perfused Post-Treatment (3 mo): T1W+C MRI => non-perfused CT => increased density in treated area and disappearance of nodular pathologic tissue Patient classified as complete responder (MDACC criteria) ...
... T1W+C MRI => perfused Post-Treatment (3 mo): T1W+C MRI => non-perfused CT => increased density in treated area and disappearance of nodular pathologic tissue Patient classified as complete responder (MDACC criteria) ...
Patient-Centered Radiology
... Thank you for choosing Newport Harbor Radiology Associates. We are the physicians who perform and interpret the procedure you had today. You can be assured that a board certified radiologist, one of our group’s expert sub-specialist physicians, supervised and interpreted your procedure today. The re ...
... Thank you for choosing Newport Harbor Radiology Associates. We are the physicians who perform and interpret the procedure you had today. You can be assured that a board certified radiologist, one of our group’s expert sub-specialist physicians, supervised and interpreted your procedure today. The re ...
Dynamic contrast-enhanced breast MRI at 7T and 3T: an intra
... obtaining metabolic and cellular information (Klomp et al. 2011; Loo et al. 2011; van der Kemp 2014) There are also drawbacks of 7T, such as a greater heterogeneity of the static magnetic field (B0) and of the applied RF field (B1+). Furthermore, breast coils had to be developed since none were comm ...
... obtaining metabolic and cellular information (Klomp et al. 2011; Loo et al. 2011; van der Kemp 2014) There are also drawbacks of 7T, such as a greater heterogeneity of the static magnetic field (B0) and of the applied RF field (B1+). Furthermore, breast coils had to be developed since none were comm ...
Procedure for Including IGRT in RTOG Protocols
... IGRT protocol. This Questionnaire should list all IGRT technologies available at that institution. Also daily QA procedures for each device should be described in detail. The QA procedure must ensure alignment of imaging and treatment beam isocenters. The process for dealing with set-up errors shoul ...
... IGRT protocol. This Questionnaire should list all IGRT technologies available at that institution. Also daily QA procedures for each device should be described in detail. The QA procedure must ensure alignment of imaging and treatment beam isocenters. The process for dealing with set-up errors shoul ...
iii. procedures - University of Mississippi Medical Center
... a. Send request to CT and schedule date and time. b. No bowel preparation is necessary unless the patient has received barium recently. c. If barium was administered a KUB is obtained and a bowel preparation will be used. d. Keep patient NPO after midnight (except contrast and medications) if the ex ...
... a. Send request to CT and schedule date and time. b. No bowel preparation is necessary unless the patient has received barium recently. c. If barium was administered a KUB is obtained and a bowel preparation will be used. d. Keep patient NPO after midnight (except contrast and medications) if the ex ...
HSS DoseMonitor:
... value that can be derived from supplying a seamlessly integrated, best-of-breed solution. This allows HSS to focus on what it does best, while its users benefit from a single sourced, multi-faceted and highly functionally rich solution, developed in partnership and collaboration with a long list of ...
... value that can be derived from supplying a seamlessly integrated, best-of-breed solution. This allows HSS to focus on what it does best, while its users benefit from a single sourced, multi-faceted and highly functionally rich solution, developed in partnership and collaboration with a long list of ...
Spectral-domain OCT in Practice
... This high speed allows high-resolution volumetric scanning across most of the macula and reduces the incidence of motion artifact compared to TD OCT. Another feature of SD OCT is high resolution. The axial (anterior-posterior) resolution for the Bioptigen system is 4.5 µm, and the lateral (nasal-tem ...
... This high speed allows high-resolution volumetric scanning across most of the macula and reduces the incidence of motion artifact compared to TD OCT. Another feature of SD OCT is high resolution. The axial (anterior-posterior) resolution for the Bioptigen system is 4.5 µm, and the lateral (nasal-tem ...
Breast image registration for PET-CT and MR based on 3D
... preliminary and mandatory step to combining anatomical and functional breast information. In this paper, we have presented an algorithm for non-rigid registration of 3D breast MRI and PET-CT images based on surface matching. The algorithm uses a nonrigid transformation model to describe the motion o ...
... preliminary and mandatory step to combining anatomical and functional breast information. In this paper, we have presented an algorithm for non-rigid registration of 3D breast MRI and PET-CT images based on surface matching. The algorithm uses a nonrigid transformation model to describe the motion o ...
Medical imaging

Medical imaging is the technique and process of creating visual representations of the interior of a body for clinical analysis and medical intervention. Medical imaging seeks to reveal internal structures hidden by the skin and bones, as well as to diagnose and treat disease. Medical imaging also establishes a database of normal anatomy and physiology to make it possible to identify abnormalities. Although imaging of removed organs and tissues can be performed for medical reasons, such procedures are usually considered part of pathology instead of medical imaging.As a discipline and in its widest sense, it is part of biological imaging and incorporates radiology which uses the imaging technologies of X-ray radiography, magnetic resonance imaging, medical ultrasonography or ultrasound, endoscopy, elastography, tactile imaging, thermography, medical photography and nuclear medicine functional imaging techniques as positron emission tomography.Measurement and recording techniques which are not primarily designed to produce images, such as electroencephalography (EEG), magnetoencephalography (MEG), electrocardiography (ECG), and others represent other technologies which produce data susceptible to representation as a parameter graph vs. time or maps which contain information about the measurement locations. In a limited comparison these technologies can be considered as forms of medical imaging in another discipline.Up until 2010, 5 billion medical imaging studies had been conducted worldwide. Radiation exposure from medical imaging in 2006 made up about 50% of total ionizing radiation exposure in the United States.In the clinical context, ""invisible light"" medical imaging is generally equated to radiology or ""clinical imaging"" and the medical practitioner responsible for interpreting (and sometimes acquiring) the images is a radiologist. ""Visible light"" medical imaging involves digital video or still pictures that can be seen without special equipment. Dermatology and wound care are two modalities that use visible light imagery. Diagnostic radiography designates the technical aspects of medical imaging and in particular the acquisition of medical images. The radiographer or radiologic technologist is usually responsible for acquiring medical images of diagnostic quality, although some radiological interventions are performed by radiologists.As a field of scientific investigation, medical imaging constitutes a sub-discipline of biomedical engineering, medical physics or medicine depending on the context: Research and development in the area of instrumentation, image acquisition (e.g. radiography), modeling and quantification are usually the preserve of biomedical engineering, medical physics, and computer science; Research into the application and interpretation of medical images is usually the preserve of radiology and the medical sub-discipline relevant to medical condition or area of medical science (neuroscience, cardiology, psychiatry, psychology, etc.) under investigation. Many of the techniques developed for medical imaging also have scientific and industrial applications.Medical imaging is often perceived to designate the set of techniques that noninvasively produce images of the internal aspect of the body. In this restricted sense, medical imaging can be seen as the solution of mathematical inverse problems. This means that cause (the properties of living tissue) is inferred from effect (the observed signal). In the case of medical ultrasonography, the probe consists of ultrasonic pressure waves and echoes that go inside the tissue to show the internal structure. In the case of projectional radiography, the probe uses X-ray radiation, which is absorbed at different rates by different tissue types such as bone, muscle and fat.The term noninvasive is used to denote a procedure where no instrument is introduced into a patient's body which is the case for most imaging techniques used.























