Exam 1 Review Sheet Chapter 15 Chemistry 110b
... Amides and lactams: methods for the synthesis of amides . Hydrolysis of amides: know the acid and base mechanisms, compare these hydrolyses with the ester case in terms of ease of hydrolysis. Lactams--nomenclature, properties, occurrence, and reactions. [10e, 804-812; 11e, 796-802] ...
... Amides and lactams: methods for the synthesis of amides . Hydrolysis of amides: know the acid and base mechanisms, compare these hydrolyses with the ester case in terms of ease of hydrolysis. Lactams--nomenclature, properties, occurrence, and reactions. [10e, 804-812; 11e, 796-802] ...
TOPIC 6. NUCLEOPHILIC SUBSTITUTIONS (chapter 6 and parts of
... Substitution reactions can be performed under different conditions which give rise to dramatically different outcomes. Nucleophilic substitution reactions can be classified as one of two types, based on these experimental observations. In order to develop predictive tools, we need to understand reas ...
... Substitution reactions can be performed under different conditions which give rise to dramatically different outcomes. Nucleophilic substitution reactions can be classified as one of two types, based on these experimental observations. In order to develop predictive tools, we need to understand reas ...
Lectures 15, 16 and 17
... carbonyl carbon to form a tetrahedral intermediate. • The difference between the two reactions is what then happens to the intermediate. • Aldehydes and ketones cannot undergo substitution because they do not have a good leaving group bonded to the newly formed sp3 hybridized carbon. ...
... carbonyl carbon to form a tetrahedral intermediate. • The difference between the two reactions is what then happens to the intermediate. • Aldehydes and ketones cannot undergo substitution because they do not have a good leaving group bonded to the newly formed sp3 hybridized carbon. ...
Chapter 1-
... The starting material may be a ketone or an ester There are two routes that start with ketones (one is shown) ...
... The starting material may be a ketone or an ester There are two routes that start with ketones (one is shown) ...
Chapter 12 Alcohols from Carbonyl Compounds: Oxidation
... The starting material may be a ketone or an ester There are two routes that start with ketones (one is shown) ...
... The starting material may be a ketone or an ester There are two routes that start with ketones (one is shown) ...
Reaction of orthoesters with alcohols in the presence of acidic
... Scheme II. This could be established by allowing the optically pure secondary alcohol (11, absolute configuration S) with orthoester in the presence of silicon dioxide which formed corresponding ether with retention of configuration as determined by ...
... Scheme II. This could be established by allowing the optically pure secondary alcohol (11, absolute configuration S) with orthoester in the presence of silicon dioxide which formed corresponding ether with retention of configuration as determined by ...
Organolithium reagent
... is with direct reaction with lithium metal, this reaction enables a number of more exotic organolithium compounds to be prepared. A third method involves the metal-halogen exchange between an organic halide compound (usually an iodide or bromide) and an organolithium species (usually n-BuLi, s-BuLi ...
... is with direct reaction with lithium metal, this reaction enables a number of more exotic organolithium compounds to be prepared. A third method involves the metal-halogen exchange between an organic halide compound (usually an iodide or bromide) and an organolithium species (usually n-BuLi, s-BuLi ...
Concerted Acid-Base Catalysis
... 1 Acid-base Catalysis General acid catalysis involves partial proton transfer from a donor that lowers the free energy of the transition state General base catalysis involves partial proton abstraction from an acceptor that lowers the free energy of the transition state Biochemical reactions suscep ...
... 1 Acid-base Catalysis General acid catalysis involves partial proton transfer from a donor that lowers the free energy of the transition state General base catalysis involves partial proton abstraction from an acceptor that lowers the free energy of the transition state Biochemical reactions suscep ...
fulltext $(function(){PrimeFaces.cw("Tooltip","widget_formSmash_items_resultList_20_j_idt799_0_j_idt801",{id:"formSmash:items:resultList:20:j_idt799:0:j_idt801",widgetVar:"widget_formSmash_items_resultList_20_j_idt799_0_j_idt801",showEffect:"fade",hideEffect:"fade",target:"formSmash:items:resultList:20:j_idt799:0:fullText"});});
... 16 O. Saidi and J. M. J. Williams, Topics in Organometallic Chemistry, ...
... 16 O. Saidi and J. M. J. Williams, Topics in Organometallic Chemistry, ...
www.studyguide.pk
... Permission to reproduce items where third-party owned material protected by copyright is included has been sought and cleared where possible. Every reasonable effort has been made by the publisher (UCLES) to trace copyright holders, but if any items requiring clearance have unwittingly been included ...
... Permission to reproduce items where third-party owned material protected by copyright is included has been sought and cleared where possible. Every reasonable effort has been made by the publisher (UCLES) to trace copyright holders, but if any items requiring clearance have unwittingly been included ...
MONOsaccharides Simple Sugars
... (Analysis for individual CHO’s) • Sugars are not volatile, so they require a derivatization step to make them “volatile”. • Volatile derivatives can be made by a simple onestep chemical reaction • Most common forms: acetates, ethyl ethers, and trimethsilyl ethers • Method used depends on sugars you ...
... (Analysis for individual CHO’s) • Sugars are not volatile, so they require a derivatization step to make them “volatile”. • Volatile derivatives can be made by a simple onestep chemical reaction • Most common forms: acetates, ethyl ethers, and trimethsilyl ethers • Method used depends on sugars you ...
Lecture
... The substitution goes on positions 2,4,6, most easy of nucleophilic reagent is entered in position of 2,6 (α-position ). The prime example of reaction of this type is an amination of pyridine with sodium of amide on Chychybabyne. The reaction flows to the mechanism SN2: ...
... The substitution goes on positions 2,4,6, most easy of nucleophilic reagent is entered in position of 2,6 (α-position ). The prime example of reaction of this type is an amination of pyridine with sodium of amide on Chychybabyne. The reaction flows to the mechanism SN2: ...
Reductive Coupling Reactions of Nitrones and Imines
... benzaldehyde or aromatic imines, resulted in the formation of homocoupling products. These two examples suggest the necessity for balancing the activation of the substrates and the strength of the reductant for efficient cross coupling. The steric bulk of the Į-substituents on the imine also plays a ...
... benzaldehyde or aromatic imines, resulted in the formation of homocoupling products. These two examples suggest the necessity for balancing the activation of the substrates and the strength of the reductant for efficient cross coupling. The steric bulk of the Į-substituents on the imine also plays a ...
ALKANOLS (ALCOHOLS)
... The prefixes di and tri are used as required to indicate more than one hydroxyl or alkyl group Isomerism and Classification: Alcohols can exhibit structural isomerism due to: The presence and position of alkyl side chains The position of the hydroxyl group Alcohols can also exhibit optical iso ...
... The prefixes di and tri are used as required to indicate more than one hydroxyl or alkyl group Isomerism and Classification: Alcohols can exhibit structural isomerism due to: The presence and position of alkyl side chains The position of the hydroxyl group Alcohols can also exhibit optical iso ...
Transgalactosylation/Hydrolysis Ratios of Various b
... the researchers because of the possibilities that this process offers (6–8). The transglycosylation reaction is kinetically controlled, and as a consequence it becomes possible to overshoot the equilibrium conversion of the reactant into product, which is not possible when using the reverse hydrolys ...
... the researchers because of the possibilities that this process offers (6–8). The transglycosylation reaction is kinetically controlled, and as a consequence it becomes possible to overshoot the equilibrium conversion of the reactant into product, which is not possible when using the reverse hydrolys ...
Chapter 10_Organohalides
... • Works well with tertiary alcohols but reaction is significant slower ...
... • Works well with tertiary alcohols but reaction is significant slower ...
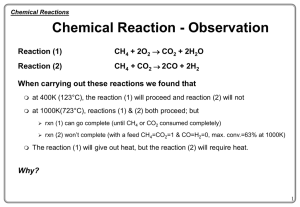
Chemical Reaction Th..
... Use of DG - Rxn(1) DG <0 at 400 & 1000K-spontaneous, Rxn(2) DG <0 at 400K, will not proceed for a reaction at ...
... Use of DG - Rxn(1) DG <0 at 400 & 1000K-spontaneous, Rxn(2) DG <0 at 400K, will not proceed for a reaction at ...
Oxidation and Reduction Reactions
... hydrogen to a carbonyl (using NaBH4 or LiAlH4 as the source of nucleophilic hydrogen). This was a chemoselective reaction – in other words, the reducing agent only reduced one functional group (the carbonyl) and left others alone (e.g. alkenes). If we want to reduce an alkene or alkyne, we need to u ...
... hydrogen to a carbonyl (using NaBH4 or LiAlH4 as the source of nucleophilic hydrogen). This was a chemoselective reaction – in other words, the reducing agent only reduced one functional group (the carbonyl) and left others alone (e.g. alkenes). If we want to reduce an alkene or alkyne, we need to u ...
Chem Stoichiometry Study Guide
... 17. Magnesium metal is added to aqueous hydrochloric acid. 18. Potassium metal is combined with chlorine gas. 19. Aqueous solutions of potassium bromide and silver nitrate are combined. ...
... 17. Magnesium metal is added to aqueous hydrochloric acid. 18. Potassium metal is combined with chlorine gas. 19. Aqueous solutions of potassium bromide and silver nitrate are combined. ...
L-13
... example, 2-decanol, were not suitable substrates for the reaction system and gave none of the desired product. However, the norborneol 2j gave allylated product 3j in 52% yield as a single isomer (entry 13). The reaction with hydroxy ester 2k gave the unsaturated ester 3k without any side products ...
... example, 2-decanol, were not suitable substrates for the reaction system and gave none of the desired product. However, the norborneol 2j gave allylated product 3j in 52% yield as a single isomer (entry 13). The reaction with hydroxy ester 2k gave the unsaturated ester 3k without any side products ...
Functional Group Isomerism
... molecules of the cis isomers than between trans isomers. • The difference between the two is that the cis isomer is a polar molecule whereas the trans isomer is non-polar. Both molecules contain polar chlorine-carbon bonds, but in the cis isomer they are both on the same side of the molecule. That m ...
... molecules of the cis isomers than between trans isomers. • The difference between the two is that the cis isomer is a polar molecule whereas the trans isomer is non-polar. Both molecules contain polar chlorine-carbon bonds, but in the cis isomer they are both on the same side of the molecule. That m ...
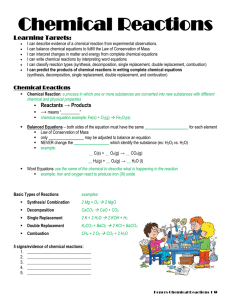
Synthesis Reaction
... I can write chemical reactions by interpreting word equations I can classify reaction types (synthesis, decomposition, single replacement, double replacement, combustion) I can predict the products of chemical reactions in writing complete chemical equations (synthesis, decomposition, single replace ...
... I can write chemical reactions by interpreting word equations I can classify reaction types (synthesis, decomposition, single replacement, double replacement, combustion) I can predict the products of chemical reactions in writing complete chemical equations (synthesis, decomposition, single replace ...
Enantioselective synthesis

Enantioselective synthesis, also called chiral synthesis or asymmetric synthesis, is defined by IUPAC as: a chemical reaction (or reaction sequence) in which one or more new elements of chirality are formed in a substrate molecule and which produces the stereoisomeric (enantiomeric or diastereoisomeric) products in unequal amounts.Put more simply: it is the synthesis of a compound by a method that favors the formation of a specific enantiomer or diastereomer.Enantioselective synthesis is a key process in modern chemistry and is particularly important in the field of pharmaceuticals, as the different enantiomers or diastereomers of a molecule often have different biological activity.