Ligand field theory
... Ligand field theory considers the effect of different ligand environments (ligand fields) on the energies of the dorbitals. The energies of the d orbitals in different environments determines the magnetic and electronic spectral properties of transition metal complexes. Ligand field theory combines ...
... Ligand field theory considers the effect of different ligand environments (ligand fields) on the energies of the dorbitals. The energies of the d orbitals in different environments determines the magnetic and electronic spectral properties of transition metal complexes. Ligand field theory combines ...
Coordination Compounds
... If Äo < P, the fourth electron enters one of the eg orbitals giving the configuration t2g3eg1 . Ligands for which Äo < P are known as weak field ligands and form high spin complexes. (ii) If Äo > P, it becomes more energetically favourable for the fourth electron to occupy a t2g orbital with configu ...
... If Äo < P, the fourth electron enters one of the eg orbitals giving the configuration t2g3eg1 . Ligands for which Äo < P are known as weak field ligands and form high spin complexes. (ii) If Äo > P, it becomes more energetically favourable for the fourth electron to occupy a t2g orbital with configu ...
Instructions for Preparing Manuscript for Bulletin of
... Two complexes of Cu (II), Ni(II) with amino acid cysteine were prepared by refluxing the amino acid and metals. The complexes were characterized by elemental analysis, FT-IR spectrum, Thermo gravimeter analysis and Uv visible spectra. In these complexes the amino acid coordinated 1:2 ratios with met ...
... Two complexes of Cu (II), Ni(II) with amino acid cysteine were prepared by refluxing the amino acid and metals. The complexes were characterized by elemental analysis, FT-IR spectrum, Thermo gravimeter analysis and Uv visible spectra. In these complexes the amino acid coordinated 1:2 ratios with met ...
doc_367
... properties of the complexes, hence complexation of transition metal atoms by ligands of different types have been of great significance. The existence of central transition metal atom in different oxidation states were found to be most promising in catalytic studies and the transition metal compound ...
... properties of the complexes, hence complexation of transition metal atoms by ligands of different types have been of great significance. The existence of central transition metal atom in different oxidation states were found to be most promising in catalytic studies and the transition metal compound ...
Lecture 1 : Metal alkene complexes
... For example, a free olefin is considered electron rich by virtue of the presence of π−electrons in its outermost valence orbital and hence it undergoes an electrophilic attack. However, the metal bound olefin complexes having predominantly σ−donation of the olefinic π−electrons and negligible metal ...
... For example, a free olefin is considered electron rich by virtue of the presence of π−electrons in its outermost valence orbital and hence it undergoes an electrophilic attack. However, the metal bound olefin complexes having predominantly σ−donation of the olefinic π−electrons and negligible metal ...
What is ligand?
... central atom, this may be done by simple ionic bonding with another set of counter ions (the "outer-sphere" ligands). ...
... central atom, this may be done by simple ionic bonding with another set of counter ions (the "outer-sphere" ligands). ...
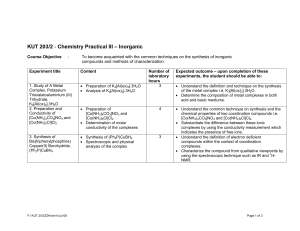
KUT 203/2 - Chemistry Practical III (Inorganic Chemistry)
... coordination compounds and the synthesis of these isomers or isolation of D- and L-isomers. • Determine the composition of isomers thus isolated through titration. • Substantiate the optical behaviour of these isomers. • Understand the concept on lingkage isomerism in coordination compounds and the ...
... coordination compounds and the synthesis of these isomers or isolation of D- and L-isomers. • Determine the composition of isomers thus isolated through titration. • Substantiate the optical behaviour of these isomers. • Understand the concept on lingkage isomerism in coordination compounds and the ...
CARBONYL COMPOUNDS
... 6. Estimate the type and the extent of interactive forces between C2H6 (MR = 30), CH3OH (MR = 30) and HCHO (MR = 30) and put these compounds in order with respect to increasing boiling point. C2H6 CH3OH HCHO Methanal is a gas, other important carbonyl compounds are …………………... Early members are solub ...
... 6. Estimate the type and the extent of interactive forces between C2H6 (MR = 30), CH3OH (MR = 30) and HCHO (MR = 30) and put these compounds in order with respect to increasing boiling point. C2H6 CH3OH HCHO Methanal is a gas, other important carbonyl compounds are …………………... Early members are solub ...
ASYMMETRIC CATALYSIS
... new metal-catalyzed reactions, it’s important to focus on certain reactivity principles and experimental details. For example, many inorganic and organometallic complexes can be converted to effective catalysts if proper conditions, appropriate ligands, and suitable solvents and addi- ...
... new metal-catalyzed reactions, it’s important to focus on certain reactivity principles and experimental details. For example, many inorganic and organometallic complexes can be converted to effective catalysts if proper conditions, appropriate ligands, and suitable solvents and addi- ...
Thermodynamics and Further Inorganic Chemistry
... • In the partially filled d-orbitals of a transition metal complex there is an energy gap between the filled and unfilled orbitals. Visible light is of the right energy to promote an electron from one energy level to the next. • The partially filled orbitals in transition metals allow them to change ...
... • In the partially filled d-orbitals of a transition metal complex there is an energy gap between the filled and unfilled orbitals. Visible light is of the right energy to promote an electron from one energy level to the next. • The partially filled orbitals in transition metals allow them to change ...
APPLICATIONS OF TRANSITION METAL MACROCYCLIC
... changes their surface properties. Dust, moisture, higher and lower temperatures will directly influence the catalytic activity of the metal. Many of these drawbacks can be eliminated by using these metals in the macrocyclic form. The common transition metals used in macrocyclic catalysts are Fe, Co, ...
... changes their surface properties. Dust, moisture, higher and lower temperatures will directly influence the catalytic activity of the metal. Many of these drawbacks can be eliminated by using these metals in the macrocyclic form. The common transition metals used in macrocyclic catalysts are Fe, Co, ...
Chapter 1: Fundamental Concepts
... Give the order of increase of D in the following sets: a) Cr(NH3)63+, CrCl63–, Cr(CN)63– b) Co(H2O)62+, Co(H2O)63+, Rh(H2O)63+ a) Cr(CN)63– > Cr(NH3)63+ > CrCl63– b) Rh(H2O)63+ > Co(H2O)63+ > Co(H2O)62+ ...
... Give the order of increase of D in the following sets: a) Cr(NH3)63+, CrCl63–, Cr(CN)63– b) Co(H2O)62+, Co(H2O)63+, Rh(H2O)63+ a) Cr(CN)63– > Cr(NH3)63+ > CrCl63– b) Rh(H2O)63+ > Co(H2O)63+ > Co(H2O)62+ ...
Chem 263 Notes March 2, 2006 Preparation of Aldehydes and
... irreversibly. Examples of strong nucleophiles are the hydride ion, H- (from reagents like lithium aluminum hydride, AlH4, and sodium borohydride, NaBH4) and alkyl anions, R- (from Grignard reagents) ...
... irreversibly. Examples of strong nucleophiles are the hydride ion, H- (from reagents like lithium aluminum hydride, AlH4, and sodium borohydride, NaBH4) and alkyl anions, R- (from Grignard reagents) ...
QSARs and Inorganic Chemistry
... • σ has been modified to separate out these two effects • These values are redefined as σR and σI , resonance and inductive respectively ...
... • σ has been modified to separate out these two effects • These values are redefined as σR and σI , resonance and inductive respectively ...
Lecture1
... Alkyl ligands Stability of metal-alkyl compounds towards water, oxygen, etc. Main group and early transition metal alkyls are very sensitive to water and oxygen. Late transition metal alkyls are more stable to water and oxygen. Both main group and transition metal alkyls are unstable towards halogen ...
... Alkyl ligands Stability of metal-alkyl compounds towards water, oxygen, etc. Main group and early transition metal alkyls are very sensitive to water and oxygen. Late transition metal alkyls are more stable to water and oxygen. Both main group and transition metal alkyls are unstable towards halogen ...
Organic Chemistry Lecture Outline Carbonyl
... NOMENCLATURE OF ALDEHYDES AND KETONES IUPAC The parent of an aldehyde or ketone is the longest, continuous carbon chain that contains the carbonyl carbon of the functional group. The parent name reflects the total number of carbon atoms in the chain (2 carbons = ethan, 3 carbons = propan, etc..). Th ...
... NOMENCLATURE OF ALDEHYDES AND KETONES IUPAC The parent of an aldehyde or ketone is the longest, continuous carbon chain that contains the carbonyl carbon of the functional group. The parent name reflects the total number of carbon atoms in the chain (2 carbons = ethan, 3 carbons = propan, etc..). Th ...
Protecting Groups Introduction to Carbonyl
... Protecting Groups Solving this problem requires a three-step strategy: [1] Convert the OH group into another functional group that does not interfere with the desired reaction. This new blocking group is called a protecting group, and the reaction that creates it is called “protection.” [2] Carry ou ...
... Protecting Groups Solving this problem requires a three-step strategy: [1] Convert the OH group into another functional group that does not interfere with the desired reaction. This new blocking group is called a protecting group, and the reaction that creates it is called “protection.” [2] Carry ou ...
Metal carbonyl

Metal carbonyls are coordination complexes of transition metals with carbon monoxide ligands. Metal carbonyls are useful in organic synthesis and as catalysts or catalyst precursors in homogeneous catalysis, such as hydroformylation and Reppe chemistry. In the Mond process, nickel carbonyl is used to produce pure nickel. In organometallic chemistry, metal carbonyls serve as precursors for the preparation of other organometalic complexes.Metal carbonyls are toxic by skin contact, inhalation or ingestion, in part because of their ability to carbonylate hemoglobin to give carboxyhemoglobin, which prevents the binding of O2.