DNA to Protein Synthesis
... DNA must be copied to messenger RNA (mRNA) mRNA goes from nucleus to the ribosomes in cytoplasm mRNA complements known as codons ...
... DNA must be copied to messenger RNA (mRNA) mRNA goes from nucleus to the ribosomes in cytoplasm mRNA complements known as codons ...
File - Thomas Tallis School
... acids fixes the way the protein folds into its three-dimensional shape. The shape gives the protein its chemical properties. DNA contains the genetic code which instructs the cell to join up the amino acids in the right order to make a particular protein. The genetic code is contained in the sequenc ...
... acids fixes the way the protein folds into its three-dimensional shape. The shape gives the protein its chemical properties. DNA contains the genetic code which instructs the cell to join up the amino acids in the right order to make a particular protein. The genetic code is contained in the sequenc ...
Reading Study Guide B
... Describe the DNA transcription process by completing each sentence. During transcription, DNA is used to make _______________________________________. Only _________________________________________________________ are transcribed. Many copies of RNA can be made from _________________________________ ...
... Describe the DNA transcription process by completing each sentence. During transcription, DNA is used to make _______________________________________. Only _________________________________________________________ are transcribed. Many copies of RNA can be made from _________________________________ ...
Final Exam Review - Blue Valley Schools
... What is a homologous structure? How do homologous structures help support the idea of common ancestry? What is a vestigial structure? What do they tell us about the evolutionary history of organisms? Natural Selection How do we summarize natural selection? 1. Variation exists among individuals withi ...
... What is a homologous structure? How do homologous structures help support the idea of common ancestry? What is a vestigial structure? What do they tell us about the evolutionary history of organisms? Natural Selection How do we summarize natural selection? 1. Variation exists among individuals withi ...
Chapter 2
... physical characteristics of an organism –the things you can see –the detectable expressions of ...
... physical characteristics of an organism –the things you can see –the detectable expressions of ...
Diapositive 1
... identified 189 (162 LCI, 27 Y2H) human proteins interacting with at least 2 ALL census genes products, which were not previously linked to ALL via mutations. Finally, we showed that EXT1, a tumor suppressor implicated in chondrosarcomagenesis, is a common interactor of Notch1 and FBW7. We speculate ...
... identified 189 (162 LCI, 27 Y2H) human proteins interacting with at least 2 ALL census genes products, which were not previously linked to ALL via mutations. Finally, we showed that EXT1, a tumor suppressor implicated in chondrosarcomagenesis, is a common interactor of Notch1 and FBW7. We speculate ...
Module 4 PowerPoint Slides - The Cancer 101 Curriculum
... Can be acquired, in which case they are caused by: ...
... Can be acquired, in which case they are caused by: ...
Gene Regulation
... arac muants are rare because the mutation must make AraC active without binding arabinose Inactivation of araC (unlike lacI) produces an ara- phenotype AraC must also be an antiactivator since... araCc mutations should be dominant (but they are not). IV. The trp operon (Negative regulation and trans ...
... arac muants are rare because the mutation must make AraC active without binding arabinose Inactivation of araC (unlike lacI) produces an ara- phenotype AraC must also be an antiactivator since... araCc mutations should be dominant (but they are not). IV. The trp operon (Negative regulation and trans ...
Gene Regulation
... arac muants are rare because the mutation must make AraC active without binding arabinose Inactivation of araC (unlike lacI) produces an ara- phenotype AraC must also be an antiactivator since... araCc mutations should be dominant (but they are not). ...
... arac muants are rare because the mutation must make AraC active without binding arabinose Inactivation of araC (unlike lacI) produces an ara- phenotype AraC must also be an antiactivator since... araCc mutations should be dominant (but they are not). ...
Novel recessive BFSP2 and PITX3 mutations: Insights into
... proteins (40 –70%), makes it tempting to speculate a dominant negative mechanism in which a PITX3 protein with reduced activation/transactivation capacity occupies the site of action of the normal counterpart.17 The novel PITX3 mutation we report here involves deletion of the same 17 bp that are dup ...
... proteins (40 –70%), makes it tempting to speculate a dominant negative mechanism in which a PITX3 protein with reduced activation/transactivation capacity occupies the site of action of the normal counterpart.17 The novel PITX3 mutation we report here involves deletion of the same 17 bp that are dup ...
Microbiology Exam II - University of Evansville Faculty Web sites
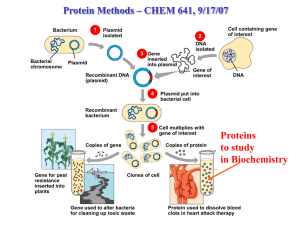
... 6. Which of the following best describes a plasmid? a. A gene within the chromosome b. Small circular piece of DNA outside the chromosome c. The genetic material of a bacteriophage d. Part of bacterial ribosomes e. A single, linear strand of DNA 7. Which of the following is NOT involved in bacteria ...
... 6. Which of the following best describes a plasmid? a. A gene within the chromosome b. Small circular piece of DNA outside the chromosome c. The genetic material of a bacteriophage d. Part of bacterial ribosomes e. A single, linear strand of DNA 7. Which of the following is NOT involved in bacteria ...
Distinguish between these 3 root types: - mvhs
... beginning of each gene that bind to ___________________ to begin transcription. ...
... beginning of each gene that bind to ___________________ to begin transcription. ...
Assessment of Alzheimer`s disease risk genes with CSF
... Two efficient mutation detection methods were used for screening our samples: single strand conformation polymorphism (SSCP) and heteroduplex analysis with mismatch-specific nuclease. For the identification and confirmation of the specific mutations, the PCR products were sequenced. Results: A misse ...
... Two efficient mutation detection methods were used for screening our samples: single strand conformation polymorphism (SSCP) and heteroduplex analysis with mismatch-specific nuclease. For the identification and confirmation of the specific mutations, the PCR products were sequenced. Results: A misse ...
Cell and Molecular Biology
... Neoplasia is an abnormal accumulation of cells that occurs because of an imbalance between cellular proliferation and cellular attrition. Cells proliferate as they pass through the cell cycle and undergo mitosis. Attrition, due to programmed cell death, removes cells from a tissue. ...
... Neoplasia is an abnormal accumulation of cells that occurs because of an imbalance between cellular proliferation and cellular attrition. Cells proliferate as they pass through the cell cycle and undergo mitosis. Attrition, due to programmed cell death, removes cells from a tissue. ...
Supplementary data
... Table ST2 shows all mutations present in cases analysed in this study, ordered by their position from 5’- to 3’- in the gene (amino acid position is given relative to the initiator methionine of the MECP2e2 isoform, as used in most previous reports). Mutations found in Glasgow as part of this study ...
... Table ST2 shows all mutations present in cases analysed in this study, ordered by their position from 5’- to 3’- in the gene (amino acid position is given relative to the initiator methionine of the MECP2e2 isoform, as used in most previous reports). Mutations found in Glasgow as part of this study ...
Keio Mutation Database (KMDB) for human
... Figure 1 upper panel shows the entrance windows of MutationView and five separate KMDBs. Figure 1 lower panel shows ‘Anatomy’ window of the JAVA version of MutationView (left), KMeyeDB (center) and KMheartDB (right). By clicking a certain anatomical part in these windows, a list of genes and/or dise ...
... Figure 1 upper panel shows the entrance windows of MutationView and five separate KMDBs. Figure 1 lower panel shows ‘Anatomy’ window of the JAVA version of MutationView (left), KMeyeDB (center) and KMheartDB (right). By clicking a certain anatomical part in these windows, a list of genes and/or dise ...
Gene Expression
... protein mRNA needs the help of tRNA and rRNA mRNA binds to a ribosome (Initiation) 3 tRNA anticodons – complementary to the mRNA codons - bring the specified amino acid into position A condensation reaction occurs to link the amino acids together (Elongation) The bond between the amino aci ...
... protein mRNA needs the help of tRNA and rRNA mRNA binds to a ribosome (Initiation) 3 tRNA anticodons – complementary to the mRNA codons - bring the specified amino acid into position A condensation reaction occurs to link the amino acids together (Elongation) The bond between the amino aci ...
THE PROTEIN SYNTHESIS ESSAY MUST: be in the FHS Essay
... CM - Commentary (Opinion or your experience) example - It was interesting to use "toys" to demonstrate how protein synthesis occurs to Ms. Antoine. ...
... CM - Commentary (Opinion or your experience) example - It was interesting to use "toys" to demonstrate how protein synthesis occurs to Ms. Antoine. ...
Mandatory additional information
... 1) The expression system (the cell type and the clone name used for the expression) ...
... 1) The expression system (the cell type and the clone name used for the expression) ...
Point mutation

A point mutation, or single base modification, is a type of mutation that causes a single nucleotide base change, insertion, or deletion of the genetic material, DNA or RNA. The term frameshift mutation indicates the addition or deletion of a base pair. A point mutant is an individual that is affected by a point mutation.Repeat induced point mutations are recurring point mutations, discussed below.