Genetic Conditions
... Understanding which chromosomes have been affected helps physicians diagnose and treat patients with genetic disorders or syndromes. A syndrome is a particular disease or disorder with a specific group of symptoms that occur together. ...
... Understanding which chromosomes have been affected helps physicians diagnose and treat patients with genetic disorders or syndromes. A syndrome is a particular disease or disorder with a specific group of symptoms that occur together. ...
Chapter 15 Controls over Genes
... Continue… • This mosaic effect is seen in human females affected by anhidrotic ectodermal dysplasia in which a mutant gene on one X chromosome results in patches of skin with no sweat glands – Figure 15.6b and 15.7 -- page 245 ...
... Continue… • This mosaic effect is seen in human females affected by anhidrotic ectodermal dysplasia in which a mutant gene on one X chromosome results in patches of skin with no sweat glands – Figure 15.6b and 15.7 -- page 245 ...
Spring 2011 Midterm Review Answers
... Even though the islands are close, they have very different climates – some more desert-like and others more tropical. He observed that the characteristics of many animals and plants varied noticeably among the different islands. His studies of his samples and observations lead him to realize ...
... Even though the islands are close, they have very different climates – some more desert-like and others more tropical. He observed that the characteristics of many animals and plants varied noticeably among the different islands. His studies of his samples and observations lead him to realize ...
Genetic Fine Structure
... Five mutant strains of Neurospora give the following results in complementation tests where a plus signifies complementation and a minus shows no complementation. Determine how many cistrons are represented by these mutations and indicate which mutants belong to each ...
... Five mutant strains of Neurospora give the following results in complementation tests where a plus signifies complementation and a minus shows no complementation. Determine how many cistrons are represented by these mutations and indicate which mutants belong to each ...
The Origins of Variation
... e.g., mitochondria - endosymbiotic origin, evidence from cell membranes, gene structure, origin of replication, the fact that mitochondrial rRNAs are more similar to endosymbiotic bacterial (Rickettsia) rRNAs than to nuclear rRNAs of eukaryotes, and ongoing movement of genetic material from mitochon ...
... e.g., mitochondria - endosymbiotic origin, evidence from cell membranes, gene structure, origin of replication, the fact that mitochondrial rRNAs are more similar to endosymbiotic bacterial (Rickettsia) rRNAs than to nuclear rRNAs of eukaryotes, and ongoing movement of genetic material from mitochon ...
Bulletin 1 - DNA: The Cookbook of Life - ctahr
... embraced, and some of which remain controversial. Our next issue of Biotech In Focus will address the DNA technologies we encounter in daily life. Thank you to our sponsors: USDA - Agricultural Research Services and University of Hawaii - CTAHR ...
... embraced, and some of which remain controversial. Our next issue of Biotech In Focus will address the DNA technologies we encounter in daily life. Thank you to our sponsors: USDA - Agricultural Research Services and University of Hawaii - CTAHR ...
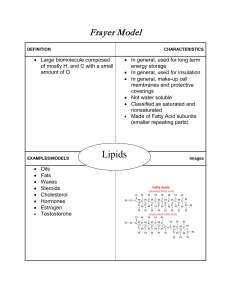
Macromolecules (Biomolecules)
... the major organic compounds that make up organisms? 2) List the four major types of Macromolecules that are necessary for life. 3) What is the name given to small molecules that make up larger molecules? 4) Listed below are the names of the four major classes of macromolecules as well as their monom ...
... the major organic compounds that make up organisms? 2) List the four major types of Macromolecules that are necessary for life. 3) What is the name given to small molecules that make up larger molecules? 4) Listed below are the names of the four major classes of macromolecules as well as their monom ...
Slide 1 - tacademy.ca
... • Down Syndrome – caused by the presence of all or part of a 21st chromosome • Turner Syndrome – caused by one or many parts of the X chromosome remaining absent during cell formation. Specific only to females. • Cystic Fibrosis – Number one most common fatally genetic disease. Caused by a single ge ...
... • Down Syndrome – caused by the presence of all or part of a 21st chromosome • Turner Syndrome – caused by one or many parts of the X chromosome remaining absent during cell formation. Specific only to females. • Cystic Fibrosis – Number one most common fatally genetic disease. Caused by a single ge ...
GENES
... transcription)in which the introns are removed and the exons are joined. in coding segments exons are part of the 1.5% coding DNA, in non coding segments introns are part of the 98.5% non coding DNA. ...
... transcription)in which the introns are removed and the exons are joined. in coding segments exons are part of the 1.5% coding DNA, in non coding segments introns are part of the 98.5% non coding DNA. ...
CHNOPS- Simulating Protein Synthesis
... place. The code, in DNA or mRNA, specifies the order in which the amino acids are joined together to form a polypeptide. The code words in mRNA, however, are not directly recognized by the corresponding amino acids. Another type of RNA called transfer RNA (tRNA) is needed to bring the mRNA and amino ...
... place. The code, in DNA or mRNA, specifies the order in which the amino acids are joined together to form a polypeptide. The code words in mRNA, however, are not directly recognized by the corresponding amino acids. Another type of RNA called transfer RNA (tRNA) is needed to bring the mRNA and amino ...
Gene Expression, Inheritance Patterns, and DNA Technology
... Somatic = Body cells; can affect organism; not passed to offspring Lethal = death, often before birth Beneficial? = better chance of reproducing and have ...
... Somatic = Body cells; can affect organism; not passed to offspring Lethal = death, often before birth Beneficial? = better chance of reproducing and have ...
Rhesus ALK-7 / ALK7 / ACVR1C Protein (Fc Tag)
... < 1.0 EU per μg of the protein as determined by the LAL method ...
... < 1.0 EU per μg of the protein as determined by the LAL method ...
Introductory Biology Primer
... G C U U G U U U A C G A A U U A G G C U U G U U U A C G A A U U A G G C U U G U U U A C G A A U U A G ...
... G C U U G U U U A C G A A U U A G G C U U G U U U A C G A A U U A G G C U U G U U U A C G A A U U A G ...
DKN_5-8 TYPE
... “This states that once ‘information’ has passed into protein it cannot get out again. In more detail, the transfer of information from nucleic acid to protein may be possible, but transfer from protein to protein, or from protein to nucleic acid is impossible. Information means here the precise dete ...
... “This states that once ‘information’ has passed into protein it cannot get out again. In more detail, the transfer of information from nucleic acid to protein may be possible, but transfer from protein to protein, or from protein to nucleic acid is impossible. Information means here the precise dete ...
Aim: How do scientists use biotechnology to manipulate genomes?
... genomes of organisms at the the ________ molecular level. ...
... genomes of organisms at the the ________ molecular level. ...
Study Questions for the Second Exam in Bio 0200
... (in other words, how does electron transport make ATP synthesis possible?) Explain the Pasteur effect (it's in your lab manual in the pathways game section) What is a photosystem? Where are photosystems located? What are photosystem I and II? How do their functions differ? In what ways is the Calvin ...
... (in other words, how does electron transport make ATP synthesis possible?) Explain the Pasteur effect (it's in your lab manual in the pathways game section) What is a photosystem? Where are photosystems located? What are photosystem I and II? How do their functions differ? In what ways is the Calvin ...
Lecture 2: Mutation and its effect
... deaminating agent such as nitrous acid intercalating agent such as Acridine Orange Transposons that insert into a gene and disrupt the normal reading frame ...
... deaminating agent such as nitrous acid intercalating agent such as Acridine Orange Transposons that insert into a gene and disrupt the normal reading frame ...
7. One gene one protein
... DNA mutations and proteins A DNA mutation changes the amino acid sequence and so a different protein may be produced. ...
... DNA mutations and proteins A DNA mutation changes the amino acid sequence and so a different protein may be produced. ...
Final Exam Review
... (a) Give the complimentary mRNA sequence to the template strand. What are the three letter “words” of mRNA called? (b) Give the complimentary tRNA sequence to the mRNA. What are the three letter “words” of tRNA called? (c) What is the amino acid sequence coded for by this DNA sequence? (d) A base is ...
... (a) Give the complimentary mRNA sequence to the template strand. What are the three letter “words” of mRNA called? (b) Give the complimentary tRNA sequence to the mRNA. What are the three letter “words” of tRNA called? (c) What is the amino acid sequence coded for by this DNA sequence? (d) A base is ...
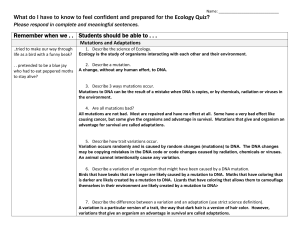
Remember when we . . Students should be able to
... Ecology is the study of organisms interacting with each other and their environment. ...
... Ecology is the study of organisms interacting with each other and their environment. ...
Chapter Outline
... d. Sickle cell disease results from a single base change in DNA where the beta-chain of hemoglobin contains valine instead of glutamate at one location and the resulting distorted hemoglobin causes red blood cells to clog vessels and die off sooner. 2. Frameshift mutations occur most often when one ...
... d. Sickle cell disease results from a single base change in DNA where the beta-chain of hemoglobin contains valine instead of glutamate at one location and the resulting distorted hemoglobin causes red blood cells to clog vessels and die off sooner. 2. Frameshift mutations occur most often when one ...
B2 Topic 1 The Components of Life
... What uses are there for genetic engineering? Bacteria Cell ...
... What uses are there for genetic engineering? Bacteria Cell ...
Point mutation

A point mutation, or single base modification, is a type of mutation that causes a single nucleotide base change, insertion, or deletion of the genetic material, DNA or RNA. The term frameshift mutation indicates the addition or deletion of a base pair. A point mutant is an individual that is affected by a point mutation.Repeat induced point mutations are recurring point mutations, discussed below.