Slide 1
... describe complex variation, we need to subdivide genotypes and phenotypes into traits. This procedure requires care and common sense and strongly depends on the nature of variation (see Basic Concepts). Traits can be of three kinds: 1) Unordered traits, such that there is no structure in their state ...
... describe complex variation, we need to subdivide genotypes and phenotypes into traits. This procedure requires care and common sense and strongly depends on the nature of variation (see Basic Concepts). Traits can be of three kinds: 1) Unordered traits, such that there is no structure in their state ...
27. The micro-evolution of FMDV
... Simple and plausible models of FMDV population genetics suggest that virus excreted by an infected animal might on average differ by 1 nucleotide mutation to its capsid genes from the virus with which an individual was infected. If this were true – and there are many interesting reasons why it might ...
... Simple and plausible models of FMDV population genetics suggest that virus excreted by an infected animal might on average differ by 1 nucleotide mutation to its capsid genes from the virus with which an individual was infected. If this were true – and there are many interesting reasons why it might ...
practice questions
... particular piece of trivia. Random terms sometimes show up on multiple-choice questions due to the need to create five different choices, but you should always have enough information to figure out the correct answer, either because one choice is clearly right or because the other four choices are c ...
... particular piece of trivia. Random terms sometimes show up on multiple-choice questions due to the need to create five different choices, but you should always have enough information to figure out the correct answer, either because one choice is clearly right or because the other four choices are c ...
Chapter_17_answers
... Point mutations can change only a tiny piece in the DNA and may or may not have dramatic results Base pair substitutions o Replacement of nucleotide pair with another pair o Silent mutations do not change which amino acid is synthesized o Missense mutations still codes for an amino acid, but the ...
... Point mutations can change only a tiny piece in the DNA and may or may not have dramatic results Base pair substitutions o Replacement of nucleotide pair with another pair o Silent mutations do not change which amino acid is synthesized o Missense mutations still codes for an amino acid, but the ...
News Release - האוניברסיטה העברית
... hybrid offspring with higher yields. First observed by Charles Darwin in 1876, heterosis was rediscovered by CSHL corn geneticist George Shull 30 years later, but how heterosis works has remained a mystery. Plants carry two copies of each gene, and Shull’s studies suggested that harmful, vigor-killi ...
... hybrid offspring with higher yields. First observed by Charles Darwin in 1876, heterosis was rediscovered by CSHL corn geneticist George Shull 30 years later, but how heterosis works has remained a mystery. Plants carry two copies of each gene, and Shull’s studies suggested that harmful, vigor-killi ...
Genes: Definition and Structure
... ribosomes, transfer RNAs (tRNAs), and a variety of protein enzymes and ‘factors’ – uses the mRNA template to direct the synthesis of a protein, a process called translation. The DNA of the chromosome contains many genes lined up one after another, but mRNAs generally contain the message for only one ...
... ribosomes, transfer RNAs (tRNAs), and a variety of protein enzymes and ‘factors’ – uses the mRNA template to direct the synthesis of a protein, a process called translation. The DNA of the chromosome contains many genes lined up one after another, but mRNAs generally contain the message for only one ...
Updated Semester Two Review Sheet Answer Key
... produced for human consumption. Many of these new species were developed using the process of selective breeding, also known as artificial selection. Discuss the differences in the process of artificial selection and natural selection. Are there benefits to using one over the other? Explain your sta ...
... produced for human consumption. Many of these new species were developed using the process of selective breeding, also known as artificial selection. Discuss the differences in the process of artificial selection and natural selection. Are there benefits to using one over the other? Explain your sta ...
DNA base sequences
... and primates has been completely sequenced and used to construct cladogram between them. The rate at which mutations occur at can be used as a molecular clock to calculate how long ago species diverged. If the DNA base sequences or two species are similar … … then few mutations have occurred … … the ...
... and primates has been completely sequenced and used to construct cladogram between them. The rate at which mutations occur at can be used as a molecular clock to calculate how long ago species diverged. If the DNA base sequences or two species are similar … … then few mutations have occurred … … the ...
PowerPoint Presentation - Chapter 17 From Gene to Protein.
... Some chemicals are base analogues that may be substituted into DNA, but they pair incorrectly during DNA replication. Other mutagens interfere with DNA replication by inserting into DNA and distorting the double helix. Still others cause chemical changes in bases that change their pairing proper ...
... Some chemicals are base analogues that may be substituted into DNA, but they pair incorrectly during DNA replication. Other mutagens interfere with DNA replication by inserting into DNA and distorting the double helix. Still others cause chemical changes in bases that change their pairing proper ...
No Slide Title
... The restriction enzyme Eco.R1 found in strain C, E. coli bacteria They don’t make straight cuts, but produce sticky ends These sticky ends can rejoin by forming hydrogen bonds and the sugar-phosphates rejoining with the help of the enzyme ligase The DNA produced by restriction enzymes cutting is cal ...
... The restriction enzyme Eco.R1 found in strain C, E. coli bacteria They don’t make straight cuts, but produce sticky ends These sticky ends can rejoin by forming hydrogen bonds and the sugar-phosphates rejoining with the help of the enzyme ligase The DNA produced by restriction enzymes cutting is cal ...
Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy
... have the disease. Daughters that inherit the mutation will be carriers. ...
... have the disease. Daughters that inherit the mutation will be carriers. ...
Characteristics of Living Things (Essay
... Part b. What is DNA translation? Where and why does it occur? In other words - why is it such an important process? Describe the major components involved in translation & explain how mRNA codons play a vital role in directing the synthesis of a very important type of organic molecule. Do not forget ...
... Part b. What is DNA translation? Where and why does it occur? In other words - why is it such an important process? Describe the major components involved in translation & explain how mRNA codons play a vital role in directing the synthesis of a very important type of organic molecule. Do not forget ...
AS 90729 version 2 Describe genetic processes Level 3 Credits 4
... of the DNA molecule. This results in two daughter strands of DNA, each with one new strand and one strand from the original (parent) molecule. Complementary base pairing ensures accuracy of replication, because each of the bases can only bond with one other specific base. C bonds with G and T bonds ...
... of the DNA molecule. This results in two daughter strands of DNA, each with one new strand and one strand from the original (parent) molecule. Complementary base pairing ensures accuracy of replication, because each of the bases can only bond with one other specific base. C bonds with G and T bonds ...
Mutations The Foundation of Creation?
... • It doesn't seem quite clear as to just how the Ychromosome could have evolved over millions of years of time given its relative inability to combat high detrimental mutation rates. ...
... • It doesn't seem quite clear as to just how the Ychromosome could have evolved over millions of years of time given its relative inability to combat high detrimental mutation rates. ...
Autosomal Dominant Inheritance
... 1% of all cases of Alzheimer is inherited Usually occurs over the age of 65 Caused by a mutation in the APP gene There is no cure or treatment to slow down the process of Alzheimer ...
... 1% of all cases of Alzheimer is inherited Usually occurs over the age of 65 Caused by a mutation in the APP gene There is no cure or treatment to slow down the process of Alzheimer ...
Sem 2 Bio Review Questions
... spots (Y) is dominant over the gene for red spots and the gene for blue skin color (B) is dominant over the gene for green skin color. What is the probability that red spotted, green skinned offspring will be produced in a cross between a parent that has green skin and is heterozygous (hybrid) for y ...
... spots (Y) is dominant over the gene for red spots and the gene for blue skin color (B) is dominant over the gene for green skin color. What is the probability that red spotted, green skinned offspring will be produced in a cross between a parent that has green skin and is heterozygous (hybrid) for y ...
Using DNA Subway in the Classroom Red Line Lesson
... First, use DNA subway to show how we can reveal features of a sequence. Create a project using a sample sequence. Once students have mastery, they can come back and create their own projects using real data. ...
... First, use DNA subway to show how we can reveal features of a sequence. Create a project using a sample sequence. Once students have mastery, they can come back and create their own projects using real data. ...
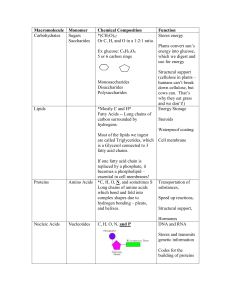
Macromolecule
... humans can’t break down cellulose, but cows can. That’s why they eat grass and we don’t!) Energy Storage Steroids Waterproof coating ...
... humans can’t break down cellulose, but cows can. That’s why they eat grass and we don’t!) Energy Storage Steroids Waterproof coating ...
Mechanisms of Evolutionary Change – “Microevolutionary Processes”
... Mechanisms of Evolutionary Change – “Microevolutionary Processes” (1) Mutation: Ultimate natural resource of evolution, occurs at the molecular level in DNA. (2) Natural Selection: A difference, on average, between the survival or fecundity of individuals with certain arrays of phenotypes as compare ...
... Mechanisms of Evolutionary Change – “Microevolutionary Processes” (1) Mutation: Ultimate natural resource of evolution, occurs at the molecular level in DNA. (2) Natural Selection: A difference, on average, between the survival or fecundity of individuals with certain arrays of phenotypes as compare ...
Practise Final exam
... Otherwise II-2 would be affected Using the above pedigree AND IGNORING the RFLP data, what is the probability that individual (?) will be affected by the disease. ...
... Otherwise II-2 would be affected Using the above pedigree AND IGNORING the RFLP data, what is the probability that individual (?) will be affected by the disease. ...
Document
... and a clone derived from that library hybridized to the 5 kb and 3.1 kb restriction fragments only. When sequenced, this clone was 720 nucleotides in length. A synthetic oligonucleotide that corresponded to amino acids 3 through 11 of this protein was produced and labeled; it hybridized to the 5 kb, ...
... and a clone derived from that library hybridized to the 5 kb and 3.1 kb restriction fragments only. When sequenced, this clone was 720 nucleotides in length. A synthetic oligonucleotide that corresponded to amino acids 3 through 11 of this protein was produced and labeled; it hybridized to the 5 kb, ...
Molecular Genetics Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice
... a. many noncoding nucleotides are present in mRNA. b. there is redundancy and ambiguity in the genetic code. c. many nucleotides are needed to code for each amino acid. d. nucleotides break off and are lost during the transcription process. e. there are termination exons near the beginning of mRNA. ...
... a. many noncoding nucleotides are present in mRNA. b. there is redundancy and ambiguity in the genetic code. c. many nucleotides are needed to code for each amino acid. d. nucleotides break off and are lost during the transcription process. e. there are termination exons near the beginning of mRNA. ...
Profil N° (à remplir par VAS) FINANCEMENT
... study IQUB, a new Cancer/Testis gene (CT gene). These genes are a key element of methods that involve a patient’s immune system. IQUB is de-repressed in in all somatic cancers that we analyzed using GeneChip expression data from a very large cancer study published by a US consortium. Moreover, mutat ...
... study IQUB, a new Cancer/Testis gene (CT gene). These genes are a key element of methods that involve a patient’s immune system. IQUB is de-repressed in in all somatic cancers that we analyzed using GeneChip expression data from a very large cancer study published by a US consortium. Moreover, mutat ...
Protein Synthesis
... a double helix shape and contains sequences of nucleotides. Each nucleotide has one of the 4 bases: Adenine (A) which always bonds with Thymine (T), and Cytosine (C) which always bonds with Guanine (G). Each stand of DNA is complementary to the other. ...
... a double helix shape and contains sequences of nucleotides. Each nucleotide has one of the 4 bases: Adenine (A) which always bonds with Thymine (T), and Cytosine (C) which always bonds with Guanine (G). Each stand of DNA is complementary to the other. ...
Point mutation

A point mutation, or single base modification, is a type of mutation that causes a single nucleotide base change, insertion, or deletion of the genetic material, DNA or RNA. The term frameshift mutation indicates the addition or deletion of a base pair. A point mutant is an individual that is affected by a point mutation.Repeat induced point mutations are recurring point mutations, discussed below.