Ch 7 Genetic Variety
... 4 chromosomes form a tetrad Genetic material is exchanged by “non-sister” chromatid on homologous chromosomes ...
... 4 chromosomes form a tetrad Genetic material is exchanged by “non-sister” chromatid on homologous chromosomes ...
DNA - Mrs-Lamberts-Biology
... DNA prior to cell division so the daughter cells both get a full set. The next two processes occur back to back, and this is how your genes make your body work. Each gene codes for specific protein(s) each individual cell needs to function properly and keep you alive. Many of these proteins are enz ...
... DNA prior to cell division so the daughter cells both get a full set. The next two processes occur back to back, and this is how your genes make your body work. Each gene codes for specific protein(s) each individual cell needs to function properly and keep you alive. Many of these proteins are enz ...
File
... effect. But, other times, the change will cause a different amino acid to be put into the protein. The effect also depends in what cell the mutation takes place. A mutation in body cells only affects the individual in which they occur, but a mutation in a gamete (sperm or egg) can be passed on to th ...
... effect. But, other times, the change will cause a different amino acid to be put into the protein. The effect also depends in what cell the mutation takes place. A mutation in body cells only affects the individual in which they occur, but a mutation in a gamete (sperm or egg) can be passed on to th ...
DNA/RNA
... 9 Must be able to replicate and must direct protein synthesis for it to play a role in inheritance ...
... 9 Must be able to replicate and must direct protein synthesis for it to play a role in inheritance ...
Lecture 1: Molecular Biology
... the ribosome incorporates amino acids into a polypeptide chain • RNA is decoded by tRNA (transfer RNA) molecules, which each transport specific amino acids to the growing chain • Translation ends when a stop codon (UAA, UAG, UGA) is reached ...
... the ribosome incorporates amino acids into a polypeptide chain • RNA is decoded by tRNA (transfer RNA) molecules, which each transport specific amino acids to the growing chain • Translation ends when a stop codon (UAA, UAG, UGA) is reached ...
DNA RNA Lecture Website
... 2. There are ___ different nucleotides (since there are four different nitrogenous bases). three nucleotides in 3. It was discovered that ______________ amino acid sequence must specify each __________. This would provide for ___ 64 possible combinations of amino acids. triplet of nucleotides is cal ...
... 2. There are ___ different nucleotides (since there are four different nitrogenous bases). three nucleotides in 3. It was discovered that ______________ amino acid sequence must specify each __________. This would provide for ___ 64 possible combinations of amino acids. triplet of nucleotides is cal ...
Introduction o Except for identical twins, have the same DNA. o
... The Function and Structure of DNA Human DNA consists of about ________________ bases, and more than _____________________ of those bases are the same in all people. The order, or ______________, of these bases determines the information available for building and maintaining an organism, similar to ...
... The Function and Structure of DNA Human DNA consists of about ________________ bases, and more than _____________________ of those bases are the same in all people. The order, or ______________, of these bases determines the information available for building and maintaining an organism, similar to ...
What are you made of?
... gradient or “need” for certain molecules by the cells • Less macromolecules in nearby cells than in the blood causes a “need” for that molecule • Cross into cells through diffusion or through active transport ...
... gradient or “need” for certain molecules by the cells • Less macromolecules in nearby cells than in the blood causes a “need” for that molecule • Cross into cells through diffusion or through active transport ...
The Universal Dogma of Genetics
... • The DNA (sequence of nitrogen bases) makes the genotype (genetic make up). The DNA is expressed as proteins (enzymes), which provide the molecular basis for phenotypic traits ...
... • The DNA (sequence of nitrogen bases) makes the genotype (genetic make up). The DNA is expressed as proteins (enzymes), which provide the molecular basis for phenotypic traits ...
How do organisms grow and heal themselves? What instructions do
... CODON each of which spells out an amino acid. If you insert or delete one base then all the groups of three (amino acid) will be changed. ...
... CODON each of which spells out an amino acid. If you insert or delete one base then all the groups of three (amino acid) will be changed. ...
Activity Apr 20, 2016 – 6.3 Genetic Mutation
... g) If a G were added to the mRNA strand between the 3rd and 4th nucleotides from the left, what mutation is this and what would the resulting mRNA look like? mRNA ...
... g) If a G were added to the mRNA strand between the 3rd and 4th nucleotides from the left, what mutation is this and what would the resulting mRNA look like? mRNA ...
Class Agenda Week of 8-13 Oct 2007
... generations of relatives who descended from Lincoln's grandparents. The gene causes spinocerebellar ataxia type 5, a degenerative neurological disorder that affects coordination, including walking, writing, speaking and swallowing. There's a 25 percent chance that Lincoln also inherited the mutation ...
... generations of relatives who descended from Lincoln's grandparents. The gene causes spinocerebellar ataxia type 5, a degenerative neurological disorder that affects coordination, including walking, writing, speaking and swallowing. There's a 25 percent chance that Lincoln also inherited the mutation ...
the new mutation theory of phenotypic evolution
... (1932) gained general support. This happened partly because most mutations experimentally obtained were deleterious and these mutations did not seem to be useful for evolution. Neo-Darwinism asserts that natural selection is the major force of evolution and has the power of creating novel characters ...
... (1932) gained general support. This happened partly because most mutations experimentally obtained were deleterious and these mutations did not seem to be useful for evolution. Neo-Darwinism asserts that natural selection is the major force of evolution and has the power of creating novel characters ...
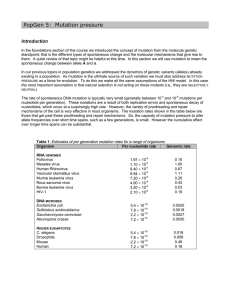
PopGen 5: Mutation pressure
... In the foundations section of this course we introduced the concept of mutation from the molecule genetic standpoint; that is the different types of spontaneous change and the molecular mechanisms that give rise to them. A quick review of that topic might be helpful at this time. In this section we ...
... In the foundations section of this course we introduced the concept of mutation from the molecule genetic standpoint; that is the different types of spontaneous change and the molecular mechanisms that give rise to them. A quick review of that topic might be helpful at this time. In this section we ...
Functional and nonfunctional mutations distinguished by random
... specific adaptive mutations; even mutations responsible for specific functional differences among proteins can evade identification when multiple nonfunctional mutations are present (3). Thus, the use of sequence comparisons is of limited utility in identifying the molecular mechanisms underlying di ...
... specific adaptive mutations; even mutations responsible for specific functional differences among proteins can evade identification when multiple nonfunctional mutations are present (3). Thus, the use of sequence comparisons is of limited utility in identifying the molecular mechanisms underlying di ...
Section 1 Workbook Unit 2 ANSWERS File
... a. What can you conclude about the effect of substitution mutations on the polypeptide produced from a strand of DNA? You can get a complete protein made unlike the other types of point mutations. The amino acid may not even change so the same protein could still be made – having no affect on the o ...
... a. What can you conclude about the effect of substitution mutations on the polypeptide produced from a strand of DNA? You can get a complete protein made unlike the other types of point mutations. The amino acid may not even change so the same protein could still be made – having no affect on the o ...
Section 1.3 Name:
... • In order to prepare for protein synthesis in the cytoplasm, DNA must copy its genetic instructions into messenger RNA (mRNA) molecules. This process is known as ____________________ (see Figure 10-7 on page 191). Transcription: ...
... • In order to prepare for protein synthesis in the cytoplasm, DNA must copy its genetic instructions into messenger RNA (mRNA) molecules. This process is known as ____________________ (see Figure 10-7 on page 191). Transcription: ...
Chapter 20 Inheritance, Genetics, and Molecular Biology So how
... o Occurs when two different alleles are equally expressed in a heterozygote Multiple alleles o The gene exists in several allelic forms o A person only has 2 of the possible alleles o A good example is the ABO blood system o IA and IB are codominant alleles o The i allele is recessive to both IA and ...
... o Occurs when two different alleles are equally expressed in a heterozygote Multiple alleles o The gene exists in several allelic forms o A person only has 2 of the possible alleles o A good example is the ABO blood system o IA and IB are codominant alleles o The i allele is recessive to both IA and ...
Protein Synthesis: A Real Adventure
... card over revealing the word. Write the word down. 4. The tRNA student will bring the word back to the ribosome. 5. The rRNA student will write down each word as delivered by the tRNA 6. After completing the sentence, a student in the group will tell your teacher the sentence. If correct, you may pi ...
... card over revealing the word. Write the word down. 4. The tRNA student will bring the word back to the ribosome. 5. The rRNA student will write down each word as delivered by the tRNA 6. After completing the sentence, a student in the group will tell your teacher the sentence. If correct, you may pi ...
It’s in the GENES COOL SCIENCE
... different from everyone else’s and can be used either to convict you or, in the case of The Innocence Project, to exonerate you, of a crime. For the layman, DNA testing has become an over-the-counter reality. Kits are available in Walmart and other retailers and online to help you discover your ance ...
... different from everyone else’s and can be used either to convict you or, in the case of The Innocence Project, to exonerate you, of a crime. For the layman, DNA testing has become an over-the-counter reality. Kits are available in Walmart and other retailers and online to help you discover your ance ...
Unit A Glossary
... shows a trait that is different from either homozygote, and usually intermediate between them. 2. Inherit, inherited The passage of traits from parent to offspring. 3. Introduced species A species that has been moved by humans from its normal habitat to a new habitat, either intentionally or by mist ...
... shows a trait that is different from either homozygote, and usually intermediate between them. 2. Inherit, inherited The passage of traits from parent to offspring. 3. Introduced species A species that has been moved by humans from its normal habitat to a new habitat, either intentionally or by mist ...
Point mutation

A point mutation, or single base modification, is a type of mutation that causes a single nucleotide base change, insertion, or deletion of the genetic material, DNA or RNA. The term frameshift mutation indicates the addition or deletion of a base pair. A point mutant is an individual that is affected by a point mutation.Repeat induced point mutations are recurring point mutations, discussed below.