Document
... Autosomal recessive and dominant traits are distinguished primarily by the pattern of transmission from parents to offspring. A person with a dominant trait usually has an affected parent unless it is due to a new mutation or incomplete penetrance is observed. Also, two affected parents can have una ...
... Autosomal recessive and dominant traits are distinguished primarily by the pattern of transmission from parents to offspring. A person with a dominant trait usually has an affected parent unless it is due to a new mutation or incomplete penetrance is observed. Also, two affected parents can have una ...
Supplemental Note
... identify classes of genes that were differentially expressed as a result of mtDNA mutations. Hiona et al., MIAME p.3 ...
... identify classes of genes that were differentially expressed as a result of mtDNA mutations. Hiona et al., MIAME p.3 ...
DNA Deoxyribonucleic Acid
... Translation Breaking the Genetic Code (See Genetic Code Handout) Scientists can use two tables that reference the genetic code. We can read the codons in a strand of mRNA and use the charts to tell us what amino acids will be added to the polypeptide chain. Summary: DNA Replication: ...
... Translation Breaking the Genetic Code (See Genetic Code Handout) Scientists can use two tables that reference the genetic code. We can read the codons in a strand of mRNA and use the charts to tell us what amino acids will be added to the polypeptide chain. Summary: DNA Replication: ...
Genetic disorders
... neural tumors (neurofibromas) dispersed anywhere on or in the body, numerous pigmented skin lesions, and pigmented iris hamartomas, also called Lisch nodules. A wide range of associated abnormalities has been reported in these patients – skeletal lesions like erosive defects, scoliosis, intraosseous ...
... neural tumors (neurofibromas) dispersed anywhere on or in the body, numerous pigmented skin lesions, and pigmented iris hamartomas, also called Lisch nodules. A wide range of associated abnormalities has been reported in these patients – skeletal lesions like erosive defects, scoliosis, intraosseous ...
Recent progress in understanding transcription factor binding
... sequence. Much more experimental and computational work will be required to extend coverage to all transcription factors and increase the accuracy and precision of the sequence-to-affinity models that can currently be derived from the data to a level where functional differences between closely rela ...
... sequence. Much more experimental and computational work will be required to extend coverage to all transcription factors and increase the accuracy and precision of the sequence-to-affinity models that can currently be derived from the data to a level where functional differences between closely rela ...
Genetics - Mrs. Yu`s Science Classes
... Proofreading of a newly attached base to the growing replicate strand is carried out by DNA polymerase. DNA polymerase checks to make sure that each newly added nucleotide correctly base pairs with the template strand. If it does not, the nucleotide is removed and replaced with the correct ...
... Proofreading of a newly attached base to the growing replicate strand is carried out by DNA polymerase. DNA polymerase checks to make sure that each newly added nucleotide correctly base pairs with the template strand. If it does not, the nucleotide is removed and replaced with the correct ...
A1981MD68300002
... from molecular biologists, to the possibility that genes may consist of much more information than that which encodes a polypeptide. We had failed to uncover the sought after operon, only to discover that a single eukaryotic gene may, in some instances, be as large and complex as several operons or ...
... from molecular biologists, to the possibility that genes may consist of much more information than that which encodes a polypeptide. We had failed to uncover the sought after operon, only to discover that a single eukaryotic gene may, in some instances, be as large and complex as several operons or ...
http://www - TeacherWeb
... How is DNA technology used to screen for cancer and other disease causing cells? How can DNA technology treat cancers and other diseases? Introduction: There are more than 4,000 genetic diseases currently identified - most are very rare, but some are relatively widespread, especially within certain ...
... How is DNA technology used to screen for cancer and other disease causing cells? How can DNA technology treat cancers and other diseases? Introduction: There are more than 4,000 genetic diseases currently identified - most are very rare, but some are relatively widespread, especially within certain ...
Remediation/Corrections Packet
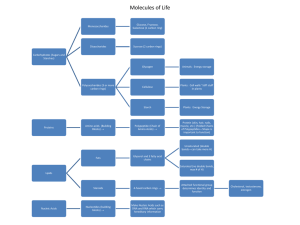
... The four main classes of organic compounds (carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids) that are essential to the proper functioning of all living things are known as polymers or macromolecules. All of these compounds are built primarily of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen but in different ratio ...
... The four main classes of organic compounds (carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids) that are essential to the proper functioning of all living things are known as polymers or macromolecules. All of these compounds are built primarily of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen but in different ratio ...
No Slide Title
... III. Transportation (Transportation) Definition: mRNA is transported from the nucleus to the cytoplasm and attaches to a ribosome. Process: (same as the definition) ...
... III. Transportation (Transportation) Definition: mRNA is transported from the nucleus to the cytoplasm and attaches to a ribosome. Process: (same as the definition) ...
Chapter 15 - Translation of mRNA
... a. Archibald Garrod proposed that some genes code for the production of a single enzyme b. Beadle and Tatum’s experiments with Neurospora led them to propose the one-gene/oneenzyme hypothesis 2. The relationship between the genetic code and protein synthesis a. During translation, the genetic code w ...
... a. Archibald Garrod proposed that some genes code for the production of a single enzyme b. Beadle and Tatum’s experiments with Neurospora led them to propose the one-gene/oneenzyme hypothesis 2. The relationship between the genetic code and protein synthesis a. During translation, the genetic code w ...
Acquired Variation
... 44 women were asked to rank the shirts in order of smell preference the scientists measured the MHC genes (genes related to smell) of each male and each female the results found that women preferred shirt smells from males who had the most different MHC genes from their own Women preferred m ...
... 44 women were asked to rank the shirts in order of smell preference the scientists measured the MHC genes (genes related to smell) of each male and each female the results found that women preferred shirt smells from males who had the most different MHC genes from their own Women preferred m ...
BIO 304: General Genetics, Fall 2003
... In this course we will examine the core concepts in molecular genetics, including DNA structure, replication and repair, gene expression, regulation of gene expression as well as topics involved in biotechnology. Upon completion of this course, you are expected to be able to: •Define and describe th ...
... In this course we will examine the core concepts in molecular genetics, including DNA structure, replication and repair, gene expression, regulation of gene expression as well as topics involved in biotechnology. Upon completion of this course, you are expected to be able to: •Define and describe th ...
Rationale of Genetic Studies Some goals of genetic studies include
... Genetically, a chromosome is just a long string of DNA. DNA is a biochemical molecule, but quantitative scientists think of it more as “information” in some sense. We think of DNA as a long string of letters that come from a four-letter alphabet: A, T, G, C (Adenine, Thymine, Guanine, Cytosine). DNA ...
... Genetically, a chromosome is just a long string of DNA. DNA is a biochemical molecule, but quantitative scientists think of it more as “information” in some sense. We think of DNA as a long string of letters that come from a four-letter alphabet: A, T, G, C (Adenine, Thymine, Guanine, Cytosine). DNA ...
Genetic Disorders and Gene Therapy
... Hybridization: Crossing individuals that are not closely related to introduce new, beneficial alleles to the population. New individuals are generally hardier than either parent. This is called ________________________. Mutations In biology, mutations are changes to the nucleotide sequence of th ...
... Hybridization: Crossing individuals that are not closely related to introduce new, beneficial alleles to the population. New individuals are generally hardier than either parent. This is called ________________________. Mutations In biology, mutations are changes to the nucleotide sequence of th ...
TRANSCRIPTION-TRANSLATION PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
... One gene, one enzyme hypothesis - A single gene controls the specificity and activity of each enzyme in a given metabolic pathway MEANING- mutation of this gene changes the ability to the cell to carry out a particular reaction, thus disrupting the pathway. ...
... One gene, one enzyme hypothesis - A single gene controls the specificity and activity of each enzyme in a given metabolic pathway MEANING- mutation of this gene changes the ability to the cell to carry out a particular reaction, thus disrupting the pathway. ...
RNA and Protein Synthesis
... Transcription • When RNA molecules are produced by copying part of the nucleotide sequence of DNA into to a complementary sequence of RNA • Transcribe = to write/copy down • When DNA’s instructions are copied by mRNA ...
... Transcription • When RNA molecules are produced by copying part of the nucleotide sequence of DNA into to a complementary sequence of RNA • Transcribe = to write/copy down • When DNA’s instructions are copied by mRNA ...
Hemagglutinin Protein (HA1 Subunit) (His Tag)
... The recombinant HA1 subunit of Influenza A virus (A/Australian shelduck/ Western Australia/1756/1983(H15N2)) comprises 342 amino acids and has a predicted molecular mass of 37.6 kDa. The apparent molecular mass of the protein is approximately 51.6 kDa in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. ...
... The recombinant HA1 subunit of Influenza A virus (A/Australian shelduck/ Western Australia/1756/1983(H15N2)) comprises 342 amino acids and has a predicted molecular mass of 37.6 kDa. The apparent molecular mass of the protein is approximately 51.6 kDa in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. ...
DNA Technology ppt 2014
... Treatment of a genetic disorder (like cystic fibrous) by correcting a defective gene that causes a deficiency of an enzyme. Nasal spray that carries normal enzyme gene. Body makes enzyme and patient breathes normally. ...
... Treatment of a genetic disorder (like cystic fibrous) by correcting a defective gene that causes a deficiency of an enzyme. Nasal spray that carries normal enzyme gene. Body makes enzyme and patient breathes normally. ...
Week 2
... • Cancer is linked with hyper-activity of growth factors of inhibition of tumor suppressor proteins • Sickle cell disease is due to the replacement of a single nucleotide, causing a change in a single amino acid in the sequence of the components of the hemoglobin complex, in turn reducing its oxygen ...
... • Cancer is linked with hyper-activity of growth factors of inhibition of tumor suppressor proteins • Sickle cell disease is due to the replacement of a single nucleotide, causing a change in a single amino acid in the sequence of the components of the hemoglobin complex, in turn reducing its oxygen ...
Point mutation

A point mutation, or single base modification, is a type of mutation that causes a single nucleotide base change, insertion, or deletion of the genetic material, DNA or RNA. The term frameshift mutation indicates the addition or deletion of a base pair. A point mutant is an individual that is affected by a point mutation.Repeat induced point mutations are recurring point mutations, discussed below.