A1981LU68900001
... better mousetrap and the world will beat a path to your door’ holds true even in scientific research! But, after all, what is a new analytical procedure other than a ‘better mousetrap’ —an improved means for doing a necessary job? The aura attached to a major scientific breakthrough often hides the ...
... better mousetrap and the world will beat a path to your door’ holds true even in scientific research! But, after all, what is a new analytical procedure other than a ‘better mousetrap’ —an improved means for doing a necessary job? The aura attached to a major scientific breakthrough often hides the ...
irons.conroeisd.net
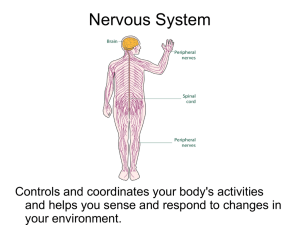
... sensory and motor information throughout the body in the form of electrical impulses. ...
... sensory and motor information throughout the body in the form of electrical impulses. ...
ppt
... At equilibrium, k1=k2. Substituting, k1/k2=[L]*[R]/[LR]=kD, the equilibrium dissociation constant ...
... At equilibrium, k1=k2. Substituting, k1/k2=[L]*[R]/[LR]=kD, the equilibrium dissociation constant ...
sensory overload - Saint Michael`s College
... Neurons can’t cope with this kind of excessive excitation. Unlike muscle tissue, they have no energy reserves or alternative energy resources. In many human-made environments, such as cinemas, rock concerts, or dance clubs, it is not only the acoustic system that is stretched to its physical and met ...
... Neurons can’t cope with this kind of excessive excitation. Unlike muscle tissue, they have no energy reserves or alternative energy resources. In many human-made environments, such as cinemas, rock concerts, or dance clubs, it is not only the acoustic system that is stretched to its physical and met ...
Document
... • Presynaptic neurons send the neuron. • Postsynaptic neurons receive the neuron. • Active neurons (excitatory) produce an action potential which travels down the neuron. • A synapse releases neurotransmitters that change the electrical potential of the next neuron. • Inactive neurons (inhibitory) s ...
... • Presynaptic neurons send the neuron. • Postsynaptic neurons receive the neuron. • Active neurons (excitatory) produce an action potential which travels down the neuron. • A synapse releases neurotransmitters that change the electrical potential of the next neuron. • Inactive neurons (inhibitory) s ...
Biology 251 Fall 2015 1 TOPIC 7: PERIPHERAL NERVOUS SYSTEM
... Responses of receptors to stimuli ...
... Responses of receptors to stimuli ...
hendrick
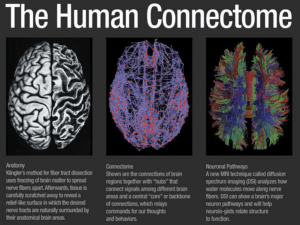
... more. A unique number identifying a single neuron in a population of 86 billion can be expressed in 37 bits of information. To identify the two neurons would take 37 + 37 = 74 bits per connection, or 518,000 bits (65 kilobytes) per neuron. Multiplying by 86 billion neurons gives a total of 5.59 peta ...
... more. A unique number identifying a single neuron in a population of 86 billion can be expressed in 37 bits of information. To identify the two neurons would take 37 + 37 = 74 bits per connection, or 518,000 bits (65 kilobytes) per neuron. Multiplying by 86 billion neurons gives a total of 5.59 peta ...
Slide 1
... Synthesized from amino acids Found in various regions of brain Affect learning, emotions, motor control Neurotransmitters – Serotonin – Histamine – Catecholamines • Dopamine • Epinephrine • Norepinephrine ...
... Synthesized from amino acids Found in various regions of brain Affect learning, emotions, motor control Neurotransmitters – Serotonin – Histamine – Catecholamines • Dopamine • Epinephrine • Norepinephrine ...
Nervous System Notes
... Synthesized from amino acids Found in various regions of brain Affect learning, emotions, motor control Neurotransmitters – Serotonin – Histamine – Catecholamines • Dopamine • Epinephrine • Norepinephrine ...
... Synthesized from amino acids Found in various regions of brain Affect learning, emotions, motor control Neurotransmitters – Serotonin – Histamine – Catecholamines • Dopamine • Epinephrine • Norepinephrine ...
No Slide Title
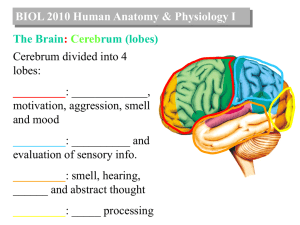
... frontal and parietal lobes is ______ ________. Ridges on either side are ____ & _____ _____ ...
... frontal and parietal lobes is ______ ________. Ridges on either side are ____ & _____ _____ ...
15_Neuro
... synapse to receptor sites on the dendrite of the next neuron. Generates the next electrical stimulus. Terminal ends of the axon release a transmitter substance that affects the dendrites of the next neuron. One way transmission of the impulse is assured because only the axons release these che ...
... synapse to receptor sites on the dendrite of the next neuron. Generates the next electrical stimulus. Terminal ends of the axon release a transmitter substance that affects the dendrites of the next neuron. One way transmission of the impulse is assured because only the axons release these che ...
structure and function of the neurologic system
... potential – Inhibitory neurotransmitters dampen Na+ influx into neuron inhibition of depolarization, so no action potential – Different neurotransmitters have different functions (some excitatory, some inhibitory) ...
... potential – Inhibitory neurotransmitters dampen Na+ influx into neuron inhibition of depolarization, so no action potential – Different neurotransmitters have different functions (some excitatory, some inhibitory) ...
Document
... - NT binds to receptors and opens ion channels that depolarize the membrane (excitatory postsynaptic potential (EPSP)) or hyperpolarize the postsynaptic membrane (inhibitory postsynaptic membrane (IPSP). Glial cells remove neurotransmitter from the synaptic cleft ...
... - NT binds to receptors and opens ion channels that depolarize the membrane (excitatory postsynaptic potential (EPSP)) or hyperpolarize the postsynaptic membrane (inhibitory postsynaptic membrane (IPSP). Glial cells remove neurotransmitter from the synaptic cleft ...
an appraisal of the mechanism of action of
... brain cortisone and adrenaline level. This factor is also contributory in anti-stress effect of Shirodhara. Probably Shirodhara normalizes the two important neurotransmitters Serotonin and Norepinephrine, which regulates a wide variety of neuropsychological processes along with sleep. Serotonin (5-h ...
... brain cortisone and adrenaline level. This factor is also contributory in anti-stress effect of Shirodhara. Probably Shirodhara normalizes the two important neurotransmitters Serotonin and Norepinephrine, which regulates a wide variety of neuropsychological processes along with sleep. Serotonin (5-h ...
The Discovery of the Endocannabinoid System
... to form connections (synapses) with the surface of target cells in the next brain area. B) At synapses, conventional neurotransmitters are released from the ends of axons and bind to receptors on target cells, causing either an excitation or inhibition of that cell within its brain circuit. The endo ...
... to form connections (synapses) with the surface of target cells in the next brain area. B) At synapses, conventional neurotransmitters are released from the ends of axons and bind to receptors on target cells, causing either an excitation or inhibition of that cell within its brain circuit. The endo ...
Evolutionary Psychology: Understanding Human Nature
... - Somatosensory cortex: area at the front of the parietal lobes that registers and processes body touch and movement sensations. - Association area: areas of the cerebral cortex that are not involved in primary motor or sensory functions; rather, they are involved in higher mental functions such as ...
... - Somatosensory cortex: area at the front of the parietal lobes that registers and processes body touch and movement sensations. - Association area: areas of the cerebral cortex that are not involved in primary motor or sensory functions; rather, they are involved in higher mental functions such as ...
Drosophila as a model to study mechanisms underlying alcohol
... invertebrates. We find synchronized neuronal networks in the brain, were the resulting patterns are measured in form of EEGs as alpha, beta, gamma and delta – waves (oscillations). These are widely regarded as functionally relevant signals of the brain. Synchronized neuronal networks are also necess ...
... invertebrates. We find synchronized neuronal networks in the brain, were the resulting patterns are measured in form of EEGs as alpha, beta, gamma and delta – waves (oscillations). These are widely regarded as functionally relevant signals of the brain. Synchronized neuronal networks are also necess ...
File - BHS AP Psychology
... response to an action potential and these neurotransmitters are chemicals that carry the neural message across the synapse to other neurons during neural transmission allowing for one nerve to communicate with another. __________ Point 9: Synapse: Students should explain that neural transmission inv ...
... response to an action potential and these neurotransmitters are chemicals that carry the neural message across the synapse to other neurons during neural transmission allowing for one nerve to communicate with another. __________ Point 9: Synapse: Students should explain that neural transmission inv ...
Molecules of Emotion
... “A major conceptual shift in neuroscience has been wrought by the realization that brain function is modulated by numerous chemicals in addition to classical neurotransmitters. Many of these informational substances are neuropeptides, originally studied in other contexts as hormones, gut peptides, o ...
... “A major conceptual shift in neuroscience has been wrought by the realization that brain function is modulated by numerous chemicals in addition to classical neurotransmitters. Many of these informational substances are neuropeptides, originally studied in other contexts as hormones, gut peptides, o ...
Antidepressants and Anxiolytics
... Anxiety • Benzos, SSRIs, others – Generalized Anxiety Disorder – Situational anxiety ...
... Anxiety • Benzos, SSRIs, others – Generalized Anxiety Disorder – Situational anxiety ...
Chapter 15 Anatomy & Physiology
... surface and the image will be transmitted through the optic nerves to the cerebral cortex. • Shortly after the photo excitation, the trans-retinal will dissociate from the rhodopsin (bleaching). The opsin will be recycled and the trans-retinal will be put back to cis-retinal using the other enzymes ...
... surface and the image will be transmitted through the optic nerves to the cerebral cortex. • Shortly after the photo excitation, the trans-retinal will dissociate from the rhodopsin (bleaching). The opsin will be recycled and the trans-retinal will be put back to cis-retinal using the other enzymes ...
Neuroplasticity-induced changes in the brain
... at the membrane resulting in the release of «an intracellular domain of Notch» (NICD). NICD then translocate to the nucleus where it regulates the transcription of various genes. γ-secretase-mediated Notch signaling plays an essential role in the regulation of cell fate during development of many or ...
... at the membrane resulting in the release of «an intracellular domain of Notch» (NICD). NICD then translocate to the nucleus where it regulates the transcription of various genes. γ-secretase-mediated Notch signaling plays an essential role in the regulation of cell fate during development of many or ...
DESIRED RESULTS (STAGE 1) - Anoka
... 2. Students will understand that there are brain functions, structures and communication systems. ...
... 2. Students will understand that there are brain functions, structures and communication systems. ...
on sleep eze - Viva Vitamins
... in our bodies in which its main biological role (besides acting as an antioxidant) is regulating circadian biorhythms. One such bioregulation is our sleep cycle. All throughout the day (but mostly at night), our pineal gland is hard at work synthesizing melatonin from L-tryptophan, secreting it into ...
... in our bodies in which its main biological role (besides acting as an antioxidant) is regulating circadian biorhythms. One such bioregulation is our sleep cycle. All throughout the day (but mostly at night), our pineal gland is hard at work synthesizing melatonin from L-tryptophan, secreting it into ...
Unit Three Nervous System
... and around them. • The actions of the nervous and endocrine systems control and regulate the body. • These two systems allow us to adjust to internal as well as external environmental changes. ...
... and around them. • The actions of the nervous and endocrine systems control and regulate the body. • These two systems allow us to adjust to internal as well as external environmental changes. ...