Nature Versus Nurture
... Early Twenties Memory systems start to decline Prefrontal cortex continues to mature New synapses in language and perception centers Myelination continues ...
... Early Twenties Memory systems start to decline Prefrontal cortex continues to mature New synapses in language and perception centers Myelination continues ...
Nerve Impulses - manorlakesscience
... electrical message between neurons to particular effector cells. ...
... electrical message between neurons to particular effector cells. ...
The Brain** in Brain Computer Interface - CBMSPC
... Neurological Injury • Injury to the nervous system often causes irreversible damage – results in disability, sometimes devastating – occasionally results in very bizarre symptoms ...
... Neurological Injury • Injury to the nervous system often causes irreversible damage – results in disability, sometimes devastating – occasionally results in very bizarre symptoms ...
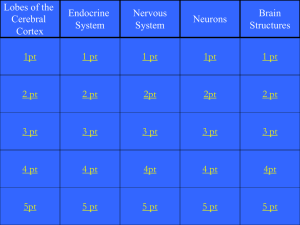
Brain Jeopardy
... between the central nervous system and the internal organs and glands – we do not consciously control it. ...
... between the central nervous system and the internal organs and glands – we do not consciously control it. ...
Nervous System The nervous system is divided into two parts: 1
... 2. Bipolar - have a process at each end. This type of neuron is relatively rare. They are found in acustic and vestibular nuclei associated with CN VIII, they act as olfactory receptors in CN I, and they are also found in the retina. 3. Pseudounipolar - single process that divides into two (sensory ...
... 2. Bipolar - have a process at each end. This type of neuron is relatively rare. They are found in acustic and vestibular nuclei associated with CN VIII, they act as olfactory receptors in CN I, and they are also found in the retina. 3. Pseudounipolar - single process that divides into two (sensory ...
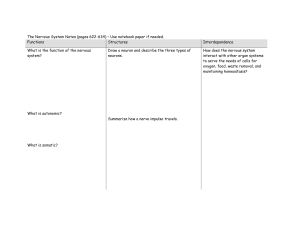
The Nervous System – Use notebook paper if
... Draw a neuron and describe the three types of neurons. ...
... Draw a neuron and describe the three types of neurons. ...
Nerve Cells
... body. At the synapse, the dendrite may have either excitatory or inhibitory receptors. Activation of these receptors results in either a small depolarization or small hyperpolarization of the plasma membrane. These depolarizations move down the dendrite to the cell body and then to the axon hillock. ...
... body. At the synapse, the dendrite may have either excitatory or inhibitory receptors. Activation of these receptors results in either a small depolarization or small hyperpolarization of the plasma membrane. These depolarizations move down the dendrite to the cell body and then to the axon hillock. ...
Drug Addiction and Reward
... antagonists, as well as other similar manipulations have no effect on rats judgements of hedonic properties of taste stimuli1 (for reviews, see Berridge ). • Many studies show that dopamine and accumbens neurons often become most active in anticipation of rewards, not during the reward phase ...
... antagonists, as well as other similar manipulations have no effect on rats judgements of hedonic properties of taste stimuli1 (for reviews, see Berridge ). • Many studies show that dopamine and accumbens neurons often become most active in anticipation of rewards, not during the reward phase ...
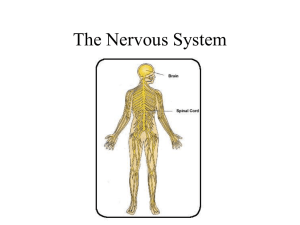
Nervous System
... Impulses jump from the axon Across the synapse To the dendrite of the next neuron ...
... Impulses jump from the axon Across the synapse To the dendrite of the next neuron ...
Neurons, Synapses and Long-term Potentiation
... changes in the cellular level • So what are the cellular changes? ...
... changes in the cellular level • So what are the cellular changes? ...
Test.
... • Also some neurons respond to specific stimuli – e.g. to faces but not to dogs. • There might even be a Clinton cell… ...
... • Also some neurons respond to specific stimuli – e.g. to faces but not to dogs. • There might even be a Clinton cell… ...
PDF
... DNA breaks, they describe the first identified Dictyostelium checkpoint – at the G2–M transition. Since Dictyostelium has vertebrate DNA repair enzymes not present in yeast or invertebrates, these findings should illuminate future studies of the cell cycle’s role in developmental processes in both D ...
... DNA breaks, they describe the first identified Dictyostelium checkpoint – at the G2–M transition. Since Dictyostelium has vertebrate DNA repair enzymes not present in yeast or invertebrates, these findings should illuminate future studies of the cell cycle’s role in developmental processes in both D ...
Directed Differentiation of Human Induced Pluripotent Stem
... reduces the excitability of GABAergic neurons. To determine whether this mutation causes similar changes in sodium channels and excitability in human neurons, we generated induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) lines from three siblings, two with the GEFS+ K1270T mutation and one without (Control). ...
... reduces the excitability of GABAergic neurons. To determine whether this mutation causes similar changes in sodium channels and excitability in human neurons, we generated induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) lines from three siblings, two with the GEFS+ K1270T mutation and one without (Control). ...
The Biological Bases of Behavior
... majority of left-handers also seem to have a left-hemispheric brain specialization ...
... majority of left-handers also seem to have a left-hemispheric brain specialization ...
Slide 1
... Ratings of religiosity & spirituality inversely correlated with the number of Serotonin 5-HT1A receptors in humans ...
... Ratings of religiosity & spirituality inversely correlated with the number of Serotonin 5-HT1A receptors in humans ...
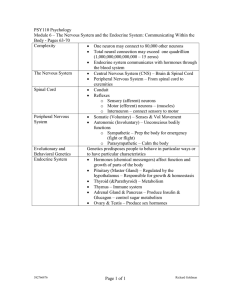
PSY110 Psychology
... o Sensory (afferent) neurons o Motor (efferent) neurons – (muscles) o Interneuron – connect sensory to motor Peripheral Nervous Somatic (Voluntary) – Senses & Vol Movement System Autonomic (Involuntary) – Unconscious bodily functions o Sympathetic – Prep the body for emergency (fight or flight) ...
... o Sensory (afferent) neurons o Motor (efferent) neurons – (muscles) o Interneuron – connect sensory to motor Peripheral Nervous Somatic (Voluntary) – Senses & Vol Movement System Autonomic (Involuntary) – Unconscious bodily functions o Sympathetic – Prep the body for emergency (fight or flight) ...
Learning and Memory Learning is defined as the acquisition of new
... neuron (nerve cell) in the brain. Memories seem to be a product of interaction between numerous neurons and multiple pathways within the brain. Brain research suggests several ways to reinforce declarative memory. For example, the more senses that are involved in processing the information, the more ...
... neuron (nerve cell) in the brain. Memories seem to be a product of interaction between numerous neurons and multiple pathways within the brain. Brain research suggests several ways to reinforce declarative memory. For example, the more senses that are involved in processing the information, the more ...
PR_161115_Inaktive_Gehirnzellen_E
... Many things we think we know about the world have their origin in popular culture, not science. The most well-known false ‘fact’ about the brain is the misconception that we only use ten percent of the brain’s overall capacity. This so-called ’ten percent myth’, while accepted as such by neuroscient ...
... Many things we think we know about the world have their origin in popular culture, not science. The most well-known false ‘fact’ about the brain is the misconception that we only use ten percent of the brain’s overall capacity. This so-called ’ten percent myth’, while accepted as such by neuroscient ...
Nervous System Neurons And Synapses
... 3. Explain what the acronym SSRIs stand for and describe the mechanism of action of SSRIs such as Prozac, in the treatment of depression. SSRIs stands for selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors. They are a class of medications that are used to treat depression, which is characterized by a deficienc ...
... 3. Explain what the acronym SSRIs stand for and describe the mechanism of action of SSRIs such as Prozac, in the treatment of depression. SSRIs stands for selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors. They are a class of medications that are used to treat depression, which is characterized by a deficienc ...
Immunocore to present at Biotech Showcase 2015 in San Francisco
... Immunocore’s ImmTAC (Immune mobilising mTCR Against Cancer) technology enables the immune system to recognise and kill cancer or viral cells. T Cell Receptors naturally recognise diseased cells and Immunocore’s competitive advantage is its ability to engineer high affinity T Cell Receptors and link ...
... Immunocore’s ImmTAC (Immune mobilising mTCR Against Cancer) technology enables the immune system to recognise and kill cancer or viral cells. T Cell Receptors naturally recognise diseased cells and Immunocore’s competitive advantage is its ability to engineer high affinity T Cell Receptors and link ...
What is memory? How does the brain perceive the outside
... barrier Remove dead cells Transport of nutrients Destroy neurotransmitters in extra cellular space ...
... barrier Remove dead cells Transport of nutrients Destroy neurotransmitters in extra cellular space ...
Pipecleaner Neuron Guide - spectrUM Discovery Area
... • Axon terminal – the terminal is the site at which information from one neuron is transmitted to the dendrite of another neuron (via a chemical signal. • Synapse- space between the axon of one neuron sending the message (releases neurotransmitter) to the dendrite of another neuron. Neurotransmitt ...
... • Axon terminal – the terminal is the site at which information from one neuron is transmitted to the dendrite of another neuron (via a chemical signal. • Synapse- space between the axon of one neuron sending the message (releases neurotransmitter) to the dendrite of another neuron. Neurotransmitt ...