Membrane potentials
... Changes in membrane permeability due to opening and closing of voltage-gated channels Resultant movement of ions. ...
... Changes in membrane permeability due to opening and closing of voltage-gated channels Resultant movement of ions. ...
Study guide unit 2
... 1. What are friction ridges and furrows and how do they relate to dactyloscopy? 2. In what ways are fingerprints permanent and unique? 3. What is the difference between a latent print and a visible print 4. What is the difference between the epidermis and the dermis of skin? 5. When (in life) do fin ...
... 1. What are friction ridges and furrows and how do they relate to dactyloscopy? 2. In what ways are fingerprints permanent and unique? 3. What is the difference between a latent print and a visible print 4. What is the difference between the epidermis and the dermis of skin? 5. When (in life) do fin ...
Neurotransmitter vs. Neuromodulator??
... Neurotransmitter Removal NT must be removed from the synaptic cleft quickly… - to prevent desensitization of postsynaptic cell to future signals - to prevent damage to the postsynaptic cell ...
... Neurotransmitter Removal NT must be removed from the synaptic cleft quickly… - to prevent desensitization of postsynaptic cell to future signals - to prevent damage to the postsynaptic cell ...
Prezentacja programu PowerPoint
... Einstein’s brain was removed within seven and a half hours of his death and was preserved for scientific studies. Einstein's brain weighed only 1,230 grams, which is less than the average adult male brain (about 1,400 grams). One of the differences that were found between Einstein’s brain compared t ...
... Einstein’s brain was removed within seven and a half hours of his death and was preserved for scientific studies. Einstein's brain weighed only 1,230 grams, which is less than the average adult male brain (about 1,400 grams). One of the differences that were found between Einstein’s brain compared t ...
Nervous System Test Review
... Cerebrum Controls It regulates all your thoughts and actions. There are many sections of the cerebrum that control what you hear, smell, how you move, how you think, write, talk and express emotions. ...
... Cerebrum Controls It regulates all your thoughts and actions. There are many sections of the cerebrum that control what you hear, smell, how you move, how you think, write, talk and express emotions. ...
PNS/Reflexes
... is glutamate. can be mechanoreceptors (respond to stretch, etc), chemoreceptors (respond to "help" signals by damaged cells), or thermoreceptors (respond to extreme temperatures) free dendritic endings, located virtually all over some transmit pain signals via type A fibers: this produces a sharp pa ...
... is glutamate. can be mechanoreceptors (respond to stretch, etc), chemoreceptors (respond to "help" signals by damaged cells), or thermoreceptors (respond to extreme temperatures) free dendritic endings, located virtually all over some transmit pain signals via type A fibers: this produces a sharp pa ...
Development of the Cerebral Cortex: VI. Growth Factors
... This growth is not due to new neurons, as the vast majority of nerve cells are present at birth. Surprisingly, two thirds of all neurons born during fetal development will die during the first decade of life in a process termed apoptosis, or programmed cell death. The remarkable growth of the brain ...
... This growth is not due to new neurons, as the vast majority of nerve cells are present at birth. Surprisingly, two thirds of all neurons born during fetal development will die during the first decade of life in a process termed apoptosis, or programmed cell death. The remarkable growth of the brain ...
Introduction To Physiology ~ LECTURE NOTES
... Claude Bernard (1813-‐78): stable internal conditions regardless of external conditions. Walter Cannon (1871-‐1945) coined the term ‘homeostasis’: it fluctuates within limited range around a set point Homeostasis me ...
... Claude Bernard (1813-‐78): stable internal conditions regardless of external conditions. Walter Cannon (1871-‐1945) coined the term ‘homeostasis’: it fluctuates within limited range around a set point Homeostasis me ...
Behavioral Neuroscience
... Cell Body: Life support center of the neuron. Dendrites: Branching extensions at the cell body. Receive messages from other neurons. Axon: Long single extension of a neuron, covered with myelin [MY-uh-lin] sheath to insulate and speed up messages through neurons. Terminal Branches of axon: Branched ...
... Cell Body: Life support center of the neuron. Dendrites: Branching extensions at the cell body. Receive messages from other neurons. Axon: Long single extension of a neuron, covered with myelin [MY-uh-lin] sheath to insulate and speed up messages through neurons. Terminal Branches of axon: Branched ...
Synaptic transmission & antipsychotic drugs
... Less risk of EPS, but other side effects may occur (e.g. blood disorders) ...
... Less risk of EPS, but other side effects may occur (e.g. blood disorders) ...
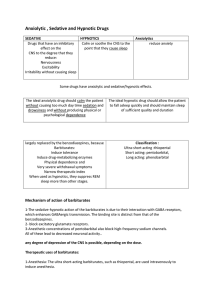
Anxiolytic , Sedative and Hypnotic Drugs
... Flumazenil (is a GABA-receptor antagonist) that can rapidly reverse the effects of benzodiazepines rapid Onset of action with short duration , Frequent administration may be necessary to maintain reversal of a long-acting benzodiazepine Side effects: 1.Dizziness, nausea, vomiting, and agitation 2.wi ...
... Flumazenil (is a GABA-receptor antagonist) that can rapidly reverse the effects of benzodiazepines rapid Onset of action with short duration , Frequent administration may be necessary to maintain reversal of a long-acting benzodiazepine Side effects: 1.Dizziness, nausea, vomiting, and agitation 2.wi ...
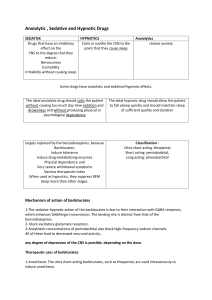
Anxiolytic , Sedative and Hypnotic Drugs SEDATIVE HYPNOTICS
... Flumazenil (is a GABA-receptor antagonist) that can rapidly reverse the effects of benzodiazepines rapid Onset of action with short duration , Frequent administration may be necessary to maintain reversal of a long-acting benzodiazepine Side effects: 1.Dizziness, nausea, vomiting, and agitation 2.wi ...
... Flumazenil (is a GABA-receptor antagonist) that can rapidly reverse the effects of benzodiazepines rapid Onset of action with short duration , Frequent administration may be necessary to maintain reversal of a long-acting benzodiazepine Side effects: 1.Dizziness, nausea, vomiting, and agitation 2.wi ...
Chapter 3 Synapses
... neural message cause a deplolarization in the next cell -70 mV up to -67 mV • Make it more likely the next cell will fire ...
... neural message cause a deplolarization in the next cell -70 mV up to -67 mV • Make it more likely the next cell will fire ...
Qhmgreif$ oftije@MtebStates ~i@)lngtOn, JEMK
... This letter is intended to wmvey the spirit of the Pediatric Labeling Section (1 11) of the Food and Ihg Modernization and Accountability Act of 1997 (FDAMA). The underlying purpose of this section was to increase the amount of information regarding pediatric use of drugs in all children. While drug ...
... This letter is intended to wmvey the spirit of the Pediatric Labeling Section (1 11) of the Food and Ihg Modernization and Accountability Act of 1997 (FDAMA). The underlying purpose of this section was to increase the amount of information regarding pediatric use of drugs in all children. While drug ...
The Nervous System and The Brain
... increase the intensity of the impulse. The neuron’s reaction is an “All or None Response” – Like firing a gun – either it fires, or it doesn’t ***Reaction Time Experiment*** http://www.bbc.co.uk/science/humanbody/sleep/sheep/ How do you know the difference between getting touched with a feather, or ...
... increase the intensity of the impulse. The neuron’s reaction is an “All or None Response” – Like firing a gun – either it fires, or it doesn’t ***Reaction Time Experiment*** http://www.bbc.co.uk/science/humanbody/sleep/sheep/ How do you know the difference between getting touched with a feather, or ...
Neurons: A fish-eye view of the brain
... (called a neurotransmitter) that travels to the receiving cell. The result may be that the receiving cell is excited, and fires a signal, or that it’s inhibited from doing so. Through the release of its neurotransmitter, a single axon can have both excitatory and inhibitory effects on the dendrites ...
... (called a neurotransmitter) that travels to the receiving cell. The result may be that the receiving cell is excited, and fires a signal, or that it’s inhibited from doing so. Through the release of its neurotransmitter, a single axon can have both excitatory and inhibitory effects on the dendrites ...
03/14 PPT
... Plan: monitor neural activation in the brain Technologies: calcium-sensitive dyes, voltage-sensitive dyes and intrinsic signals (changes in blood flow, oxygen levels) Results: •Odors activate a few glomeruli •Same glomeruli activated on repeated exposure •Different odors activate different glomeruli ...
... Plan: monitor neural activation in the brain Technologies: calcium-sensitive dyes, voltage-sensitive dyes and intrinsic signals (changes in blood flow, oxygen levels) Results: •Odors activate a few glomeruli •Same glomeruli activated on repeated exposure •Different odors activate different glomeruli ...
CommonlyAbusedDrugs
... patented by Merck pharmaceuticals on December 24, 1912, but it wasn't until the mid 1970s that articles related to its psychoactivity began showing up in scholarly journals. In the late '70s and early '80s MDMA was used as a psychotherapeutic tool and also started to become available on the street ...
... patented by Merck pharmaceuticals on December 24, 1912, but it wasn't until the mid 1970s that articles related to its psychoactivity began showing up in scholarly journals. In the late '70s and early '80s MDMA was used as a psychotherapeutic tool and also started to become available on the street ...
PP text version
... membrane potential of cells is usually negative (inside of cell more negative than outside) range is -50 to -90 mV. -70 mV = -70 X 10-3 V = -0.07 V membrane potential is due to permeability of membrane to potassium ions (K+) and maintained by an ionic pump called the Na-K ATPase (pumps three N ...
... membrane potential of cells is usually negative (inside of cell more negative than outside) range is -50 to -90 mV. -70 mV = -70 X 10-3 V = -0.07 V membrane potential is due to permeability of membrane to potassium ions (K+) and maintained by an ionic pump called the Na-K ATPase (pumps three N ...
Structure of a Neuron
... negatively charged compared to the outside of the cell extracellular fluid (ECF) – The cell is able to maintain a resting membrane potential of -70 mV (negative charge on the inside of membrane by active transport and specific voltage gated channels. ...
... negatively charged compared to the outside of the cell extracellular fluid (ECF) – The cell is able to maintain a resting membrane potential of -70 mV (negative charge on the inside of membrane by active transport and specific voltage gated channels. ...
Brain-Class Notes
... go through this organ on their way to other parts of the brain for processing Also plays a function in motor control ...
... go through this organ on their way to other parts of the brain for processing Also plays a function in motor control ...
How the Brain Pays Attention
... smile or a frown. Parkinson’s disease manifests itself in motor difficulty. But autism can cause clumsiness, and Parkinson’s may cause mentally diffuse thoughts, and both entail altered perceptual sensitivities. Unless we understand the whole system, we will design treatments that may address isolat ...
... smile or a frown. Parkinson’s disease manifests itself in motor difficulty. But autism can cause clumsiness, and Parkinson’s may cause mentally diffuse thoughts, and both entail altered perceptual sensitivities. Unless we understand the whole system, we will design treatments that may address isolat ...