Central Nervous System (CNS)
... of ions controlled by Na+/K+ pump that require ATP • Nerve impulse starts when the membrane of the nerve depolarizes due to some stimulus, chemical, temp. changes, mechanical, etc…. • Depolarization is caused by the influx of Na+ which causes the membrane to become more positive. This starts an acti ...
... of ions controlled by Na+/K+ pump that require ATP • Nerve impulse starts when the membrane of the nerve depolarizes due to some stimulus, chemical, temp. changes, mechanical, etc…. • Depolarization is caused by the influx of Na+ which causes the membrane to become more positive. This starts an acti ...
HUMAN PHYSIOLOGY
... I. There are two different subtypes of ACh receptors: nicotinic and muscarinic. A. Nicotinic receptors enclose membrane channels and open when ACh bonds to the receptor. This causes a depolarization called an excitatory postsynaptic potential (EPSP) in skeletal muscle cells. B. The binding of ACh to ...
... I. There are two different subtypes of ACh receptors: nicotinic and muscarinic. A. Nicotinic receptors enclose membrane channels and open when ACh bonds to the receptor. This causes a depolarization called an excitatory postsynaptic potential (EPSP) in skeletal muscle cells. B. The binding of ACh to ...
Unit XIV: Regulation
... - Cell body – contains all the normal cell parts nucleus, mitochondria, golgi, ER, cytoplasm, etc. - Dendrites – receptors on the cell body, receive impulses, used to pick up stimuli - Axon – long fiber that extends from the cell body, carries the impulse - Schwann’s Cells produce a Myelin sheath – ...
... - Cell body – contains all the normal cell parts nucleus, mitochondria, golgi, ER, cytoplasm, etc. - Dendrites – receptors on the cell body, receive impulses, used to pick up stimuli - Axon – long fiber that extends from the cell body, carries the impulse - Schwann’s Cells produce a Myelin sheath – ...
Ch 13 - lanoue
... The “Catcher” - Hold your thumb and index finger two inches apart while your partner drops a ruler between them. The “Dropper” – hold ruler vertical and drop it between your partner’s thumb and index finger. The distance the ruler falls before he/she stops it with his thumb and finger indicates thei ...
... The “Catcher” - Hold your thumb and index finger two inches apart while your partner drops a ruler between them. The “Dropper” – hold ruler vertical and drop it between your partner’s thumb and index finger. The distance the ruler falls before he/she stops it with his thumb and finger indicates thei ...
Chapter 12 The Nervous System
... • The Schwann cells line the length of the axon in the PNS. • The myelin sheath is a fatty layer that formed by the Schwann cell that wraps around the axon. • The gap between each Schwann cell is called the node of Ranvier. The axon is exposed in this gap and allows the impulse to jump from one node ...
... • The Schwann cells line the length of the axon in the PNS. • The myelin sheath is a fatty layer that formed by the Schwann cell that wraps around the axon. • The gap between each Schwann cell is called the node of Ranvier. The axon is exposed in this gap and allows the impulse to jump from one node ...
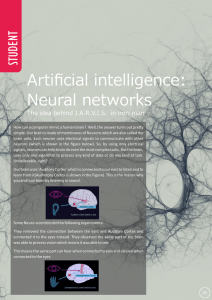
Artificial intelligence: Neural networks
... brain uses to process any kind of data. It has an input layer, one or more hidden layers and an output layer. In machine learning and deep learning problems, a neural network is one of the most widely used algorithms which is used to process data that helps a machine learn different things (like a hu ...
... brain uses to process any kind of data. It has an input layer, one or more hidden layers and an output layer. In machine learning and deep learning problems, a neural network is one of the most widely used algorithms which is used to process data that helps a machine learn different things (like a hu ...
Treatment and Therapies
... • Callosotomy- treats epilepsy well (cases even cures) • More success in removing the hemisphere(hemispherectomy) ...
... • Callosotomy- treats epilepsy well (cases even cures) • More success in removing the hemisphere(hemispherectomy) ...
File
... and metabolism within nerve cells Neurons: Cells responsible for conducting electrochemical messages throughout the body ...
... and metabolism within nerve cells Neurons: Cells responsible for conducting electrochemical messages throughout the body ...
Thinking About Psychology: The Science of Mind and Behavior
... 1. Define psychoactive drugs, and explain the cycle of dependence, tolerance, and withdrawal. 2. Describe the physiological and psychological effects of alcohol. 3. Describe the physiological and psychological effects of stimulants. 4. Describe the physiological and psychological effects of hallucin ...
... 1. Define psychoactive drugs, and explain the cycle of dependence, tolerance, and withdrawal. 2. Describe the physiological and psychological effects of alcohol. 3. Describe the physiological and psychological effects of stimulants. 4. Describe the physiological and psychological effects of hallucin ...
The effects of electrical microstimulation on cortical signal propagation
... • The correspondence between the actual and predicted hand position decreased in sessions BCWH (Wilcoxon signed-rank test). • The R for X-position decreased 28.1% and 17.2% in Monkey 2. The R for Yposition decreased 16.7% and 15.6% in Monkeys 1 and 2, respectively. • This decrease indicates that the ...
... • The correspondence between the actual and predicted hand position decreased in sessions BCWH (Wilcoxon signed-rank test). • The R for X-position decreased 28.1% and 17.2% in Monkey 2. The R for Yposition decreased 16.7% and 15.6% in Monkeys 1 and 2, respectively. • This decrease indicates that the ...
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM - Tamalpais Union High School District
... • Dopamine also sends signals that help coordinate your skeletal muscle movements • Parkinson’s Disease – deficient dopamine production – tremors ...
... • Dopamine also sends signals that help coordinate your skeletal muscle movements • Parkinson’s Disease – deficient dopamine production – tremors ...
Chapter 27 Lecture notes
... A. Drugs often produce their effect by altering the neurotransmitter or the receptor to the transmitter. B. The effects of several commonly used drugs are as listed below: 1. Caffeine increases alertness by countering the effects of inhibitory signals. 2. Nicotine activates acetylcholine receptors a ...
... A. Drugs often produce their effect by altering the neurotransmitter or the receptor to the transmitter. B. The effects of several commonly used drugs are as listed below: 1. Caffeine increases alertness by countering the effects of inhibitory signals. 2. Nicotine activates acetylcholine receptors a ...
Chapter 48: Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling Reading Guide 48.1
... 26. A single postsynaptic neuron can be affected by neurotransmitter molecules released by many other neurons, some releasing excitatory and some releasing inhibitory neurotransmitters. What will determine whether an action potential is generated in the postsynaptic neuron? 27. Table 48.2 in your te ...
... 26. A single postsynaptic neuron can be affected by neurotransmitter molecules released by many other neurons, some releasing excitatory and some releasing inhibitory neurotransmitters. What will determine whether an action potential is generated in the postsynaptic neuron? 27. Table 48.2 in your te ...
Slide ()
... whereasKandel neurons that receive input only from the ipsilateral eye (I) fall into group ...
... whereasKandel neurons that receive input only from the ipsilateral eye (I) fall into group ...
NERVOUS SYSTEM CNS-Central Nervous System PNS
... 2. While he could be confused with having prion-related disorders or Alzheimer’s disease because of his symptoms, he is actually suffering from something else. What neurovascular condition is he suffering from? Explain what this condition is. ...
... 2. While he could be confused with having prion-related disorders or Alzheimer’s disease because of his symptoms, he is actually suffering from something else. What neurovascular condition is he suffering from? Explain what this condition is. ...
primary visual cortex
... How is information about light relayed to the brain? • Visual information is relayed to the brain via many pathways. The largest and most studied visual pathway is the retina-geniculate-striate pathway. • Within this pathway is the optic chiasm: at this point, axons from the nasal halves of the ret ...
... How is information about light relayed to the brain? • Visual information is relayed to the brain via many pathways. The largest and most studied visual pathway is the retina-geniculate-striate pathway. • Within this pathway is the optic chiasm: at this point, axons from the nasal halves of the ret ...
Chapter 48: Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling Reading Guide 48.1
... 26. A single postsynaptic neuron can be affected by neurotransmitter molecules released by many other neurons, some releasing excitatory and some releasing inhibitory neurotransmitters. What will determine whether an action potential is generated in the postsynaptic neuron? 27. Table 48.2 in your te ...
... 26. A single postsynaptic neuron can be affected by neurotransmitter molecules released by many other neurons, some releasing excitatory and some releasing inhibitory neurotransmitters. What will determine whether an action potential is generated in the postsynaptic neuron? 27. Table 48.2 in your te ...
Smoking & Drinking
... such as high altitude training to increase the number of red blood cells which can then be stored for a few days prior to an event (which carry more oxygen due to increased haemoglobin levels)? • Discuss the moral and ethical issues involved with drugs in sport ...
... such as high altitude training to increase the number of red blood cells which can then be stored for a few days prior to an event (which carry more oxygen due to increased haemoglobin levels)? • Discuss the moral and ethical issues involved with drugs in sport ...
Spinal nerves
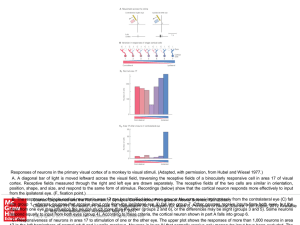
... Many of the areas Brodmann defined based solely on their neuronal organization have since been correlated closely to diverse cortical functions. For example, Brodmann areas 1, 2 and 3 are the primary somatosensory cortex; area 4 is the primary motor cortex; area 17 is the primary visual cortex; and ...
... Many of the areas Brodmann defined based solely on their neuronal organization have since been correlated closely to diverse cortical functions. For example, Brodmann areas 1, 2 and 3 are the primary somatosensory cortex; area 4 is the primary motor cortex; area 17 is the primary visual cortex; and ...
ppt - Le Moyne College
... – Thought cells continuous – Created way to stain nervous tissue so that only 1 in 100 neurons can be seen ...
... – Thought cells continuous – Created way to stain nervous tissue so that only 1 in 100 neurons can be seen ...
Abstract View OPTICAL RECORDING OF THE TRITONIA SWIMMING CENTRAL PATTERN GENERATOR. ;
... We recorded action potential activity from the isolated brain of the nudibranch seaslug Tritonia diomedea during fictive swimming. Candidate central pattern generator (CPG) interneurons were identified by their bursting patterns and positions in the brain. Previously identifed populations of interne ...
... We recorded action potential activity from the isolated brain of the nudibranch seaslug Tritonia diomedea during fictive swimming. Candidate central pattern generator (CPG) interneurons were identified by their bursting patterns and positions in the brain. Previously identifed populations of interne ...
Nervous system - Lancaster High School
... Carry impulses from the CNS to effectors (muscles or glands) ...
... Carry impulses from the CNS to effectors (muscles or glands) ...