Old Red Sandstone Rocks of Great Britain
... Continuous sea-cliff exposures of Walls Formation. Continuous sea-cliff exposures of cyclic lacustrine, fluvial and aeolian facies of the Brindister Flagstone Formation. Also a fossil fish GCR site. Fossil fish GCR site. Spectacular sea-cliff and foreshore exposures of lacustrine Melby Formation. Be ...
... Continuous sea-cliff exposures of Walls Formation. Continuous sea-cliff exposures of cyclic lacustrine, fluvial and aeolian facies of the Brindister Flagstone Formation. Also a fossil fish GCR site. Fossil fish GCR site. Spectacular sea-cliff and foreshore exposures of lacustrine Melby Formation. Be ...
Wadhwan Formation of Western India
... Detrital mineral composition of a sandstone is primarily controlled by source rock composition and plate tectonic setting. However, several other processes such as climate and weathering, depositional reworking and diagenesis also affect the relative abundance of detrital grains in terrigenous sedim ...
... Detrital mineral composition of a sandstone is primarily controlled by source rock composition and plate tectonic setting. However, several other processes such as climate and weathering, depositional reworking and diagenesis also affect the relative abundance of detrital grains in terrigenous sedim ...
Study Guide
... 1. Igneous rocks that are dense and dark-colored. They form from magma that is rich in iron and magnesium and poor in silica. 2. Thick, gooey, molten material inside a volcano or deep inside Earth 3. Igneous rocks that are light-colored and have a lower density. They form from thick, stiff magma tha ...
... 1. Igneous rocks that are dense and dark-colored. They form from magma that is rich in iron and magnesium and poor in silica. 2. Thick, gooey, molten material inside a volcano or deep inside Earth 3. Igneous rocks that are light-colored and have a lower density. They form from thick, stiff magma tha ...
North America`s Midcontinent Rift: When Rift Met LIP
... Flood basalts, Isle Royale National Park ...
... Flood basalts, Isle Royale National Park ...
Mesa Central of México: Stratigraphy, structure, and Cenozoic
... maps is the geological cartography (scale 1:50,000) of the Institute of Geology of the Autonomous University of San Luis Potosí, published in the Technical Reports series. These maps cover the San Luis Potosí state and neighboring regions. The second set of geologic maps was published by the Mexican ...
... maps is the geological cartography (scale 1:50,000) of the Institute of Geology of the Autonomous University of San Luis Potosí, published in the Technical Reports series. These maps cover the San Luis Potosí state and neighboring regions. The second set of geologic maps was published by the Mexican ...
The remarkable African Planation Surface
... by a veneer of generally rounded rocks—rounded by the action of water. There seems to be some confusion associated with planation surfaces. A planation surface is eroded into hard rock or sometimes into unconsolidated sediment by some watery erosive mechanism, usually leaving behind a veneer of roun ...
... by a veneer of generally rounded rocks—rounded by the action of water. There seems to be some confusion associated with planation surfaces. A planation surface is eroded into hard rock or sometimes into unconsolidated sediment by some watery erosive mechanism, usually leaving behind a veneer of roun ...
EESUnit 2 With LEP (6-27-08)
... This unit is focused on the formation and processes that govern Earth’s materials such as rocks, minerals, soil, mountain formation, and plate movement. Included are the impacts of human conditions on the availability of resources with their economical implications as well as the impact of plate mov ...
... This unit is focused on the formation and processes that govern Earth’s materials such as rocks, minerals, soil, mountain formation, and plate movement. Included are the impacts of human conditions on the availability of resources with their economical implications as well as the impact of plate mov ...
Introduction - Beck-Shop
... of the earliest differentiation processes on Earth is limited because information retrieved from the earliest crust is punctuated by large gaps. Earth’s earliest primitive crust most probably was mafic, and formed on top of a previously convecting magma ocean of uncertain depth (Boyet et al., 2003). ...
... of the earliest differentiation processes on Earth is limited because information retrieved from the earliest crust is punctuated by large gaps. Earth’s earliest primitive crust most probably was mafic, and formed on top of a previously convecting magma ocean of uncertain depth (Boyet et al., 2003). ...
SXR339 Ancient Mountains ISBN0749258470
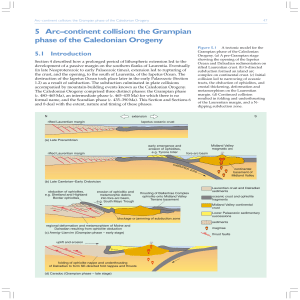
... Highland Border Complex). This fault is thought to indicate the position of an ancient suture zone. Two larger bodies, the Shetland ophiolite and the Ballantrae Complex lie far from this suture zone and their position merits further investigation. The Shetland ophiolite lies immediately to the east ...
... Highland Border Complex). This fault is thought to indicate the position of an ancient suture zone. Two larger bodies, the Shetland ophiolite and the Ballantrae Complex lie far from this suture zone and their position merits further investigation. The Shetland ophiolite lies immediately to the east ...
Geologic Map of the Baker Quadrangle, Lemhi County, Idaho: DWM
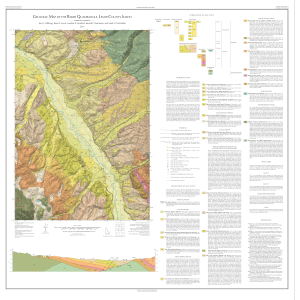
... Janecke and Blankenau (2003) interpreted the Salmon basin as one of several supradetachment basins that formed in east-central Idaho and western Montana between 46 and 31 Ma (late middle Eocene to early Oligocene). Blankenau (1999) studied the structure and stratigraphy in the southern portion of th ...
... Janecke and Blankenau (2003) interpreted the Salmon basin as one of several supradetachment basins that formed in east-central Idaho and western Montana between 46 and 31 Ma (late middle Eocene to early Oligocene). Blankenau (1999) studied the structure and stratigraphy in the southern portion of th ...
sedimentation and sedimentary rocks
... accumulations of natural rocky or mineral grains deposited from a fluid phase (water or air) by physical, chemical or biochemical processes. In a strictly etymological sense, the name "sediment" should be restricted solely to material deposited by gravity from rivers or sea-waters, and consisting of ...
... accumulations of natural rocky or mineral grains deposited from a fluid phase (water or air) by physical, chemical or biochemical processes. In a strictly etymological sense, the name "sediment" should be restricted solely to material deposited by gravity from rivers or sea-waters, and consisting of ...
Geochemistry of Jurassic Oceanic Crust beneath
... 1996; Thirlwall, 1997). Estimates of recycling ages are critically dependent on the effects of hydrothermal alteration near the ridge axis and the subduction process on the Pb isotope systematics of ocean crust. Ocean island basalts have long been considered to be one of the major means for evaluati ...
... 1996; Thirlwall, 1997). Estimates of recycling ages are critically dependent on the effects of hydrothermal alteration near the ridge axis and the subduction process on the Pb isotope systematics of ocean crust. Ocean island basalts have long been considered to be one of the major means for evaluati ...
SILURIAN CLIFFS
... years ago and ended 416 million years ago, lasting 27 million years. The Silurian is an important time in the Earth’s history. The rifting and dispersal of the Rodinia supercontinent, which had started in the Proterozoic eon, was substituted with the reassembling and reunion of the pieces of the con ...
... years ago and ended 416 million years ago, lasting 27 million years. The Silurian is an important time in the Earth’s history. The rifting and dispersal of the Rodinia supercontinent, which had started in the Proterozoic eon, was substituted with the reassembling and reunion of the pieces of the con ...
47. the ocean/continent transition beneath the iberia abyssal plain
... The first quantitatively rigorous fit of North America to Europe was performed by Bullard et al. (1965). They confirmed that, once the Bay of Biscay itself had been closed by a clockwise rotation of Iberia against Europe, the southeast Grand Banks margin could be matched with the west Iberia Margin. ...
... The first quantitatively rigorous fit of North America to Europe was performed by Bullard et al. (1965). They confirmed that, once the Bay of Biscay itself had been closed by a clockwise rotation of Iberia against Europe, the southeast Grand Banks margin could be matched with the west Iberia Margin. ...
Advances in the geology of the Tobacco Root Mountains, Montana
... shear and transposition of compositional layering, and the degree to which isotopic geochronometers were reset demonstrate an event that was orogenic in character and scope. Because the evidence for this orogeny and most of its known effects are found in Montana, we designate this the Big Sky orogen ...
... shear and transposition of compositional layering, and the degree to which isotopic geochronometers were reset demonstrate an event that was orogenic in character and scope. Because the evidence for this orogeny and most of its known effects are found in Montana, we designate this the Big Sky orogen ...
Sample pages 2 PDF
... The spatial juxtaposition of the Earth and Moon early in the history of the solar system (Ringwood 1986) requires both have been affected by early meteorite bombardment periods, documented on the Moon at ~3.95–3.85 Ga (Ryder 1990) and earlier periods. However, to date no shock-produced planar deform ...
... The spatial juxtaposition of the Earth and Moon early in the history of the solar system (Ringwood 1986) requires both have been affected by early meteorite bombardment periods, documented on the Moon at ~3.95–3.85 Ga (Ryder 1990) and earlier periods. However, to date no shock-produced planar deform ...
The Tien Shan Early Paleozoic tectonics and geodynamics
... [9] Microcontinent, continental island arc. In the Paleozoic the Tien Shan rocks composed a few tectonic blocks, having an old continental crust and separated by oceanic basins. A continental block of this kind can be ranked as a microcontinent or as a continental island arc, volcanic or nonvolcanic ...
... [9] Microcontinent, continental island arc. In the Paleozoic the Tien Shan rocks composed a few tectonic blocks, having an old continental crust and separated by oceanic basins. A continental block of this kind can be ranked as a microcontinent or as a continental island arc, volcanic or nonvolcanic ...
42. The New England Seamounts
... seamounts, and because alteration of the enclosed basaltic clasts is extremely variable, some of the clasts are thought to have been displaced, during the volcanic events, from pre-existing volcanic units on the crest and flanks of the seamount. At Site 382 beside Nashville Seamount, the latest sign ...
... seamounts, and because alteration of the enclosed basaltic clasts is extremely variable, some of the clasts are thought to have been displaced, during the volcanic events, from pre-existing volcanic units on the crest and flanks of the seamount. At Site 382 beside Nashville Seamount, the latest sign ...
Rankin et al AJS 2007
... At least two major Paleozoic compressional orogenic events affected central New England. During the Middle to Late Ordovician, previously amalgamated terranes collided with a volcanic arc or arcs off the east coast of Laurentia and, as the last remaining crust of the Iapetus Ocean west of that was c ...
... At least two major Paleozoic compressional orogenic events affected central New England. During the Middle to Late Ordovician, previously amalgamated terranes collided with a volcanic arc or arcs off the east coast of Laurentia and, as the last remaining crust of the Iapetus Ocean west of that was c ...
GEOLOGIC MAP OF SOUTHEASTERN ALASKA INTRODUCTION
... particular unit in this category are generally similar in lithic type, stratigraphic position, and age of deposition and are, unless otherwise noted, interpreted to be generally correlative. Such strata generally constitute formations, lithic components of formations or groups, or unnamed geologic u ...
... particular unit in this category are generally similar in lithic type, stratigraphic position, and age of deposition and are, unless otherwise noted, interpreted to be generally correlative. Such strata generally constitute formations, lithic components of formations or groups, or unnamed geologic u ...
Convergent Plate Boundaries - North Coast Distance Education
... Collisions between two continents are occurring in several places.The most dramatic is the one that produced the Himalaya Mountains and Tibetan Plateau of southern Asia. The Himalayas, Earth’s highest mountain belt, is a wide and highly deformed zone of mountains that rose as India collided with the ...
... Collisions between two continents are occurring in several places.The most dramatic is the one that produced the Himalaya Mountains and Tibetan Plateau of southern Asia. The Himalayas, Earth’s highest mountain belt, is a wide and highly deformed zone of mountains that rose as India collided with the ...
Cowie, Stonehaven
... and early summer, and especially at low tide. Rocks are displayed that tell an amazing story of an ancient ocean that was destroyed by colliding continents whose edges were then buckled to form high mountains. Eroded debris from these mountains is seen side by side across the Highland Boundary Fault ...
... and early summer, and especially at low tide. Rocks are displayed that tell an amazing story of an ancient ocean that was destroyed by colliding continents whose edges were then buckled to form high mountains. Eroded debris from these mountains is seen side by side across the Highland Boundary Fault ...
structure and tectonics of the southern gebel duwi area, eastern
... Arabian Shield (Moore, 1979). Following Cretaceous sediments ...
... Arabian Shield (Moore, 1979). Following Cretaceous sediments ...
vi. north moluccas
... appears to exclusively suggest a Late Triassic age; e.g. Martini et al., 2004). This series has been interpreted as a Late Triassic intra-cratonic rift sequence. The Triassic is overlain by a highly condensed Early-Middle Jurassic limestone (e.g. Wanner & Knipscheer 1951) or may locally be missing c ...
... appears to exclusively suggest a Late Triassic age; e.g. Martini et al., 2004). This series has been interpreted as a Late Triassic intra-cratonic rift sequence. The Triassic is overlain by a highly condensed Early-Middle Jurassic limestone (e.g. Wanner & Knipscheer 1951) or may locally be missing c ...
Geology of granite - Royal Society of Western Australia
... Only a small amount of granite is generated in this situation where oceanic crust is pulled apart, but where continents are pulled apart some of the older continental crust may be partly melted and rise as granitic magma. A good example of this can be seen on the east coast of Greenland which was ri ...
... Only a small amount of granite is generated in this situation where oceanic crust is pulled apart, but where continents are pulled apart some of the older continental crust may be partly melted and rise as granitic magma. A good example of this can be seen on the east coast of Greenland which was ri ...
Geological history of Earth
The geological history of Earth follows the major events in Earth's past based on the geologic time scale, a system of chronological measurement based on the study of the planet's rock layers (stratigraphy). Earth formed about 4.54 billion years ago by accretion from the solar nebula, a disk-shaped mass of dust and gas left over from the formation of the Sun, which also created the rest of the Solar System.Earth was initially molten due to extreme volcanism and frequent collisions with other bodies. Eventually, the outer layer of the planet cooled to form a solid crust when water began accumulating in the atmosphere. The Moon formed soon afterwards, possibly as the result of a Mars-sized object with about 10% of the Earth's mass impacting the planet in a glancing blow. Some of this object's mass merged with the Earth, significantly altering its internal composition, and a portion was ejected into space. Some of the material survived to form an orbiting moon. Outgassing and volcanic activity produced the primordial atmosphere. Condensing water vapor, augmented by ice delivered from comets, produced the oceans.As the surface continually reshaped itself over hundreds of millions of years, continents formed and broke apart. They migrated across the surface, occasionally combining to form a supercontinent. Roughly 750 million years ago, the earliest-known supercontinent Rodinia, began to break apart. The continents later recombined to form Pannotia, 600 to 540 million years ago, then finally Pangaea, which broke apart 180 million years ago.The present pattern of ice ages began about 40 million years ago, then intensified at the end of the Pliocene. The polar regions have since undergone repeated cycles of glaciation and thaw, repeating every 40,000–100,000 years. The last glacial period of the current ice age ended about 10,000 years ago.