Field guide to the geological evolution of the Maastrichtian
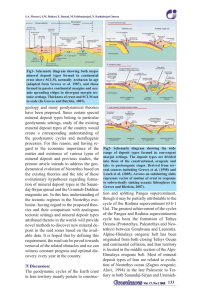
... largely divided the succession into alternating fossiliferous beds, which attracted great attention, and thick intervening clastics, volcaniclastics and igneous units, which were invariably undivided and attracted little or no interest. The fossiliferous, predominantly carbonate sediments were heavi ...
... largely divided the succession into alternating fossiliferous beds, which attracted great attention, and thick intervening clastics, volcaniclastics and igneous units, which were invariably undivided and attracted little or no interest. The fossiliferous, predominantly carbonate sediments were heavi ...
Lecture 6 - Mantle and Basalts
... contain melt; they ascend by “creep”. Adiabatic melting occurs when rising mantle does not cool along the geotherm, but instead it remains hot. This allows it to reach the mantle solidus that has a shallower slope on the P-T diagram (see diagram below). The melting is eutectic involving olivine, opx ...
... contain melt; they ascend by “creep”. Adiabatic melting occurs when rising mantle does not cool along the geotherm, but instead it remains hot. This allows it to reach the mantle solidus that has a shallower slope on the P-T diagram (see diagram below). The melting is eutectic involving olivine, opx ...
geologic map (scale 1 :250000) of the penokean orogen, central
... tectonically dismembered and reassembled sequences of volcanic and sedimentary rocks that are difficult to correlate with assurance from one structural panel to another. These greatly deformed rocks are unconformably overlain by less deformed sedimentary strata of the Animikie Group, which are inter ...
... tectonically dismembered and reassembled sequences of volcanic and sedimentary rocks that are difficult to correlate with assurance from one structural panel to another. These greatly deformed rocks are unconformably overlain by less deformed sedimentary strata of the Animikie Group, which are inter ...
Detrital geochronology and geochemistry of Cretaceous–Early
... The GHZ comprises amphibolite-grade metasedimentary and meta-igneous rocks of the Greater Himalayan sequence [32,34,36]. In much of Nepal, the Greater Himalayan sequence has a simple threemember tectonostratigraphy [24,35]. Formation I mainly consists of pelitic schist and paragneiss; Formation II i ...
... The GHZ comprises amphibolite-grade metasedimentary and meta-igneous rocks of the Greater Himalayan sequence [32,34,36]. In much of Nepal, the Greater Himalayan sequence has a simple threemember tectonostratigraphy [24,35]. Formation I mainly consists of pelitic schist and paragneiss; Formation II i ...
10. METAMORPHOSED SEDIMENTARY (VOLCANICLASTIC
... time. Modal contents of chlorite range from about 3% to nearly 70%. Chlorite fills interstices; is part of the fine-grained matrix; is the main constituent of most burrows; fills veins; and replaces primary feldspar crystals, glass(?), and ghost-like rock fragments (Pl. 1, Fig. 2). It is weakly bire ...
... time. Modal contents of chlorite range from about 3% to nearly 70%. Chlorite fills interstices; is part of the fine-grained matrix; is the main constituent of most burrows; fills veins; and replaces primary feldspar crystals, glass(?), and ghost-like rock fragments (Pl. 1, Fig. 2). It is weakly bire ...
the granulite belt of lapland and the belomorides
... the mobile belt. Allowing for their epicontinental nature, their early Proterozoic age (2.0—2.4 Ga) and for their deformation by the 1.9 Ga Karelian event, we suggest that the Jatulian formations belong to the Belomorides. We propose to re-interpret the Belomorian fold belt in terms of a Wilson cycl ...
... the mobile belt. Allowing for their epicontinental nature, their early Proterozoic age (2.0—2.4 Ga) and for their deformation by the 1.9 Ga Karelian event, we suggest that the Jatulian formations belong to the Belomorides. We propose to re-interpret the Belomorian fold belt in terms of a Wilson cycl ...
deep sea drilling in the northern indian ocean
... Ice streams reached the Antarctic seas as early as 40 Ma, but major ice-sheet formation on Antarctica apparently did not occur until some 25 m.y. ago. Northern hemisphere ice sheets did not begin to develop until sometime after 15 Ma, and major northern hemisphere continental glaciations did not sta ...
... Ice streams reached the Antarctic seas as early as 40 Ma, but major ice-sheet formation on Antarctica apparently did not occur until some 25 m.y. ago. Northern hemisphere ice sheets did not begin to develop until sometime after 15 Ma, and major northern hemisphere continental glaciations did not sta ...
geology and chromite deposits of the camaguey district camaguey
... of reef origin. For the most part they form small masses from a foot to a few dozen feet thick and a few hundred to 2,000 feet long; the largest mass, which forms Loma Yucatan, is several thousand feet long and appears to be several hundred feet thick. Many of the lenses are composed of gray to whit ...
... of reef origin. For the most part they form small masses from a foot to a few dozen feet thick and a few hundred to 2,000 feet long; the largest mass, which forms Loma Yucatan, is several thousand feet long and appears to be several hundred feet thick. Many of the lenses are composed of gray to whit ...
Geologic History of the Tucson Mountains Jan C. Rasmussen
... chemical oxidation (due to pyrite weathering) that created the acid necessary to oxidize many of the Morenci Assemblage porphyry copper deposits. This oxidation produced widespread supergene enrichment (mainly as chalcocite with attendant malachite, azurite, and chrysocolla) so that the lower grade ...
... chemical oxidation (due to pyrite weathering) that created the acid necessary to oxidize many of the Morenci Assemblage porphyry copper deposits. This oxidation produced widespread supergene enrichment (mainly as chalcocite with attendant malachite, azurite, and chrysocolla) so that the lower grade ...
DNR San Juan Islands Brandon
... San Juan-Cascade nappes (modified from Brandon and others, 1988; see Table 1 for further details). Each column represents a separate terrane with its name appearing below. The continuous portion of a column shows rock units that are connected by demonstrable strati graphic contacts. Breaks in a colum ...
... San Juan-Cascade nappes (modified from Brandon and others, 1988; see Table 1 for further details). Each column represents a separate terrane with its name appearing below. The continuous portion of a column shows rock units that are connected by demonstrable strati graphic contacts. Breaks in a colum ...
geologic trips to the Sea Ranch
... terraces were preserved as the land continued to be uplifted. The oldest terraces are the highest on the hillside. The meadow is the youngest terrace. Ten thousand years ago, at the end of the Wisconsin glacial episode, sea level was low and the shoreline was several miles west of its present positi ...
... terraces were preserved as the land continued to be uplifted. The oldest terraces are the highest on the hillside. The meadow is the youngest terrace. Ten thousand years ago, at the end of the Wisconsin glacial episode, sea level was low and the shoreline was several miles west of its present positi ...
Summary of Northeast Asia geodynamics and tectonics*
... continental-margin rocks, oceanic crust and overlying units, and oceanic mantle. Units are interpreted to have formed during tectonic juxtaposition in a zone of major thrusting of one lithosphere plate beneath another, generally in zones of thrusting along the margin of a continent or an island arc. ...
... continental-margin rocks, oceanic crust and overlying units, and oceanic mantle. Units are interpreted to have formed during tectonic juxtaposition in a zone of major thrusting of one lithosphere plate beneath another, generally in zones of thrusting along the margin of a continent or an island arc. ...
Geology SCarnarvon Regional - Offshore Petroleum Exploration
... depositional environment (Gorter et al, 1994). Preservation of this formation is largely restricted to the southern Gascoyne Sub-basin, whereas the Kopke Formation (type section in Yaringa 1), a package of coarsening upwards sandstone unit with minor dolomite and siltstone, extends further north to ...
... depositional environment (Gorter et al, 1994). Preservation of this formation is largely restricted to the southern Gascoyne Sub-basin, whereas the Kopke Formation (type section in Yaringa 1), a package of coarsening upwards sandstone unit with minor dolomite and siltstone, extends further north to ...
Post-Paleozoic activity
... southern and central Appalachians, which had undergone Late Paleozoic transpression, probably stood higher than the northern Appalachians, which had undergone transtension (Gates, oral communication, 1978). Accordingly, Carboniferous basins have not been reported from the Alleghanides, although mari ...
... southern and central Appalachians, which had undergone Late Paleozoic transpression, probably stood higher than the northern Appalachians, which had undergone transtension (Gates, oral communication, 1978). Accordingly, Carboniferous basins have not been reported from the Alleghanides, although mari ...
Vol. 17. No.1 2008
... include volcanogenic massive sulfide types Geodynamic Settings of the Mineral (Franklin et al., 2005) similar to Cyprus, Oman, and magmatic podiform chromite Deposits on the Sanandaj-Sirjan Zone deposits (±PGE) like those in Iran, Turkey and Urumieh-Dokhtar Arc The supercontinental cycle of Pangaea ...
... include volcanogenic massive sulfide types Geodynamic Settings of the Mineral (Franklin et al., 2005) similar to Cyprus, Oman, and magmatic podiform chromite Deposits on the Sanandaj-Sirjan Zone deposits (±PGE) like those in Iran, Turkey and Urumieh-Dokhtar Arc The supercontinental cycle of Pangaea ...
seismic survey - Mineral Resources Tasmania
... siltstone, shales, gravels, conglomerates and lignite beds. Volcanism was prevalent during the mid to late Tertiary, producing a variety of basalts. Matthews (1983) sub-divided the Tertiary stratigraphy as follows: a) Palaeocene to Eocene; clay sand and lignite b) Mid Eocene to Pliocene; basalts cla ...
... siltstone, shales, gravels, conglomerates and lignite beds. Volcanism was prevalent during the mid to late Tertiary, producing a variety of basalts. Matthews (1983) sub-divided the Tertiary stratigraphy as follows: a) Palaeocene to Eocene; clay sand and lignite b) Mid Eocene to Pliocene; basalts cla ...
Geology of the Gorny Altai subduction–accretion complex, southern
... plate tectonic framework since Dewey and Bird (1970). The former, also called Pacific-type (Matsuda and Uyeda, 1971) or Miyashiro-type (Maruyama, 1997), sis characterized by the formation of subduction–accretion complexes involving high-P/T metamorphic (HP) rocks, and extensive calc-alkaline magmatis ...
... plate tectonic framework since Dewey and Bird (1970). The former, also called Pacific-type (Matsuda and Uyeda, 1971) or Miyashiro-type (Maruyama, 1997), sis characterized by the formation of subduction–accretion complexes involving high-P/T metamorphic (HP) rocks, and extensive calc-alkaline magmatis ...
Mesozoic fill-sequences in Hefei Basin: Implication for Dabie
... 3 Basin-fill sequence and evolution It is found that the fill-sequences of Hefei basin show obviously distinct lithofacies, depositional architectures and regional geodynamics in the Jurassic and the late Jurassic-Cretaceous respectively, which may be divided by angular unconformities (fig. 4). 3.1 ...
... 3 Basin-fill sequence and evolution It is found that the fill-sequences of Hefei basin show obviously distinct lithofacies, depositional architectures and regional geodynamics in the Jurassic and the late Jurassic-Cretaceous respectively, which may be divided by angular unconformities (fig. 4). 3.1 ...
Cretaceous–early Tertiary arc and fore
... Eocene sediments reveal notable stratigraphical and petrological similarities to the Marianas fore-arc and the eastern Halmahera Basement Complex is interpreted as a pre-Oligocene fore-arc lacking an accretionary complex. There is some evidence that the pre-Oligocene volcanic arc behind this fore-ar ...
... Eocene sediments reveal notable stratigraphical and petrological similarities to the Marianas fore-arc and the eastern Halmahera Basement Complex is interpreted as a pre-Oligocene fore-arc lacking an accretionary complex. There is some evidence that the pre-Oligocene volcanic arc behind this fore-ar ...
Summary of Research Projects John W. Shervais Department of Geology Professor and Head
... One of the fundamental questions in the planetary evolution of Earth centers on when modern style plate tectonic processes, driven by the sinking of dense lithospheric plates, became the dominant mode of thermal convection and crustal deformation. This project examines rock assemblages in the Wasatc ...
... One of the fundamental questions in the planetary evolution of Earth centers on when modern style plate tectonic processes, driven by the sinking of dense lithospheric plates, became the dominant mode of thermal convection and crustal deformation. This project examines rock assemblages in the Wasatc ...
Physical Geography
... main theories. Both involve accretion, or the sticking together of molecules and particles. They have the same basic idea -- about 4.6 billion years ago, the Earth formed as particles collected within a giant disc of gas orbiting what would become our sun. Once the sun ignited, it blew all of the ex ...
... main theories. Both involve accretion, or the sticking together of molecules and particles. They have the same basic idea -- about 4.6 billion years ago, the Earth formed as particles collected within a giant disc of gas orbiting what would become our sun. Once the sun ignited, it blew all of the ex ...
A new look at the Altaids: A superorogenic complex in northern and
... by the Urals, on the south by the 'Intermediate Units' consisting of the Alay Microcontinent, the Tarim Block and south China carrying also the Manchuride Orogenic Belt and on the northeast by the Siberian Craton. Within this frame the superorogenic system evolved along two major arc systems, both i ...
... by the Urals, on the south by the 'Intermediate Units' consisting of the Alay Microcontinent, the Tarim Block and south China carrying also the Manchuride Orogenic Belt and on the northeast by the Siberian Craton. Within this frame the superorogenic system evolved along two major arc systems, both i ...
preview PDF only - California State University Stanislaus
... is far-traveled (1100 km) from 45 to 0 Ma and experiences 40° of large-scale rotation in a clockwise sense. This sense of rotation is contrary to the overall, post-Cretaceous counterclockwise rotations measured by Gose and Swartz (1977) and Gose (1985) in rocks from Honduras. In the Pacific-derived ...
... is far-traveled (1100 km) from 45 to 0 Ma and experiences 40° of large-scale rotation in a clockwise sense. This sense of rotation is contrary to the overall, post-Cretaceous counterclockwise rotations measured by Gose and Swartz (1977) and Gose (1985) in rocks from Honduras. In the Pacific-derived ...
early evolution of the North American Cordillera Baltican and
... Northwest Passage and southward propagation of subduction along western Laurentia. ...
... Northwest Passage and southward propagation of subduction along western Laurentia. ...
Geological history of Earth
The geological history of Earth follows the major events in Earth's past based on the geologic time scale, a system of chronological measurement based on the study of the planet's rock layers (stratigraphy). Earth formed about 4.54 billion years ago by accretion from the solar nebula, a disk-shaped mass of dust and gas left over from the formation of the Sun, which also created the rest of the Solar System.Earth was initially molten due to extreme volcanism and frequent collisions with other bodies. Eventually, the outer layer of the planet cooled to form a solid crust when water began accumulating in the atmosphere. The Moon formed soon afterwards, possibly as the result of a Mars-sized object with about 10% of the Earth's mass impacting the planet in a glancing blow. Some of this object's mass merged with the Earth, significantly altering its internal composition, and a portion was ejected into space. Some of the material survived to form an orbiting moon. Outgassing and volcanic activity produced the primordial atmosphere. Condensing water vapor, augmented by ice delivered from comets, produced the oceans.As the surface continually reshaped itself over hundreds of millions of years, continents formed and broke apart. They migrated across the surface, occasionally combining to form a supercontinent. Roughly 750 million years ago, the earliest-known supercontinent Rodinia, began to break apart. The continents later recombined to form Pannotia, 600 to 540 million years ago, then finally Pangaea, which broke apart 180 million years ago.The present pattern of ice ages began about 40 million years ago, then intensified at the end of the Pliocene. The polar regions have since undergone repeated cycles of glaciation and thaw, repeating every 40,000–100,000 years. The last glacial period of the current ice age ended about 10,000 years ago.