PEPTIDE BONDS AND POLYPEPTIDES OLIGOPEPTIDE
... •Fred Sanger sequenced the first protein in 1953: bovine insulin 1st Nobel, because it showed that: the sequence is precisely defined only L-amino acids are found they are linked by peptide bonds •thousands of proteins have now been sequenced each is unique •Why is the primary structure important? h ...
... •Fred Sanger sequenced the first protein in 1953: bovine insulin 1st Nobel, because it showed that: the sequence is precisely defined only L-amino acids are found they are linked by peptide bonds •thousands of proteins have now been sequenced each is unique •Why is the primary structure important? h ...
How does DNA determine the traits of organisms?
... How does DNA determine the traits of organisms? (A review of transcription and translation) Introduction In this assessment, you will examine the DNA sequence of a fictitious organism: the Snork! Snorks were discovered on the planet “Dee Enae” in a distant solar system. Snorks have only one chromoso ...
... How does DNA determine the traits of organisms? (A review of transcription and translation) Introduction In this assessment, you will examine the DNA sequence of a fictitious organism: the Snork! Snorks were discovered on the planet “Dee Enae” in a distant solar system. Snorks have only one chromoso ...
Animation Script for Translation
... 1. In translation, the cell uses an mRNA strand as a template to assemble proteins. The cell has just transcribed this mRNA strand from its DNA, and it now translates the mRNA’s nucleotide sequence into a chain of amino acids. This chain, called a polypeptide, forms the basic structure of a protein. ...
... 1. In translation, the cell uses an mRNA strand as a template to assemble proteins. The cell has just transcribed this mRNA strand from its DNA, and it now translates the mRNA’s nucleotide sequence into a chain of amino acids. This chain, called a polypeptide, forms the basic structure of a protein. ...
Nucleosides, Nucleotides, and Nucleic Acids
... are joined together by phosphodiester linkages with the aid of DNA polymerase. Each new strand grows in its 59n39 direction. ...
... are joined together by phosphodiester linkages with the aid of DNA polymerase. Each new strand grows in its 59n39 direction. ...
Genetics
... 8. A rod-shaped structure of tightly coiled DNA found in the cell nucleus of plants and animals. 11. A combination of atoms, and also the basic building-block of DNA and RNA. Each molecule has its own shape and attaches only to certain other molecules to form the DNA helix. 12. A winding shape, simi ...
... 8. A rod-shaped structure of tightly coiled DNA found in the cell nucleus of plants and animals. 11. A combination of atoms, and also the basic building-block of DNA and RNA. Each molecule has its own shape and attaches only to certain other molecules to form the DNA helix. 12. A winding shape, simi ...
Lecture 7
... Although insects have shorter generation times that mammals and many more numbers of replication, number of mutations appear to be independent of the number of generations but dependent upon time ...
... Although insects have shorter generation times that mammals and many more numbers of replication, number of mutations appear to be independent of the number of generations but dependent upon time ...
UTACCEL 2010
... By understanding the function of a gene in one organism, scientists can get an idea of what function that gene may perform in a more complex organism such as humans. The knowledge gained can then be applied to various fields such as medicine, biological engineering and forensics. ...
... By understanding the function of a gene in one organism, scientists can get an idea of what function that gene may perform in a more complex organism such as humans. The knowledge gained can then be applied to various fields such as medicine, biological engineering and forensics. ...
Protein Synthesis
... to a ribosome. Translation begins at AUG, the start codon. Each transfer RNA has an anticodon whose bases are complementary to a codon on the mRNA strand. The ribosome positions the start codon to attract its anticodon, which is part of the tRNA that binds methionine. The ribosome also binds the nex ...
... to a ribosome. Translation begins at AUG, the start codon. Each transfer RNA has an anticodon whose bases are complementary to a codon on the mRNA strand. The ribosome positions the start codon to attract its anticodon, which is part of the tRNA that binds methionine. The ribosome also binds the nex ...
How does DNA store and transmit cell information?
... the same as mRNA except the Ts are replaced with Us ...
... the same as mRNA except the Ts are replaced with Us ...
Protein Synthesis – Level 1
... 2. If the underlined portions represent introns, what will the mature mRNA be/read? 3. Prior to leaving the nucleus, what will be added to the mature mRNA? What will the mRNA look like after this occurs? What is the purpose of this processing? ...
... 2. If the underlined portions represent introns, what will the mature mRNA be/read? 3. Prior to leaving the nucleus, what will be added to the mature mRNA? What will the mRNA look like after this occurs? What is the purpose of this processing? ...
December 7, 2010 - Ms. Chambers' Biology
... Why was Gatorade used instead of water in yesterday’s lab activity? What role did the components of the Gatorade play in extracting your DNA? How could extracting DNA from human cells be useful in today’s society? ...
... Why was Gatorade used instead of water in yesterday’s lab activity? What role did the components of the Gatorade play in extracting your DNA? How could extracting DNA from human cells be useful in today’s society? ...
Chapter 16 - HCC Learning Web
... mRNA is further processed before leaving the nucleus. III. Eukaryotic cells modify RNA after transcription. A. Alteration of mRNA Ends Fig. 17.10 Page 343 At the 5' end it is given a cap and at the 3' end a poly-A tail. B. Split Genes and RNA Splicing The noncoding segments of nucleic acid that lie ...
... mRNA is further processed before leaving the nucleus. III. Eukaryotic cells modify RNA after transcription. A. Alteration of mRNA Ends Fig. 17.10 Page 343 At the 5' end it is given a cap and at the 3' end a poly-A tail. B. Split Genes and RNA Splicing The noncoding segments of nucleic acid that lie ...
Observations and Analysis of Snork DNA
... o Start a conversion about errors in DNA? Good or bad? o PPT on Mutations ...
... o Start a conversion about errors in DNA? Good or bad? o PPT on Mutations ...
R N A & PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
... The decoding of an mRNA message into a polypeptide chain (protein) is called translation, which takes place on ribosomes Amino Acids are transported by ribosomes & tRNA molecules, which have specific regions that bond to AA The loop attachment has a sequence of 3 nucleotides called anticodons. The t ...
... The decoding of an mRNA message into a polypeptide chain (protein) is called translation, which takes place on ribosomes Amino Acids are transported by ribosomes & tRNA molecules, which have specific regions that bond to AA The loop attachment has a sequence of 3 nucleotides called anticodons. The t ...
Protein Digestion and Absorption
... Proteins are sequences of amino acids (AA) linked by peptide bonds. There are twenty amino acids of which nine are essential and eleven are non-essential. Essential amino acids include phenylalanine, valine, threonine, tryptophan, isoleucine, methionine, leucine, lysine, and histidine. These AA are ...
... Proteins are sequences of amino acids (AA) linked by peptide bonds. There are twenty amino acids of which nine are essential and eleven are non-essential. Essential amino acids include phenylalanine, valine, threonine, tryptophan, isoleucine, methionine, leucine, lysine, and histidine. These AA are ...
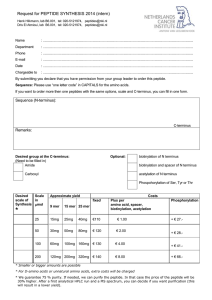
Scale - Netherlands Cancer Institute
... By submitting you declare that you have permission from your group leader to order this peptide. Sequence: Please use “one letter code” in CAPITALS for the amino acids. If you want to order more then one peptides with the same options, scale and C-terminus, you can fill in one form. ...
... By submitting you declare that you have permission from your group leader to order this peptide. Sequence: Please use “one letter code” in CAPITALS for the amino acids. If you want to order more then one peptides with the same options, scale and C-terminus, you can fill in one form. ...
8 th Grade Genes and Survival Test – Study Guide
... 8th Grade Genes and Survival Test – Study Guide There is test on ________________________ that covers all of the concepts on this study guide. This completed guide is due on the day of the test or you receive a zero on it! Please use your notes and textbook to locate definitions and answers for all ...
... 8th Grade Genes and Survival Test – Study Guide There is test on ________________________ that covers all of the concepts on this study guide. This completed guide is due on the day of the test or you receive a zero on it! Please use your notes and textbook to locate definitions and answers for all ...
File
... • Takes place in the nucleus. • A specific gene of DNA is transcribed into mRNA by RNA polymerase. • The instructions for making a protein are transferred from the nucleus to the ribosome. ...
... • Takes place in the nucleus. • A specific gene of DNA is transcribed into mRNA by RNA polymerase. • The instructions for making a protein are transferred from the nucleus to the ribosome. ...
Genetics Unit Test
... d. amino acid. 27. In what type of mutation is one base left out? a. substitution c. insertion b. deletion d. cell 28. DNA is made of subunits called what? a. proteins c. traits b. deoxyribonucleic acids d. nucleotides 29. Nucleotides are made of a sugar, a phosphate, and a a. base. c. gene. b. prot ...
... d. amino acid. 27. In what type of mutation is one base left out? a. substitution c. insertion b. deletion d. cell 28. DNA is made of subunits called what? a. proteins c. traits b. deoxyribonucleic acids d. nucleotides 29. Nucleotides are made of a sugar, a phosphate, and a a. base. c. gene. b. prot ...
DNA Keychains: Spell Your Initials Using the Genetic Code!!!!! This
... 2. If your last bead was a sugar, then you will need to add a phosphate bead. Add a phosphate bead to each strand. Make sure to thread BOTH wires through these beads. 3. If your l ...
... 2. If your last bead was a sugar, then you will need to add a phosphate bead. Add a phosphate bead to each strand. Make sure to thread BOTH wires through these beads. 3. If your l ...
Mutations Worksheet
... 6. In order to reduce the number of mutations drastically organisms have enzymes that proofread new strands of DNA and RNA and fix mutations. Mutation rates vary depending on species from mutation rates as low as 1 mistake per 100 million to 1 billion nucleotides, mostly in bacteria, and as high as ...
... 6. In order to reduce the number of mutations drastically organisms have enzymes that proofread new strands of DNA and RNA and fix mutations. Mutation rates vary depending on species from mutation rates as low as 1 mistake per 100 million to 1 billion nucleotides, mostly in bacteria, and as high as ...
Cell Building Blocks
... The secondary structure is formed by hydrogen bonds between amino acids. The polypeptide can coil into a helix or form a pleated sheet. The tertiary structure refers to the three-dimensional folding of the helix or pleated sheet. Quaternary The quaternary structure refers to the spatial relationship ...
... The secondary structure is formed by hydrogen bonds between amino acids. The polypeptide can coil into a helix or form a pleated sheet. The tertiary structure refers to the three-dimensional folding of the helix or pleated sheet. Quaternary The quaternary structure refers to the spatial relationship ...
Mr. David Cortens In Vivo Synthesis of ?Click? Functionalized
... antigen binding domain is reduced to a single variable domain, the VHH. The cloned and isolated VHH domain, or Nanobody(Nb), is a very stable polypeptide and is the smallest intact antigen binding fragment known (5). They are coded by a single gene, which makes them easy to manipulate. The fact that ...
... antigen binding domain is reduced to a single variable domain, the VHH. The cloned and isolated VHH domain, or Nanobody(Nb), is a very stable polypeptide and is the smallest intact antigen binding fragment known (5). They are coded by a single gene, which makes them easy to manipulate. The fact that ...
Genetic code

The genetic code is the set of rules by which information encoded within genetic material (DNA or mRNA sequences) is translated into proteins by living cells. Biological decoding is accomplished by the ribosome, which links amino acids in an order specified by mRNA, using transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules to carry amino acids and to read the mRNA three nucleotides at a time. The genetic code is highly similar among all organisms and can be expressed in a simple table with 64 entries.The code defines how sequences of these nucleotide triplets, called codons, specify which amino acid will be added next during protein synthesis. With some exceptions, a three-nucleotide codon in a nucleic acid sequence specifies a single amino acid. Because the vast majority of genes are encoded with exactly the same code (see the RNA codon table), this particular code is often referred to as the canonical or standard genetic code, or simply the genetic code, though in fact some variant codes have evolved. For example, protein synthesis in human mitochondria relies on a genetic code that differs from the standard genetic code.While the genetic code determines the protein sequence for a given coding region, other genomic regions can influence when and where these proteins are produced.