maize silage sampling and interpretation of analysis
... board, divide the sample at right angles into four piles to achieve a final sample size of 0.5kg. Place the entire 0.5 kg sample into a clean plastic bag and ensure as much of the air is removed, as possible. For further information see the Forage Analytical Assurance Group website - http://www.faag ...
... board, divide the sample at right angles into four piles to achieve a final sample size of 0.5kg. Place the entire 0.5 kg sample into a clean plastic bag and ensure as much of the air is removed, as possible. For further information see the Forage Analytical Assurance Group website - http://www.faag ...
Cloning and Sequence Analysis of the xylL Gene Responsible for
... pCSP21 digested with ClaI was introduced into the polyclonal region of pBluescript II SK(+) vector to make pRES3. The subclones of pRES301, pRES401, and pRES403 were further constructed by digestion of the pCSP21 with various enzymes. The physical maps of those clones are shown in Fig. 2. Editing an ...
... pCSP21 digested with ClaI was introduced into the polyclonal region of pBluescript II SK(+) vector to make pRES3. The subclones of pRES301, pRES401, and pRES403 were further constructed by digestion of the pCSP21 with various enzymes. The physical maps of those clones are shown in Fig. 2. Editing an ...
Molecular Beacon Product Sheet
... prepare chimeric 2‟-F-RNA/DNA phosphorothioate oligonucleotides which exhibit enhanced binding to the RNA target, are substrates for RNase H, and are highly nuclease resistant (1). Fluorine has an interesting combination of properties, combining electronegativity similar to a hydroxyl group with siz ...
... prepare chimeric 2‟-F-RNA/DNA phosphorothioate oligonucleotides which exhibit enhanced binding to the RNA target, are substrates for RNase H, and are highly nuclease resistant (1). Fluorine has an interesting combination of properties, combining electronegativity similar to a hydroxyl group with siz ...
Calculating Nucleic Acid or Protein Concentration
... upon the particular amino acid concentration of that protein. In addition, buffer type, ionic strength and ...
... upon the particular amino acid concentration of that protein. In addition, buffer type, ionic strength and ...
Regional Differences in Protein Synthesis within the Lens of
... Utilization of 3SS-methionine by cells of the rat lens was studied by combined autoradiographic and chemical techniques. Part of the methionine teas converted to cysteine, glutathione, and taurine. Protein synthesis was essentially restricted to the lens cortex, and appeared to be largely attributab ...
... Utilization of 3SS-methionine by cells of the rat lens was studied by combined autoradiographic and chemical techniques. Part of the methionine teas converted to cysteine, glutathione, and taurine. Protein synthesis was essentially restricted to the lens cortex, and appeared to be largely attributab ...
Predicting Protein Stability Changes upon Mutation Using Database
... energetic criteria obviously involve hydrophobicity. In the few studies analysing mutations of solvent accessible residues, the stability changes are correlated with statistical propensities of single amino acids to be in a-helices or b-strands (MunÄoz & Serrano, 1994), or with distance-dependent re ...
... energetic criteria obviously involve hydrophobicity. In the few studies analysing mutations of solvent accessible residues, the stability changes are correlated with statistical propensities of single amino acids to be in a-helices or b-strands (MunÄoz & Serrano, 1994), or with distance-dependent re ...
Fatty Acid Catabolism
... will yield more energy than oxidized forms of carbon. (2) Because fatty acids are lipids, they are hydrophobic. They do not need to be solvated in contrast to carbohydrates such as glycogen. Dehydrated glycogen will absorb twice its dry weight of water when it is rehydrated. The long greasy tails of ...
... will yield more energy than oxidized forms of carbon. (2) Because fatty acids are lipids, they are hydrophobic. They do not need to be solvated in contrast to carbohydrates such as glycogen. Dehydrated glycogen will absorb twice its dry weight of water when it is rehydrated. The long greasy tails of ...
Characterization of Rice Anthranilate Synthase
... of AS ␣-subunits of dicotyledonous plants and microorganisms (Fig. 1). The NH2-terminal regions of OASA1 and OASA2 exhibited almost no sequence similarity to each other. Likewise, the NH2-terminal sequences of other plant homologs are highly variable and are predicted to contain plastid-localization ...
... of AS ␣-subunits of dicotyledonous plants and microorganisms (Fig. 1). The NH2-terminal regions of OASA1 and OASA2 exhibited almost no sequence similarity to each other. Likewise, the NH2-terminal sequences of other plant homologs are highly variable and are predicted to contain plastid-localization ...
... Protein patterns of collagens under reducing condition are shown in Fig. 1. Differences in protein patterns of different collagens were observed. The result revealed that PSC comprised β and α chains as the major constituents. With respect to PSC, It possibly contained both (α1)3 homotrimer and (α1) ...
Лекция 2. Структура и функция белка
... an amino group bonded to the same carbon atom (the a carbon) (Fig. 5-2). They differ from each other in their side chains, or R groups, which vary in structure, size, and electric charge, and influence the solubility of amino acids in water. When the R group contains additional carbons in a chain, t ...
... an amino group bonded to the same carbon atom (the a carbon) (Fig. 5-2). They differ from each other in their side chains, or R groups, which vary in structure, size, and electric charge, and influence the solubility of amino acids in water. When the R group contains additional carbons in a chain, t ...
[7] Semisynthesis of Proteins Containing Selenocysteine
... By ROBERT J. HONDAL and RONALD T. RAINEs ...
... By ROBERT J. HONDAL and RONALD T. RAINEs ...
Kein Folientitel
... varieties; (b) essentially biological processes for the production of plants or animals. 2. Inventions which concern plants or animals shall be patentable if the technical feasibility of the invention is not confined to a particular plant or animal variety. 3. Paragraph 1(b) shall be without prejudi ...
... varieties; (b) essentially biological processes for the production of plants or animals. 2. Inventions which concern plants or animals shall be patentable if the technical feasibility of the invention is not confined to a particular plant or animal variety. 3. Paragraph 1(b) shall be without prejudi ...
Dynamic Programming
... The first four sequences possibly derive from closely related species and the last three from three more distant species. Since A occurs with high frequency in the first four sequences, the observed number of pairings of A with A will be higher than is appropriate if we are comparing more distantly ...
... The first four sequences possibly derive from closely related species and the last three from three more distant species. Since A occurs with high frequency in the first four sequences, the observed number of pairings of A with A will be higher than is appropriate if we are comparing more distantly ...
Phenylketonuria Phenylketonuria
... penetrance is the likelihood that a given gene will have any expression at all Monogenic disorders are detrmined by a single mutant gene (aka. Mendelian disorders)- eg. Huntingtons, cystic fibrosis Mendelian disorders can be either autosomal recessive, autosomal dominant or X_linked (an example of x ...
... penetrance is the likelihood that a given gene will have any expression at all Monogenic disorders are detrmined by a single mutant gene (aka. Mendelian disorders)- eg. Huntingtons, cystic fibrosis Mendelian disorders can be either autosomal recessive, autosomal dominant or X_linked (an example of x ...
Pdf - Text of NPTEL IIT Video Lectures
... occurs in all living organisms to transmit the genetic material from one to the next generation. The two copy of nucleic acid are synthesized from one parent molecule during this process of cell division in such a manner, that each daughter cell obtains one copy of genetic material. Now, when we loo ...
... occurs in all living organisms to transmit the genetic material from one to the next generation. The two copy of nucleic acid are synthesized from one parent molecule during this process of cell division in such a manner, that each daughter cell obtains one copy of genetic material. Now, when we loo ...
Molecular Evolution of Functional Nucleic Acids
... similar to those of protein enzymes and antibodies, respectively, though functional nucleic acids with activity superior to the corresponding protein have not been reported yet. Thus far, various RNA/DNA enzymes were reported, including the enzyme that catalyzes the isomerization of a bridged biphen ...
... similar to those of protein enzymes and antibodies, respectively, though functional nucleic acids with activity superior to the corresponding protein have not been reported yet. Thus far, various RNA/DNA enzymes were reported, including the enzyme that catalyzes the isomerization of a bridged biphen ...
Bioinformatics Research and Resources at the University of
... Importance of mixed protocols, such as Rosetta by D. Baker and colleagues (more when Monte Carlo protocols for global optimization are introduced) ...
... Importance of mixed protocols, such as Rosetta by D. Baker and colleagues (more when Monte Carlo protocols for global optimization are introduced) ...
History and Philosophy of Science
... BLAST differs from many of the informatics tools that we have considered in the course. Essentially it finds a sequence’s nearest neighbors within a database with minimal concern for the content. Unlike discovery or analysis tools, BLAST gathers information and leaves the interpretation to the user. ...
... BLAST differs from many of the informatics tools that we have considered in the course. Essentially it finds a sequence’s nearest neighbors within a database with minimal concern for the content. Unlike discovery or analysis tools, BLAST gathers information and leaves the interpretation to the user. ...
NEW YORK STATE MEDICAID PROGRAM LABORATORY
... detects multiple drug classes, should be billed using code 80100. Each step in the sequential development of a chromatograph is NOT considered a separate procedure. When an analytical condition, e.g., column temperature or flow rate, is changed such that additional controls must be run, subsequent a ...
... detects multiple drug classes, should be billed using code 80100. Each step in the sequential development of a chromatograph is NOT considered a separate procedure. When an analytical condition, e.g., column temperature or flow rate, is changed such that additional controls must be run, subsequent a ...
The f ructokinase f rom Rhizobium leguminosarum
... isolated on a 2 4 kb BamHl fragment from the cosmid pLA72 by complementation analysis of the Tn5-induced frk mutant BAL79, and confirmed by hybridization analysis. The nucleotide sequence of the frk gene was found to contain an open reading frame consisting of 978 bp encoding 326 amino acids, which ...
... isolated on a 2 4 kb BamHl fragment from the cosmid pLA72 by complementation analysis of the Tn5-induced frk mutant BAL79, and confirmed by hybridization analysis. The nucleotide sequence of the frk gene was found to contain an open reading frame consisting of 978 bp encoding 326 amino acids, which ...
Sequence Alignment
... lengths. Amino acid substitution matrices will turn match lengths into alignment scores (S). More commonly l = ln(1/p) is used. Number of longest run HSP will be estimated E = Kmne-lS How good a sequence score is evaluated based on how many HSPs (i.e. E value) one would expect for that score. ...
... lengths. Amino acid substitution matrices will turn match lengths into alignment scores (S). More commonly l = ln(1/p) is used. Number of longest run HSP will be estimated E = Kmne-lS How good a sequence score is evaluated based on how many HSPs (i.e. E value) one would expect for that score. ...
Temperature, pressure, and electrochemical
... the composition of proteomes in organisms adapted to different environments. Patterns in the compositions of proteomes that support life in different parts of the biosphere have received considerable attention in recent years (Elser et al., 2000; Gasch et al., 2000; Fukuchi and Nishikawa, 2001; Krei ...
... the composition of proteomes in organisms adapted to different environments. Patterns in the compositions of proteomes that support life in different parts of the biosphere have received considerable attention in recent years (Elser et al., 2000; Gasch et al., 2000; Fukuchi and Nishikawa, 2001; Krei ...
Characterisation of the diol dehydratase pdu operon of Lactobacillus
... the degrees of homologies observed with other dehydratases, the molecular mass deduced from the ORFs as well as the genetic environment of these genes showed that this protein is rather a diol dehydratase than a glycerol dehydratase. Therefore, the name previously used to design the gene, dha [10], ...
... the degrees of homologies observed with other dehydratases, the molecular mass deduced from the ORFs as well as the genetic environment of these genes showed that this protein is rather a diol dehydratase than a glycerol dehydratase. Therefore, the name previously used to design the gene, dha [10], ...
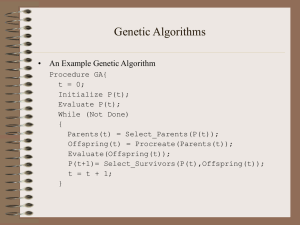
Genetic Algorithms
... • Crossover is usually the primary operator with mutation serving only as a mechanism to introduce diversity in the population. • However, when designing a GA to solve a problem it is not uncommon that one will have to develop unique crossover and mutation operators that take advantage of the struct ...
... • Crossover is usually the primary operator with mutation serving only as a mechanism to introduce diversity in the population. • However, when designing a GA to solve a problem it is not uncommon that one will have to develop unique crossover and mutation operators that take advantage of the struct ...
Genetic code

The genetic code is the set of rules by which information encoded within genetic material (DNA or mRNA sequences) is translated into proteins by living cells. Biological decoding is accomplished by the ribosome, which links amino acids in an order specified by mRNA, using transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules to carry amino acids and to read the mRNA three nucleotides at a time. The genetic code is highly similar among all organisms and can be expressed in a simple table with 64 entries.The code defines how sequences of these nucleotide triplets, called codons, specify which amino acid will be added next during protein synthesis. With some exceptions, a three-nucleotide codon in a nucleic acid sequence specifies a single amino acid. Because the vast majority of genes are encoded with exactly the same code (see the RNA codon table), this particular code is often referred to as the canonical or standard genetic code, or simply the genetic code, though in fact some variant codes have evolved. For example, protein synthesis in human mitochondria relies on a genetic code that differs from the standard genetic code.While the genetic code determines the protein sequence for a given coding region, other genomic regions can influence when and where these proteins are produced.










![[7] Semisynthesis of Proteins Containing Selenocysteine](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/004768810_1-d08ecd7536246bbf8b4baa16bb630c93-300x300.png)