Review over DNA, RNA, proteins, viruses, bacteria, DNA technology
... ii. Replication requires DNA polymerase plus many other essential cellular enzymes, occurs bi-directionally, and differs in the production of the leading and lagging strands. LO 3.3 The student is able to describe representations and models that illustrate how genetic information is copied for ...
... ii. Replication requires DNA polymerase plus many other essential cellular enzymes, occurs bi-directionally, and differs in the production of the leading and lagging strands. LO 3.3 The student is able to describe representations and models that illustrate how genetic information is copied for ...
... f) promoter: Binds RNA polymerase, begins mRNA production. g) antibiotic resistance gene: Bacteria with the plasmid will be resistant to the antibiotic, allowing selection for those bacterial that contain the plasmid. h) origin of replication. Allows plasmid to be replicated in bacteria. iv) Provide ...
Recombinant thrombin receptor and related pharmaceuticals
... When activated as a measure of thrombosis by measuring the proposed model of the in situ receptor is shoWn in FIG. 2. amount of an antibody or fragment bound to the cleaved Referring again to FIG. 1, the thrombin-catalyZed cleav activation peptide, Wherein an amount of the cleaved acti age site is r ...
... When activated as a measure of thrombosis by measuring the proposed model of the in situ receptor is shoWn in FIG. 2. amount of an antibody or fragment bound to the cleaved Referring again to FIG. 1, the thrombin-catalyZed cleav activation peptide, Wherein an amount of the cleaved acti age site is r ...
"Evolution of Hemoglobin in Primates," in Evolving Genes and Proteins
... the referents, we find a relatively large number of amino -acid substitutions in the hemoglobins of the Primates during their long evolutionary history. This implies a large number of point mutations. The amino acid substitutions at many positions in the sequences are considered chemically equivalen ...
... the referents, we find a relatively large number of amino -acid substitutions in the hemoglobins of the Primates during their long evolutionary history. This implies a large number of point mutations. The amino acid substitutions at many positions in the sequences are considered chemically equivalen ...
Prokaryotic orthologues of mitochondrial alternative oxidase and plastid terminal oxidase
... of the membrane-bound diiron carboxylate group of proteins. AOX is a ubiquinol oxidase present in all higher plants, as well as some algae, fungi, and protists. It may serve to dampen reactive oxygen species generation by the respiratory electron transport chain. PTOX is a plastoquinol oxidase in pl ...
... of the membrane-bound diiron carboxylate group of proteins. AOX is a ubiquinol oxidase present in all higher plants, as well as some algae, fungi, and protists. It may serve to dampen reactive oxygen species generation by the respiratory electron transport chain. PTOX is a plastoquinol oxidase in pl ...
The Effect of Antibiotics on Synthesis of Mucopeptide
... Hancock (1960) modified by including a wash in water after treatment with hot trichloroacetic acid, TCA (otherwise the trypsin was inactivated) and by raising the concentration of trypsin to ~oopgfml.The mucopeptide residue was finally washed in water to remove trypsin and hydrolysis products. Walls ...
... Hancock (1960) modified by including a wash in water after treatment with hot trichloroacetic acid, TCA (otherwise the trypsin was inactivated) and by raising the concentration of trypsin to ~oopgfml.The mucopeptide residue was finally washed in water to remove trypsin and hydrolysis products. Walls ...
Regulation of the Escherichia coli Tryptophan Operon by Early
... I Taken in part from a thesis submitted to Marquette University by W.A.H. in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the Ph.D. degree. ...
... I Taken in part from a thesis submitted to Marquette University by W.A.H. in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the Ph.D. degree. ...
Unsaturated Fatty Acids, Desaturases, and Human Health
... FADS2AT1 contains only three histidine boxes without cytochrome b5 domain. This structure suggested that the role of the alternative transcript would be associated with the desaturation of nonmethylene interrupted PUFA.35 The seven alternative transcripts of FADS3 exhibited a variety of structural a ...
... FADS2AT1 contains only three histidine boxes without cytochrome b5 domain. This structure suggested that the role of the alternative transcript would be associated with the desaturation of nonmethylene interrupted PUFA.35 The seven alternative transcripts of FADS3 exhibited a variety of structural a ...
Control of Growth and of the Nuclear Division Cycle in Neurospora
... zoopfii (126), and in the slime mold Physarium polycephalum (124). Many data are also available on the yeast S. cerevisiae. Two groups of workers (19, 185) have shown that RNA per cell (or the RNA/DNA ratio) varies with the growth rate in batch cultures, although in a nonlinear fashion, and less sha ...
... zoopfii (126), and in the slime mold Physarium polycephalum (124). Many data are also available on the yeast S. cerevisiae. Two groups of workers (19, 185) have shown that RNA per cell (or the RNA/DNA ratio) varies with the growth rate in batch cultures, although in a nonlinear fashion, and less sha ...
Antioxidant activities of dithiol alpha
... alpha-lipoic acid has been shown to increase ATP production due to its role in the oxidation of pyruvate and alpha-ketoglutarate in the mitochondria. Alpha-lipoic acid administration has been shown to be effective in preventing pathology in various experimental models in which reactive oxygen specie ...
... alpha-lipoic acid has been shown to increase ATP production due to its role in the oxidation of pyruvate and alpha-ketoglutarate in the mitochondria. Alpha-lipoic acid administration has been shown to be effective in preventing pathology in various experimental models in which reactive oxygen specie ...
biomolecules Feb 16 17.notebook
... Polypeptides are polymers of amino acids joined by peptide bonds. Peptide bonds are polar covalent bonds, allowing hydrogen bonding between amino acids. This influences the three dimensional shape of proteins. ...
... Polypeptides are polymers of amino acids joined by peptide bonds. Peptide bonds are polar covalent bonds, allowing hydrogen bonding between amino acids. This influences the three dimensional shape of proteins. ...
BIOSYNTHESIS OF AMINO ACIDS, NUCLEOTIDES, AND
... tetramer with two copies of two different subunits, contains both iron and molybdenum; its redox centers have a total of 2 Mo, 32 Fe, and 30 S per tetramer. About half of the iron and sulfur is present as two bridged pairs of 4Fe-4S centers called P clusters; the remainder is present as part of a no ...
... tetramer with two copies of two different subunits, contains both iron and molybdenum; its redox centers have a total of 2 Mo, 32 Fe, and 30 S per tetramer. About half of the iron and sulfur is present as two bridged pairs of 4Fe-4S centers called P clusters; the remainder is present as part of a no ...
The Role of the Krebs Cycle in Conjugation in
... azide and to bacteriophages), genetic analysis showed that these unselected markers were linked to one another as well as to the selected, auxotrophic markers (Lederberg, 1947). Despite this continuity of linkage, however, the genetic data were inconsistent with a completely linear arrangement of th ...
... azide and to bacteriophages), genetic analysis showed that these unselected markers were linked to one another as well as to the selected, auxotrophic markers (Lederberg, 1947). Despite this continuity of linkage, however, the genetic data were inconsistent with a completely linear arrangement of th ...
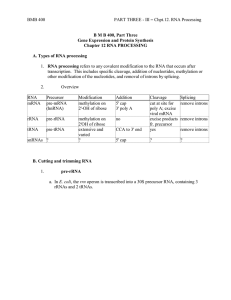
Chpt12_RNAProcessing.doc
... cleave a particular mRNA, thereby turning off expression of a particular gene. If over-expression or ectopic expression of a defined gene were the cause of some pathology (e.g. some form of cancer), then reducing its expression could have therapeutic value. Other RNAs possibly involved in catalysis, ...
... cleave a particular mRNA, thereby turning off expression of a particular gene. If over-expression or ectopic expression of a defined gene were the cause of some pathology (e.g. some form of cancer), then reducing its expression could have therapeutic value. Other RNAs possibly involved in catalysis, ...
Identification of a novel duplication in the APC gene using multiple
... Amsterdam, Netherlands) contains 20 paired probes from the APC region, to examine two fragments of the promoter region, 50 untranslated mRNA region and coding exons of the APC gene; the last exon is divided into three fragments (start, middle, end). Two probes for the APC wild-type sequence at mutat ...
... Amsterdam, Netherlands) contains 20 paired probes from the APC region, to examine two fragments of the promoter region, 50 untranslated mRNA region and coding exons of the APC gene; the last exon is divided into three fragments (start, middle, end). Two probes for the APC wild-type sequence at mutat ...
Differential Regulation of a-Lactalbumin and
... gland on various days of pregnancy and lactation. Chart 8 pups during lactation; casein messenger levels are dimin shows total protein synthesized as a function of the pg of ished (Chart 9A). When a-lactalbumin mRNA activity was measured at RNA added to the translation system. It is apparent from th ...
... gland on various days of pregnancy and lactation. Chart 8 pups during lactation; casein messenger levels are dimin shows total protein synthesized as a function of the pg of ished (Chart 9A). When a-lactalbumin mRNA activity was measured at RNA added to the translation system. It is apparent from th ...
The Role of the Krebs Cycle in Conjugation in
... azide and to bacteriophages), genetic analysis showed that these unselected markers were linked to one another as well as to the selected, auxotrophic markers (Lederberg, 1947). Despite this continuity of linkage, however, the genetic data were inconsistent with a completely linear arrangement of th ...
... azide and to bacteriophages), genetic analysis showed that these unselected markers were linked to one another as well as to the selected, auxotrophic markers (Lederberg, 1947). Despite this continuity of linkage, however, the genetic data were inconsistent with a completely linear arrangement of th ...
Review Molecular Biology in Arteriosclerosis Research
... clone isolated.45 In this case, the cDNA was prepared from highly purified apo II mRNA, thereby simplifying the identification of the cDNA clone. The apo II cDNA clone was also identified in unfractionated liver cDNA libraries by hybridization with a kinetically fractionated cDNA probe6 and by a plu ...
... clone isolated.45 In this case, the cDNA was prepared from highly purified apo II mRNA, thereby simplifying the identification of the cDNA clone. The apo II cDNA clone was also identified in unfractionated liver cDNA libraries by hybridization with a kinetically fractionated cDNA probe6 and by a plu ...
The Process of Translation
... The Genetic Code Codons are written in terms of their base sequence in mRNA. Degeneracy allows for a certain amount of change, or mutation, in the DNA without affecting the protein ultimately produced. ...
... The Genetic Code Codons are written in terms of their base sequence in mRNA. Degeneracy allows for a certain amount of change, or mutation, in the DNA without affecting the protein ultimately produced. ...
Distributed Atomic Polarizabilities of Amino Acids and their
... useful because functional groups represent the way in which chemists reduce molecules for synthetic and engineering purposes. In fact, a given molecular property may especially originate from one particular group. In this respect, the transferability of atomic and functional group properties is a ke ...
... useful because functional groups represent the way in which chemists reduce molecules for synthetic and engineering purposes. In fact, a given molecular property may especially originate from one particular group. In this respect, the transferability of atomic and functional group properties is a ke ...
We have, using a unique data base, successfully genotyped
... Most of the presumably recombinant haplotypes appear to be ancient crossovers that became common and not to be common because of frequent ongoing recombination. The implication is that since humans expanded out of Africa each extant copy of each of the 17 haplotypes has a history of evolving by desc ...
... Most of the presumably recombinant haplotypes appear to be ancient crossovers that became common and not to be common because of frequent ongoing recombination. The implication is that since humans expanded out of Africa each extant copy of each of the 17 haplotypes has a history of evolving by desc ...
Pepsinogen and Pepsin - The Journal of General Physiology
... because the loss of function had a high temperature coefficient, it seems probable that the viscosity and functional changes resulted from denaturation that followed reduction of the second disulfide bond. The third disulfide bridge is different from the other two as shown by its resistance to reduc ...
... because the loss of function had a high temperature coefficient, it seems probable that the viscosity and functional changes resulted from denaturation that followed reduction of the second disulfide bond. The third disulfide bridge is different from the other two as shown by its resistance to reduc ...
Isolation of casein from milk
... • Is a phosphoprotein, which has phosphate groups attached to some of the amino acid side chains. Mostly these amino acid are serine and threonine. • casein is a mixture of at least three similar proteins, which differ primarily in molecular weight and amount of phosphorus they contain (number of ph ...
... • Is a phosphoprotein, which has phosphate groups attached to some of the amino acid side chains. Mostly these amino acid are serine and threonine. • casein is a mixture of at least three similar proteins, which differ primarily in molecular weight and amount of phosphorus they contain (number of ph ...
... β-strands adjacent to each other, forming a barrel that satisfies all mainchain hydrogen bonds, this is important since there are no donors or acceptors in the membrane. The outside of the barrel will be non-polar, meaning every 2nd residue in the strand will be non-polar. 5. (12 pts) Briefly descri ...
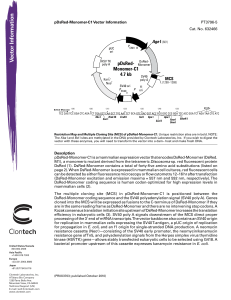
pDsRed-Monomer-C1 Vector Information
... DsRed-Monomer coding sequence and the SV40 polyadenylation signal (SV40 poly A). Genes cloned into the MCS will be expressed as fusions to the C-terminus of DsRed-Monomer if they are in the same reading frame as DsRed-Monomer and there are no intervening stop codons. A Kozak consensus translation in ...
... DsRed-Monomer coding sequence and the SV40 polyadenylation signal (SV40 poly A). Genes cloned into the MCS will be expressed as fusions to the C-terminus of DsRed-Monomer if they are in the same reading frame as DsRed-Monomer and there are no intervening stop codons. A Kozak consensus translation in ...
Genetic code

The genetic code is the set of rules by which information encoded within genetic material (DNA or mRNA sequences) is translated into proteins by living cells. Biological decoding is accomplished by the ribosome, which links amino acids in an order specified by mRNA, using transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules to carry amino acids and to read the mRNA three nucleotides at a time. The genetic code is highly similar among all organisms and can be expressed in a simple table with 64 entries.The code defines how sequences of these nucleotide triplets, called codons, specify which amino acid will be added next during protein synthesis. With some exceptions, a three-nucleotide codon in a nucleic acid sequence specifies a single amino acid. Because the vast majority of genes are encoded with exactly the same code (see the RNA codon table), this particular code is often referred to as the canonical or standard genetic code, or simply the genetic code, though in fact some variant codes have evolved. For example, protein synthesis in human mitochondria relies on a genetic code that differs from the standard genetic code.While the genetic code determines the protein sequence for a given coding region, other genomic regions can influence when and where these proteins are produced.