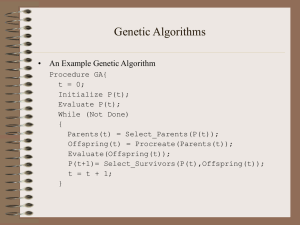
Genetic Algorithms
... • Crossover is usually the primary operator with mutation serving only as a mechanism to introduce diversity in the population. • However, when designing a GA to solve a problem it is not uncommon that one will have to develop unique crossover and mutation operators that take advantage of the struct ...
... • Crossover is usually the primary operator with mutation serving only as a mechanism to introduce diversity in the population. • However, when designing a GA to solve a problem it is not uncommon that one will have to develop unique crossover and mutation operators that take advantage of the struct ...
Introduction to Genetics
... needs to inherit one O gene for him to be a ginger cat. A normal female is XX genetic makeup. She must inherit two O genes to be a ginger cat. The O gene is called a sex-linked gene because it is carried on a sex chromosome. If the female cat inherits only one O gene, she will be tortoiseshell (hete ...
... needs to inherit one O gene for him to be a ginger cat. A normal female is XX genetic makeup. She must inherit two O genes to be a ginger cat. The O gene is called a sex-linked gene because it is carried on a sex chromosome. If the female cat inherits only one O gene, she will be tortoiseshell (hete ...
Biosc_48_Chapter_5_lecture
... Also called anaerobic metabolism or lactic acid fermentation (Similar to how yeast ferments glucose into alcohol) Still yields a net gain of 2 ATP a. Muscle cells can survive for awhile without oxygen by using lactic acid fermentation. b. RBCs can only use lactic acid fermentation because they lack ...
... Also called anaerobic metabolism or lactic acid fermentation (Similar to how yeast ferments glucose into alcohol) Still yields a net gain of 2 ATP a. Muscle cells can survive for awhile without oxygen by using lactic acid fermentation. b. RBCs can only use lactic acid fermentation because they lack ...
Intermediary Metabolism of Carbohydrate, Protein, and Fat
... Regulation of metabolism is ultimately regulation of the enzyme catalysts in pathways. There are various kinds of regulation to be considered, all of which are important and often interact in intermediary metabolism. First, the amount of an enzyme can be increased or decreased, by changing its rate ...
... Regulation of metabolism is ultimately regulation of the enzyme catalysts in pathways. There are various kinds of regulation to be considered, all of which are important and often interact in intermediary metabolism. First, the amount of an enzyme can be increased or decreased, by changing its rate ...
Textile Dyeing
... converted to undissociated carboxyl groups owing to the addition of acid HX It causes the positively charged wool (H3N+.W.COOH) to take up an equivalent amount of acid anions X hence build the bond in between dye molecule and the fiber ...
... converted to undissociated carboxyl groups owing to the addition of acid HX It causes the positively charged wool (H3N+.W.COOH) to take up an equivalent amount of acid anions X hence build the bond in between dye molecule and the fiber ...
Acid CleavageLDeprotection in Fmoc/tBu Solid
... useful (5). Carpino again, together with Han, introduced the Fmoc-protecting group in 1970 (6,7). The combined application of the orthogonal FmocltBu-pair in a new SPPS strategy followed in 1978 by Atherton et al. (8) and independently by Chang and Meienhofer (9). Only in recent years, however, has ...
... useful (5). Carpino again, together with Han, introduced the Fmoc-protecting group in 1970 (6,7). The combined application of the orthogonal FmocltBu-pair in a new SPPS strategy followed in 1978 by Atherton et al. (8) and independently by Chang and Meienhofer (9). Only in recent years, however, has ...
Partitioning the Genetic Variance
... In lecture 2, we showed how to partition genotypic values G into their expected values based on additivity (G A ) and deviations from the additivity as a result of dominance (δ ) For this decomposition, individuals with alleles Ai and Aj at a locus have a mean genotypic value of Gij = GijA + δij = µ ...
... In lecture 2, we showed how to partition genotypic values G into their expected values based on additivity (G A ) and deviations from the additivity as a result of dominance (δ ) For this decomposition, individuals with alleles Ai and Aj at a locus have a mean genotypic value of Gij = GijA + δij = µ ...
Adverse Effects of Excessive Leucine Intake Depend on Dietary
... long been known that the adverse effects of excessive amino acid intake depend on dietary protein levels. Male rats were divided into 12 groups (n56) and fed for 1 wk a diet containing low (6%), moderate (12%) or high (40%) protein. Different levels of Leu (0, 2, 4, and 8%) were added to the diets. ...
... long been known that the adverse effects of excessive amino acid intake depend on dietary protein levels. Male rats were divided into 12 groups (n56) and fed for 1 wk a diet containing low (6%), moderate (12%) or high (40%) protein. Different levels of Leu (0, 2, 4, and 8%) were added to the diets. ...
Variations in amino acid composition in bacterial single stranded
... pylori, (Epsilonproteobacteria), Escherichia coli (Gammaproteobacteria), and Streptomyces coelicolor (Actinobacteria). These species with solved SSB structures were selected since they possess 38 %, 50 % and 72 % GC ratio in their genomes, respectively (6, 17, 18). Since OB fold is shown to be more ...
... pylori, (Epsilonproteobacteria), Escherichia coli (Gammaproteobacteria), and Streptomyces coelicolor (Actinobacteria). These species with solved SSB structures were selected since they possess 38 %, 50 % and 72 % GC ratio in their genomes, respectively (6, 17, 18). Since OB fold is shown to be more ...
Get - Wiley Online Library
... As with most molecules with rotational freedom about single bonds, certain conformations of nucleotides are usually preferred as a result of steric constraints. Ranges of torsion angle are commonly defined by the Klyne–Prelog nomenclature developed for spectroscopists, in which those of approximately ...
... As with most molecules with rotational freedom about single bonds, certain conformations of nucleotides are usually preferred as a result of steric constraints. Ranges of torsion angle are commonly defined by the Klyne–Prelog nomenclature developed for spectroscopists, in which those of approximately ...
Small, Smaller, Smallest: The Origins and Evolution of Ancient Dual
... short open reading frames (ORFs) for Nasuia-ALF. Previous research indicated that the small genomes of Hodgkinia and Zinderia use an alternative genetic code that has reassigned the UGA stop codon to tryptophan (McCutcheon et al. 2009b; McCutcheon and Moran 2010). To see if this is the case for Nasu ...
... short open reading frames (ORFs) for Nasuia-ALF. Previous research indicated that the small genomes of Hodgkinia and Zinderia use an alternative genetic code that has reassigned the UGA stop codon to tryptophan (McCutcheon et al. 2009b; McCutcheon and Moran 2010). To see if this is the case for Nasu ...
Weak Selection and Protein Evolution
... Escherichia coli show roughly similar levels of protein polymorphism although their historical population sizes presumably differ greatly. This “invariance of heterozygosity” (Lewontin 1974) was argued as strong evidence against the neutral model. Protein divergence and the neutral model ...
... Escherichia coli show roughly similar levels of protein polymorphism although their historical population sizes presumably differ greatly. This “invariance of heterozygosity” (Lewontin 1974) was argued as strong evidence against the neutral model. Protein divergence and the neutral model ...
Hydrogen Bonds and Hydrophobic Interactions of Porphyrins in
... standing goal in structural biology, as they are crucial for the structure and function of the proteins [1]. The directionality of the hydrogen bond is very important since it allows the chemist to control the geometry of the complexes and to design precisely complementary hosts for a given guest. S ...
... standing goal in structural biology, as they are crucial for the structure and function of the proteins [1]. The directionality of the hydrogen bond is very important since it allows the chemist to control the geometry of the complexes and to design precisely complementary hosts for a given guest. S ...
VITAMINS-5
... • Naturally occurring deficiency is rare in humans • Only observed in cases of sever malnutrition • Experimentally induced deficiency: headache, fatigue, insomnia, intestinal disturbances, numbness and tingling of their hands and feet • Research on experimental animals to understand deficiency • Sym ...
... • Naturally occurring deficiency is rare in humans • Only observed in cases of sever malnutrition • Experimentally induced deficiency: headache, fatigue, insomnia, intestinal disturbances, numbness and tingling of their hands and feet • Research on experimental animals to understand deficiency • Sym ...
Obtaining genetic testing in pediatric epilepsy
... Classification of genetic variants. Variants are either benign or pathogenic, but determining into which category a previously undescribed variant falls can be complicated. Variants that do not change protein structure generally would be predicted to be benign. Variants that likely result in a chang ...
... Classification of genetic variants. Variants are either benign or pathogenic, but determining into which category a previously undescribed variant falls can be complicated. Variants that do not change protein structure generally would be predicted to be benign. Variants that likely result in a chang ...
Statistical analysis of DNA microarray data
... Given a amino acid sequence, find compatible structures ---- Useful for finding homologous structures when doing homology modeling Given a preliminary or model structure, test its validity --- Useful for the final phase of homology modeling Given a structure, find compatible sequences ---- Use ...
... Given a amino acid sequence, find compatible structures ---- Useful for finding homologous structures when doing homology modeling Given a preliminary or model structure, test its validity --- Useful for the final phase of homology modeling Given a structure, find compatible sequences ---- Use ...
Industrial biotechnology: Tools and applications
... synthetic biological circuit, holds significant promises to the understanding, design, and construction of customized gene expression networks [32]. Scientists are attempting to create de novo genomes in synthetic microorganisms which are easier to understand and manipulate compared to those availab ...
... synthetic biological circuit, holds significant promises to the understanding, design, and construction of customized gene expression networks [32]. Scientists are attempting to create de novo genomes in synthetic microorganisms which are easier to understand and manipulate compared to those availab ...
Mapping Post-Transcriptional Modifications onto Transfer
... all modified nucleosides, except pseudouridine, which is an isomer of uridine, are detected at a higher mass than the canonical nucleoside, the type and position of the modification within the digestion product can be mapped using mass spectrometry. To map mod ...
... all modified nucleosides, except pseudouridine, which is an isomer of uridine, are detected at a higher mass than the canonical nucleoside, the type and position of the modification within the digestion product can be mapped using mass spectrometry. To map mod ...
The main theoretical questions
... Nucleic acids are required for the storage and expression of genetic information. There are two chemically distinct types of nucleic acids: deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA). DNA is present not only in chromosomes in the nucleus of eukaryotic organisms, but also in mitochondria ...
... Nucleic acids are required for the storage and expression of genetic information. There are two chemically distinct types of nucleic acids: deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA). DNA is present not only in chromosomes in the nucleus of eukaryotic organisms, but also in mitochondria ...
here - Solve ME/CFS Initiative
... Stress on a biological system produces symptoms that vary upon the individual. May cause variations between people with ME/CFS . ME/CFS still may be an umbrella term for a number of similar disorders (spectrum disorder). ...
... Stress on a biological system produces symptoms that vary upon the individual. May cause variations between people with ME/CFS . ME/CFS still may be an umbrella term for a number of similar disorders (spectrum disorder). ...
Ontogenetic Changes in the Rates of Protein Synthesis and
... The present study applies tracer methodology to the investigation of fetal leucine metabolism at midgestation (73-88 days), a time when the fetus is only 5-10% of its birth weight. We focused attention on the essential amino acid leucine for two reasons: 1) it has dual importance as a constituent of ...
... The present study applies tracer methodology to the investigation of fetal leucine metabolism at midgestation (73-88 days), a time when the fetus is only 5-10% of its birth weight. We focused attention on the essential amino acid leucine for two reasons: 1) it has dual importance as a constituent of ...
Abstract 1
... We found 10 µM RNA to be an appropriate concentration for screening various small compounds for their ability to form non-covalent complexes. Signals consistent with specific non-covalent binding of neomycin to A-site RNA were observed using both Electrospray and MALDI. An approximately linear relat ...
... We found 10 µM RNA to be an appropriate concentration for screening various small compounds for their ability to form non-covalent complexes. Signals consistent with specific non-covalent binding of neomycin to A-site RNA were observed using both Electrospray and MALDI. An approximately linear relat ...
Lipids
... Tocopherols constitute a series of related benzopyranols (or methyl tocols) that occur in vegetable oils. In the tocopherols, the C16 side chain is saturated, and in the tocotrienols it contains three double bonds. The four main constituents are termed - alpha (5,7,8-trimethyl), beta (5,8-dimethyl), ...
... Tocopherols constitute a series of related benzopyranols (or methyl tocols) that occur in vegetable oils. In the tocopherols, the C16 side chain is saturated, and in the tocotrienols it contains three double bonds. The four main constituents are termed - alpha (5,7,8-trimethyl), beta (5,8-dimethyl), ...
si RNA
... The use of RNA interference for artificially manipulating gene expression was initially limited by the activation of cellular antiviral mechanisms. Exposure of cells to sequences longer than 30 nucleotides induces interferon gene expression resulting in non-specific RNA degradation and reduced prote ...
... The use of RNA interference for artificially manipulating gene expression was initially limited by the activation of cellular antiviral mechanisms. Exposure of cells to sequences longer than 30 nucleotides induces interferon gene expression resulting in non-specific RNA degradation and reduced prote ...
Genetic code

The genetic code is the set of rules by which information encoded within genetic material (DNA or mRNA sequences) is translated into proteins by living cells. Biological decoding is accomplished by the ribosome, which links amino acids in an order specified by mRNA, using transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules to carry amino acids and to read the mRNA three nucleotides at a time. The genetic code is highly similar among all organisms and can be expressed in a simple table with 64 entries.The code defines how sequences of these nucleotide triplets, called codons, specify which amino acid will be added next during protein synthesis. With some exceptions, a three-nucleotide codon in a nucleic acid sequence specifies a single amino acid. Because the vast majority of genes are encoded with exactly the same code (see the RNA codon table), this particular code is often referred to as the canonical or standard genetic code, or simply the genetic code, though in fact some variant codes have evolved. For example, protein synthesis in human mitochondria relies on a genetic code that differs from the standard genetic code.While the genetic code determines the protein sequence for a given coding region, other genomic regions can influence when and where these proteins are produced.























