Lecture 27
... In order to sequence entire genomes, segments need to be assembled into contigs (contiguous blocks) to establish the correct order of the sequence. Chromosome walking may be one way to do so, but is prohibitively expensive. Two methods have been used recently: 1. Conventional genome sequencing-low r ...
... In order to sequence entire genomes, segments need to be assembled into contigs (contiguous blocks) to establish the correct order of the sequence. Chromosome walking may be one way to do so, but is prohibitively expensive. Two methods have been used recently: 1. Conventional genome sequencing-low r ...
Dna, Protein Synthesis, and gene expression
... Not all genes are expressed at the same time An organisms expresses genes at different times in different areas Each cell type will express a different subset of genes This can be seen by looking at the ____________ ...
... Not all genes are expressed at the same time An organisms expresses genes at different times in different areas Each cell type will express a different subset of genes This can be seen by looking at the ____________ ...
Lec. 25 - Translation 3
... • Are there any potential deficiencies with this model or the data that support it? • How could it be made stronger? ...
... • Are there any potential deficiencies with this model or the data that support it? • How could it be made stronger? ...
Amino acids
... Oxygen binding leads to structural (conformational) changes in binding site, which are transmitted to neighboring subunits through contacts between subunits ...
... Oxygen binding leads to structural (conformational) changes in binding site, which are transmitted to neighboring subunits through contacts between subunits ...
Review Problems for amino acids, carbohydrates, glycolysis and the
... muscle ache and fatigue, but is temporary and is usually not harmful” Please think about the following: 1- Is lactic acid actually the product of anaerobic glycolysis in mammals? If not, what is? (there are actually two major compounds formed, one of which you should know). 2- Is this compound an ac ...
... muscle ache and fatigue, but is temporary and is usually not harmful” Please think about the following: 1- Is lactic acid actually the product of anaerobic glycolysis in mammals? If not, what is? (there are actually two major compounds formed, one of which you should know). 2- Is this compound an ac ...
Molecules of Life
... • It is the reason red blood cells carry oxygen. • Remember, only red blood cells need haemoglobin, so brain or liver cells wouldn’t make it. ...
... • It is the reason red blood cells carry oxygen. • Remember, only red blood cells need haemoglobin, so brain or liver cells wouldn’t make it. ...
Review Problems for amino acids, carbohydrates, glycolysis and the
... muscle ache and fatigue, but is temporary and is usually not harmful” Please think about the following: 1- Is lactic acid actually the product of anaerobic glycolysis in mammals? If not, what is? (there are actually two major compounds formed, one of which you should know). 2- Is this compound an ac ...
... muscle ache and fatigue, but is temporary and is usually not harmful” Please think about the following: 1- Is lactic acid actually the product of anaerobic glycolysis in mammals? If not, what is? (there are actually two major compounds formed, one of which you should know). 2- Is this compound an ac ...
Biology Chapters 8 and 9 Test Review
... o Stem Cells are used for research and have no specialized function at the time. o AUG is a ‘start code’ that also stands for methionine. o UUU—phenylalanine. o UAA, UAG, and UGA are all stop codes. o The missing enzymes from PKU convert phenyalanine to tyrosine. o DNA often reads the first two lett ...
... o Stem Cells are used for research and have no specialized function at the time. o AUG is a ‘start code’ that also stands for methionine. o UUU—phenylalanine. o UAA, UAG, and UGA are all stop codes. o The missing enzymes from PKU convert phenyalanine to tyrosine. o DNA often reads the first two lett ...
EREG Human - CellSystems
... temperature for 3 weeks, should be stored desiccated below -18°C. Upon reconstitution Epiregulin should be stored at 4°C between 2-7 days and for future use below -18°C.For long term storage it is recommended to add a carrier protein (0.1% HSA or BSA).Please prevent freeze-thaw cycles. ...
... temperature for 3 weeks, should be stored desiccated below -18°C. Upon reconstitution Epiregulin should be stored at 4°C between 2-7 days and for future use below -18°C.For long term storage it is recommended to add a carrier protein (0.1% HSA or BSA).Please prevent freeze-thaw cycles. ...
Chapter 2 - (www.ramsey.k12.nj.us).
... include oxygen and some also have nitrogen, phosphorus and sulfur. Carbon can form thousands of different compounds because it can form 4 strong covalent bonds ...
... include oxygen and some also have nitrogen, phosphorus and sulfur. Carbon can form thousands of different compounds because it can form 4 strong covalent bonds ...
Protein Synthesis Lesson Plan
... This lesson plan was designed for my first period seventh grade Life Science class. The majority of these students are in the academically enriched program, were they are not necessarily identified gifted, but they should be able to comprehend information at a higher level then the general education ...
... This lesson plan was designed for my first period seventh grade Life Science class. The majority of these students are in the academically enriched program, were they are not necessarily identified gifted, but they should be able to comprehend information at a higher level then the general education ...
Genetics exam 4
... B. The code is not universal among organisms C. Some amino acids have more than one codon D. Frameshift mutations are tolerated E. Stop codons may have corresponding tRNA molecules _____ Normal self-termination of transcription occurs due to the presence of A. stem-loop sequences in mRNA B. Terminat ...
... B. The code is not universal among organisms C. Some amino acids have more than one codon D. Frameshift mutations are tolerated E. Stop codons may have corresponding tRNA molecules _____ Normal self-termination of transcription occurs due to the presence of A. stem-loop sequences in mRNA B. Terminat ...
Protein Structure
... hydrogen bonded to another electronegative atom • These bonds can occur between two molecules (like water) or within the same molecule (like DNA and like you will see with proteins…) ...
... hydrogen bonded to another electronegative atom • These bonds can occur between two molecules (like water) or within the same molecule (like DNA and like you will see with proteins…) ...
Honors Biology
... Final Exam Review Sheet 1. Protein Synthesis base triplets/codons/anticodons: what are they?, what type of information do they represent?, to what molecules do these terms refer to? redundancy of the DNA code: what advantage does having multiple codons for a single amino acid give when a mutatio ...
... Final Exam Review Sheet 1. Protein Synthesis base triplets/codons/anticodons: what are they?, what type of information do they represent?, to what molecules do these terms refer to? redundancy of the DNA code: what advantage does having multiple codons for a single amino acid give when a mutatio ...
Name: Correctly complete the following statements with a term that
... 28. At a conference, the speaker's grand finale was sautéing mealworms (insect larvae) in butter and serving them to the audience. They were crunchy (like popcorn) because their exoskeletons contain the polysaccharide (a) linolenic acid (b) cellulose (c) collagen (d) glycogen (e) chitin. 29. ______ ...
... 28. At a conference, the speaker's grand finale was sautéing mealworms (insect larvae) in butter and serving them to the audience. They were crunchy (like popcorn) because their exoskeletons contain the polysaccharide (a) linolenic acid (b) cellulose (c) collagen (d) glycogen (e) chitin. 29. ______ ...
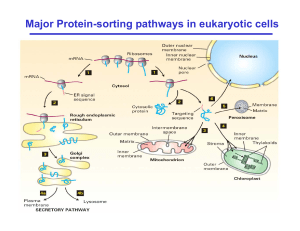
Major Protein-sorting pathways in eukaryotic cells
... Key elements for the Protein targeting events 1. Signal sequence: the amino acid sequence of a protein that provides the information to target the protein to a particular organelle. 2. Receptors for the signal sequences. 3. Translocation channels that allow transfer of proteins across the membrane ...
... Key elements for the Protein targeting events 1. Signal sequence: the amino acid sequence of a protein that provides the information to target the protein to a particular organelle. 2. Receptors for the signal sequences. 3. Translocation channels that allow transfer of proteins across the membrane ...
Biochemistry Quiz
... 22. The main difference between the secondary and quaternary structure of a protein is (a) bond angles between amino acids (b) sequence of amino acids (c) number of polypeptides in the molecule (d) the folding pattern of the molecule (e) The disulphide bridges 23. The 'primary structure' of a protei ...
... 22. The main difference between the secondary and quaternary structure of a protein is (a) bond angles between amino acids (b) sequence of amino acids (c) number of polypeptides in the molecule (d) the folding pattern of the molecule (e) The disulphide bridges 23. The 'primary structure' of a protei ...
Document
... Foldit is a revolutionary new computer game enabling you to contribute to important scientific research. Join this free online game and help us predict the folds of unsolved proteins as well as designing new proteins to cure diseases. We’re collecting data to find out if humans' pattern-recognition ...
... Foldit is a revolutionary new computer game enabling you to contribute to important scientific research. Join this free online game and help us predict the folds of unsolved proteins as well as designing new proteins to cure diseases. We’re collecting data to find out if humans' pattern-recognition ...
BIO 304 Genetics
... 5. A ____auxotrophic / mutant_ strain of Neurospora is one that requires a particular medium additive which is not required by wildtype mold. 6. ____eukaryote__ are organisms whose cells have nuclei and membrane-bound structures. 7. ____replication________ is another term for DNA-dependent DNA synth ...
... 5. A ____auxotrophic / mutant_ strain of Neurospora is one that requires a particular medium additive which is not required by wildtype mold. 6. ____eukaryote__ are organisms whose cells have nuclei and membrane-bound structures. 7. ____replication________ is another term for DNA-dependent DNA synth ...
Mutations and Genetic Disease Most genetic diseases are caused
... This image and caption from The Book of Man by Walter Bodmer and Robin McKie. The type of mutation exemplified in sickle cell anemia is called a substitution, because one nucleotide base is substituted for another. Other types of mutations include insertions and deletions, both of which can have dis ...
... This image and caption from The Book of Man by Walter Bodmer and Robin McKie. The type of mutation exemplified in sickle cell anemia is called a substitution, because one nucleotide base is substituted for another. Other types of mutations include insertions and deletions, both of which can have dis ...
Student Procedures
... showing gradual changes over time from earlier forms to modern forms, and more are being found every year. All of this indicates that common ancestors connect all life forms to each other, much like the way you are related to your cousins because you have the same grandparents. When this flow of lif ...
... showing gradual changes over time from earlier forms to modern forms, and more are being found every year. All of this indicates that common ancestors connect all life forms to each other, much like the way you are related to your cousins because you have the same grandparents. When this flow of lif ...
Basic Principle in Plant Physiology
... •Amino acids released from protein turnover can be resynthesized into proteins. •Excess amino acids are degraded into specific compounds that can be used in other metabolic pathways. •This process begins with the removal of the amino group, which can be converted to urea and excreted. •The a-ketoids ...
... •Amino acids released from protein turnover can be resynthesized into proteins. •Excess amino acids are degraded into specific compounds that can be used in other metabolic pathways. •This process begins with the removal of the amino group, which can be converted to urea and excreted. •The a-ketoids ...
Name Date__________________ DNA and Protein Synthesis
... Click Next on the lower right hand corner to take the interactive quiz and write the correct answers below 1.Transcription is the first step of Protein Synthesis and it occurs in the: 2. Translation is the second step of Protein Synthesis and it occurs in the: 3. If a DNA sequence consists of 12 nuc ...
... Click Next on the lower right hand corner to take the interactive quiz and write the correct answers below 1.Transcription is the first step of Protein Synthesis and it occurs in the: 2. Translation is the second step of Protein Synthesis and it occurs in the: 3. If a DNA sequence consists of 12 nuc ...
a. carbohydrates - Valhalla High School
... • DNA is the hereditary material passed from one generation to the next during reproduction. ...
... • DNA is the hereditary material passed from one generation to the next during reproduction. ...
The Basics: A general review of molecular biology: DNA
... 5. Pair the cysteines to form a disulfide bond. ...
... 5. Pair the cysteines to form a disulfide bond. ...
Genetic code

The genetic code is the set of rules by which information encoded within genetic material (DNA or mRNA sequences) is translated into proteins by living cells. Biological decoding is accomplished by the ribosome, which links amino acids in an order specified by mRNA, using transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules to carry amino acids and to read the mRNA three nucleotides at a time. The genetic code is highly similar among all organisms and can be expressed in a simple table with 64 entries.The code defines how sequences of these nucleotide triplets, called codons, specify which amino acid will be added next during protein synthesis. With some exceptions, a three-nucleotide codon in a nucleic acid sequence specifies a single amino acid. Because the vast majority of genes are encoded with exactly the same code (see the RNA codon table), this particular code is often referred to as the canonical or standard genetic code, or simply the genetic code, though in fact some variant codes have evolved. For example, protein synthesis in human mitochondria relies on a genetic code that differs from the standard genetic code.While the genetic code determines the protein sequence for a given coding region, other genomic regions can influence when and where these proteins are produced.