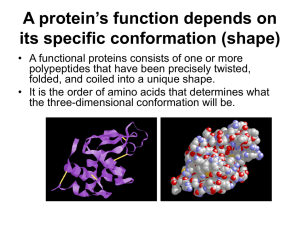
A protein’s function depends on its specific conformation
... secondary, and tertiary structure, are used to organize the folding within a single polypeptide. • Quarternary structure arises when two or more polypeptides join to form a protein. ...
... secondary, and tertiary structure, are used to organize the folding within a single polypeptide. • Quarternary structure arises when two or more polypeptides join to form a protein. ...
Biochemistry - Bishop Ireton High School
... use their stored glucose but first they must break the polymer up into the monomer glucose. • This requires the reverse reaction of dehydration synthesis. Instead of pulling out a water molecule, a water molecule is added to break the bond. • One monomer will get the H, the other the OH ...
... use their stored glucose but first they must break the polymer up into the monomer glucose. • This requires the reverse reaction of dehydration synthesis. Instead of pulling out a water molecule, a water molecule is added to break the bond. • One monomer will get the H, the other the OH ...
Just as 26 letters of the alphabet make up all words in the English
... Just as 26 letters of the alphabet make up all words in the English language, 20 amino acids make up all of the proteins in your body. The structure of a protein is determined by the order of its amino acids. If two amino acids change places, the entire protein changes. The function of a protein dep ...
... Just as 26 letters of the alphabet make up all words in the English language, 20 amino acids make up all of the proteins in your body. The structure of a protein is determined by the order of its amino acids. If two amino acids change places, the entire protein changes. The function of a protein dep ...
Amino Acids, Proteins and Enzymes
... • vasopressin and oxytocin are both nonapeptides but have quite different biological functions • vasopressin is an antidiuretic hormone • oxytocin affects contractions of the uterus in childbirth and the muscles of the breast that aid in the secretion of milk ...
... • vasopressin and oxytocin are both nonapeptides but have quite different biological functions • vasopressin is an antidiuretic hormone • oxytocin affects contractions of the uterus in childbirth and the muscles of the breast that aid in the secretion of milk ...
Biochemistry: the chemical makeup of living things
... from the combination of more than one polypeptide folded chain. ** Not all proteins have this structure ...
... from the combination of more than one polypeptide folded chain. ** Not all proteins have this structure ...
Bio 112 17 sp11
... Base-pair substitution • replaces one nucleotide and its partner with another pair of nucleotides • can cause missense or nonsense mutations Missense • mutations still code for an amino acid, but not necessarily the right amino acid Nonsense mutations • change an amino acid codon into a stop codon, ...
... Base-pair substitution • replaces one nucleotide and its partner with another pair of nucleotides • can cause missense or nonsense mutations Missense • mutations still code for an amino acid, but not necessarily the right amino acid Nonsense mutations • change an amino acid codon into a stop codon, ...
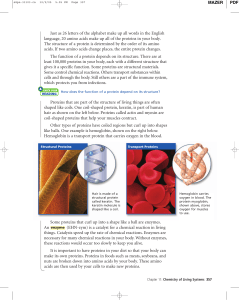
PROTEIN[1]
... bloodstream, but some remain in the enterocytes and are used to synthesize enzymes and new cells • >99% of protein enters the bloodstream as amino acids • Absorption of whole protein can cause a severe allergic reaction ...
... bloodstream, but some remain in the enterocytes and are used to synthesize enzymes and new cells • >99% of protein enters the bloodstream as amino acids • Absorption of whole protein can cause a severe allergic reaction ...
DNA - Paxon Biology
... - The replacement of one base pair with another. - Occurs when a nucleotide and its partner from the complementary DNA strand are replaced with another pair of nucleotides. - Depending on how base-pair substitutions are translated, they can result in little or no change in the protein encoded by the ...
... - The replacement of one base pair with another. - Occurs when a nucleotide and its partner from the complementary DNA strand are replaced with another pair of nucleotides. - Depending on how base-pair substitutions are translated, they can result in little or no change in the protein encoded by the ...
Macromolecules
... Steroids are made up of four fused rings, i.e. Cholesterol. This is a component of animal cellmembranes and is used for making other steroids such as sex-hormones. Cholesterol is used in the manufacture of Bile (important in the digestion of fats) and Estrogen, Progesterone and Testosterone ...
... Steroids are made up of four fused rings, i.e. Cholesterol. This is a component of animal cellmembranes and is used for making other steroids such as sex-hormones. Cholesterol is used in the manufacture of Bile (important in the digestion of fats) and Estrogen, Progesterone and Testosterone ...
Extension and Enrichment
... Examine the amino acid chart provided and review the properties of the different amino acids. 1. Hydrophobic side chains (R) primarily contain _________________ atoms. ...
... Examine the amino acid chart provided and review the properties of the different amino acids. 1. Hydrophobic side chains (R) primarily contain _________________ atoms. ...
Molecular biology for bioinformatics
... strand, and vice versa; if there is a c on the one strand, its ”partner” on the other strand will always be a g, and vice versa. When a cell divides to form daughter cells, DNA is replicated by untwisting the two strands and using each strand as a template to produce its chemical mirror image. 2. Tr ...
... strand, and vice versa; if there is a c on the one strand, its ”partner” on the other strand will always be a g, and vice versa. When a cell divides to form daughter cells, DNA is replicated by untwisting the two strands and using each strand as a template to produce its chemical mirror image. 2. Tr ...
Download PDF
... capture, proton and ion gradients, and conversion to mechanical energy. In addition, we will explore the thermodynamics of electron transport, proton pumping, and ATP biosynthesis. 3. Molecular biosynthesis. Most organisms can biosynthesize amino acids, lipids, nucleotides, vitamins, and cofactors u ...
... capture, proton and ion gradients, and conversion to mechanical energy. In addition, we will explore the thermodynamics of electron transport, proton pumping, and ATP biosynthesis. 3. Molecular biosynthesis. Most organisms can biosynthesize amino acids, lipids, nucleotides, vitamins, and cofactors u ...
MUTATIONS
... Mutations can change the meaning of genes • Mutations are permanent changes in the DNA base sequence • Simplest mutation is a point mutation or a change in a single nucleotide that affects one codon • The triplet code has some flexibility because several different codons code for the same aa, so som ...
... Mutations can change the meaning of genes • Mutations are permanent changes in the DNA base sequence • Simplest mutation is a point mutation or a change in a single nucleotide that affects one codon • The triplet code has some flexibility because several different codons code for the same aa, so som ...
• Mutations are permanent changes in the DNA base sequence
... Mutations can change the meaning of genes • Mutations are permanent changes in the DNA base sequence • Simplest mutation is a point mutation or a change in a single nucleotide that affects one codon • The triplet code has some flexibility because several different codons code for the same aa, so som ...
... Mutations can change the meaning of genes • Mutations are permanent changes in the DNA base sequence • Simplest mutation is a point mutation or a change in a single nucleotide that affects one codon • The triplet code has some flexibility because several different codons code for the same aa, so som ...
Chapter 17 (part 2) - University of Nevada, Reno
... • Proteins digested to amino acids and small peptides in the stomach • Acid environment denatures proteins making them more accessible to proteases. • Pepsin is a major stomach protease, has pH optimum of 2.0 • Protein degradation continues in the lumen of ...
... • Proteins digested to amino acids and small peptides in the stomach • Acid environment denatures proteins making them more accessible to proteases. • Pepsin is a major stomach protease, has pH optimum of 2.0 • Protein degradation continues in the lumen of ...
Gene Expression
... performs a specialized function in the cell. The human genome contains more than 25,000 genes. ...
... performs a specialized function in the cell. The human genome contains more than 25,000 genes. ...
Most common elements in living things are carbon, hydrogen
... functional group (-COOH) is found on the end of the fatty acid that does NOT attach to glycerol. CIRCLE AND LABEL the carboxyl groups in the 2 fatty acids on this worksheet. Color the fatty acid chains the same colors for carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen as you did before. A special type of lipid called ...
... functional group (-COOH) is found on the end of the fatty acid that does NOT attach to glycerol. CIRCLE AND LABEL the carboxyl groups in the 2 fatty acids on this worksheet. Color the fatty acid chains the same colors for carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen as you did before. A special type of lipid called ...
NEW Topic 2 Genes and Health Objectives
... 11. Understand the process of protein synthesis (transcription) including the role of RNA polymerase, translation, messenger RNA, transfer RNA, ribosomes and the role of start and stop codons. 12. Understand the roles of the DNA template (antisense) strand in transcription, codons on messenger RNA a ...
... 11. Understand the process of protein synthesis (transcription) including the role of RNA polymerase, translation, messenger RNA, transfer RNA, ribosomes and the role of start and stop codons. 12. Understand the roles of the DNA template (antisense) strand in transcription, codons on messenger RNA a ...
Organic molecules
... **can bond to many different elements **can bond to other C atoms **form covalent bonds **can form single, double, triple bonds **can form a chain or ring • Carbon compounds: 4 found in all living things: carbohydrates, lipids, nucleic acids, proteins ...
... **can bond to many different elements **can bond to other C atoms **form covalent bonds **can form single, double, triple bonds **can form a chain or ring • Carbon compounds: 4 found in all living things: carbohydrates, lipids, nucleic acids, proteins ...
Amino acids and protein (lect 3%2c 2015)
... – Lysozyme, an enzyme that attacks bacteria, consists of a polypeptide chain of 129 amino acids. –The precise primary structure of a protein is determined by inherited genetic information carried on DNA. – At one end is an amino acid with a free amino group the (the N-terminus) and at the other is a ...
... – Lysozyme, an enzyme that attacks bacteria, consists of a polypeptide chain of 129 amino acids. –The precise primary structure of a protein is determined by inherited genetic information carried on DNA. – At one end is an amino acid with a free amino group the (the N-terminus) and at the other is a ...
Document
... This overview of the metabolic networks show why we now need computers, particulary if we want to predict cell behaviour! In recent years these needs have led to the development of ”Systems Biology”, which involves mathematical analysis and modelling of living cells. Hint: think about this figure b ...
... This overview of the metabolic networks show why we now need computers, particulary if we want to predict cell behaviour! In recent years these needs have led to the development of ”Systems Biology”, which involves mathematical analysis and modelling of living cells. Hint: think about this figure b ...
STUDY GUIDE SEMESTER 2 EXAM 4 Dr. Marks Name: Class
... Refer to the illustration above. The anticodons for the codons in the mRNA with the sequence CUCAAGUGCUUC are ...
... Refer to the illustration above. The anticodons for the codons in the mRNA with the sequence CUCAAGUGCUUC are ...
CARBOHYDRATES Carbohydrates are made up of carbon
... 2. They help in maintaining the composition of protoplasm. 3. They are used in the formation of various structures in the body eg keratin in the hair, nails, hooves, horns, feathers etc. 4. They are important in the formation of enzymes, which speed up chemical reactions in organisms.. 5. They form ...
... 2. They help in maintaining the composition of protoplasm. 3. They are used in the formation of various structures in the body eg keratin in the hair, nails, hooves, horns, feathers etc. 4. They are important in the formation of enzymes, which speed up chemical reactions in organisms.. 5. They form ...
Biochemistry Notes 2012
... • Atoms - basic building blocks of all matter. • Elements – pure substances that can’t be broken down into other substances. (atoms) • Molecules – two or more atoms joined together by chemical bonds. (smallest combination that can’t be divided without changing its chemical and physical properties) • ...
... • Atoms - basic building blocks of all matter. • Elements – pure substances that can’t be broken down into other substances. (atoms) • Molecules – two or more atoms joined together by chemical bonds. (smallest combination that can’t be divided without changing its chemical and physical properties) • ...
Quiz 7
... 1. Which of the following are typical of both mitosis and of the first division of meiosis? a) The genetic material in the nucleus is duplicated prior to division; b) Spindle fibers form; c) Two nuclei form as a result of the division; d) None of the above; e) a,b,c are true 2. At the end of Telopha ...
... 1. Which of the following are typical of both mitosis and of the first division of meiosis? a) The genetic material in the nucleus is duplicated prior to division; b) Spindle fibers form; c) Two nuclei form as a result of the division; d) None of the above; e) a,b,c are true 2. At the end of Telopha ...
Genetic code

The genetic code is the set of rules by which information encoded within genetic material (DNA or mRNA sequences) is translated into proteins by living cells. Biological decoding is accomplished by the ribosome, which links amino acids in an order specified by mRNA, using transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules to carry amino acids and to read the mRNA three nucleotides at a time. The genetic code is highly similar among all organisms and can be expressed in a simple table with 64 entries.The code defines how sequences of these nucleotide triplets, called codons, specify which amino acid will be added next during protein synthesis. With some exceptions, a three-nucleotide codon in a nucleic acid sequence specifies a single amino acid. Because the vast majority of genes are encoded with exactly the same code (see the RNA codon table), this particular code is often referred to as the canonical or standard genetic code, or simply the genetic code, though in fact some variant codes have evolved. For example, protein synthesis in human mitochondria relies on a genetic code that differs from the standard genetic code.While the genetic code determines the protein sequence for a given coding region, other genomic regions can influence when and where these proteins are produced.




![PROTEIN[1]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008787601_1-982d6894226491a6819f7f792fa348f2-300x300.png)

















