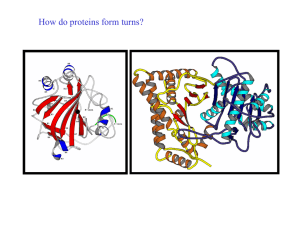
How do proteins form turns? - UF Macromolecular Structure Group
... side chains, main chain groups and bound solvent ...
... side chains, main chain groups and bound solvent ...
Authors` pre-proof version - University of Connecticut
... aaRS are universally distributed within the three domains (with the exception of some aaRS requiring tRNA-dependent amino acid synthesis, and domain-specific class I and class II LysRS families (Ibba et al. 1997), many, if not most of these groups have undergone horizontal gene transfer across all t ...
... aaRS are universally distributed within the three domains (with the exception of some aaRS requiring tRNA-dependent amino acid synthesis, and domain-specific class I and class II LysRS families (Ibba et al. 1997), many, if not most of these groups have undergone horizontal gene transfer across all t ...
Mitosis, Meiosis, DNA Notes
... using genetic code from DNA and carried out by RNA. A. Translation – process of forming proteins from mRNA. 1. mRNA leaves nucleus (nuclear pores) and goes to ribosomes. 2. mRNA is grouped into 3 consecutive bases called codons. a) Each codon corresponds with a certain amino acid. ...
... using genetic code from DNA and carried out by RNA. A. Translation – process of forming proteins from mRNA. 1. mRNA leaves nucleus (nuclear pores) and goes to ribosomes. 2. mRNA is grouped into 3 consecutive bases called codons. a) Each codon corresponds with a certain amino acid. ...
Similarity
... It is easy to score if an amino acid is identical to another (the score is 1 if identical and 0 if not). However, it is not easy to give a score for amino acids that are somewhat similar. ...
... It is easy to score if an amino acid is identical to another (the score is 1 if identical and 0 if not). However, it is not easy to give a score for amino acids that are somewhat similar. ...
Where in the cell is your protein most likely found?
... Transmembrane Helices Hidden Markov Models (TMHMM) • A Hidden Markov Model is a probabilistic model developed from observed sequences of proteins of a known function. • TMHMM is a tool used to predict the presence of transmembrane helices in proteins. The results will indicate the segments of the ...
... Transmembrane Helices Hidden Markov Models (TMHMM) • A Hidden Markov Model is a probabilistic model developed from observed sequences of proteins of a known function. • TMHMM is a tool used to predict the presence of transmembrane helices in proteins. The results will indicate the segments of the ...
Chapter 8 Microbial Genetics
... • DNA is a long molecule • E.coli chromosome has 4 million base pairs (nucleotides) • DNA is replicated segment by segment ...
... • DNA is a long molecule • E.coli chromosome has 4 million base pairs (nucleotides) • DNA is replicated segment by segment ...
A unified model of the standard genetic code
... the SGC. Observing that 64 is equal not only to 43 but also to 26 , the codon table can be organized as a 6D hypercube or 6D vector space (Z2 )6 over the binary field Z2 = {0, 1} [24]. The phenotypic graphs of amino acids have been obtained from the topology of the SGC [15]. Additionally, circular r ...
... the SGC. Observing that 64 is equal not only to 43 but also to 26 , the codon table can be organized as a 6D hypercube or 6D vector space (Z2 )6 over the binary field Z2 = {0, 1} [24]. The phenotypic graphs of amino acids have been obtained from the topology of the SGC [15]. Additionally, circular r ...
Ch.05The Structure and Function of Large Biological Molecules
... Steps of Chaperonin 2 The cap attaches, causing the 3 ...
... Steps of Chaperonin 2 The cap attaches, causing the 3 ...
Ch.05The Structure and Function of Large Biological Molecules
... crystallize into a fiber; capacity to carry oxygen is greatly reduced. ...
... crystallize into a fiber; capacity to carry oxygen is greatly reduced. ...
Protein Analysis
... – This residue cyclizes under acidic conditions to give a PTH amino acid and a peptide shortened by one amino acid residue. – This PTH-amino acid is identified by HPLC. – Automated repeated Edman degradation by a sequenator that can analyze sequences of about 50 amino acids long. – The amino acid co ...
... – This residue cyclizes under acidic conditions to give a PTH amino acid and a peptide shortened by one amino acid residue. – This PTH-amino acid is identified by HPLC. – Automated repeated Edman degradation by a sequenator that can analyze sequences of about 50 amino acids long. – The amino acid co ...
chapter_6_-_plus_ch_review
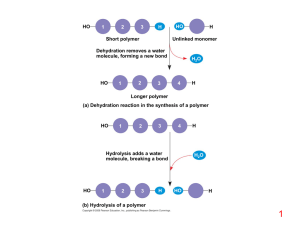
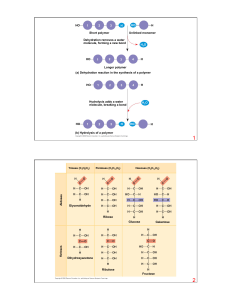
... include carboxyl group, amine group and R group. 3. The bonds between the protein’s building blocks have a specific name – what is it? 4. A simple chain of these building blocks is not a completely functional protein. What has to happen to the chain to make a functional protein? 5. What does the ter ...
... include carboxyl group, amine group and R group. 3. The bonds between the protein’s building blocks have a specific name – what is it? 4. A simple chain of these building blocks is not a completely functional protein. What has to happen to the chain to make a functional protein? 5. What does the ter ...
Processes of Evolution
... Individuals of a population are selected for because of the genetic phenotype Populations evolve because of the individual phenotypes that are selected for. Only the members of the same species can produce viable, fertile offspring in the next generation. This is a method of establishing if individu ...
... Individuals of a population are selected for because of the genetic phenotype Populations evolve because of the individual phenotypes that are selected for. Only the members of the same species can produce viable, fertile offspring in the next generation. This is a method of establishing if individu ...
A unified model of the standard genetic code
... the SGC. Observing that 64 is equal not only to 43 but also to 26 , the codon table can be organized as a 6D hypercube or 6D vector space (Z2 )6 over the binary field Z2 = {0, 1} [24]. The phenotypic graphs of amino acids have been obtained from the topology of the SGC [15]. Additionally, circular r ...
... the SGC. Observing that 64 is equal not only to 43 but also to 26 , the codon table can be organized as a 6D hypercube or 6D vector space (Z2 )6 over the binary field Z2 = {0, 1} [24]. The phenotypic graphs of amino acids have been obtained from the topology of the SGC [15]. Additionally, circular r ...
Ch.05The Structure and Function of Large Biological Molecules
... Steps of Chaperonin 2 The cap attaches, causing the 3 ...
... Steps of Chaperonin 2 The cap attaches, causing the 3 ...
Human Genetics--BIOL 102 Summer Lab 2--The
... translation initiation codon, aka the START codon? (Hint: its sequence is always ATG) 7. Again using the CDS to tell you where translation began and stopped, please tell me which of the three STOP codons the beta-globin gene uses to signal to the ribosome that it can stop adding amino acids to the p ...
... translation initiation codon, aka the START codon? (Hint: its sequence is always ATG) 7. Again using the CDS to tell you where translation began and stopped, please tell me which of the three STOP codons the beta-globin gene uses to signal to the ribosome that it can stop adding amino acids to the p ...
Pipecleaner Proteins Lab
... formats so that we can better understand them. Scientific models may also help us to do things that would otherwise be impossible. For example, there is no way that we could have sequenced the 6 billion bases in the human genome without prior experience with simpler organisms like nematodes with gen ...
... formats so that we can better understand them. Scientific models may also help us to do things that would otherwise be impossible. For example, there is no way that we could have sequenced the 6 billion bases in the human genome without prior experience with simpler organisms like nematodes with gen ...
Pipecleaner Proteins Lab
... formats so that we can better understand them. Scientific models may also help us to do things that would otherwise be impossible. For example, there is no way that we could have sequenced the 6 billion bases in the human genome without prior experience with simpler organisms like nematodes with gen ...
... formats so that we can better understand them. Scientific models may also help us to do things that would otherwise be impossible. For example, there is no way that we could have sequenced the 6 billion bases in the human genome without prior experience with simpler organisms like nematodes with gen ...
5.2 Human Genetic Disorders File
... chromosomal mutations POINT > Describe examples of genetic diseases caused by single gene mutations POINT > Identify human diseases caused by chromosomal mutations POINT > Explain Pedigree analysis ...
... chromosomal mutations POINT > Describe examples of genetic diseases caused by single gene mutations POINT > Identify human diseases caused by chromosomal mutations POINT > Explain Pedigree analysis ...
Introduction-1
... an organism consists of a very long sequence of four different nucleotides with bases A, C, G, T. Genomic DNA is a double-stranded helix comprised of two complementary strands, held together by A-T and C-G base pairs. The entire genome is replicated by DNA polymerases (a protein) and passed on to da ...
... an organism consists of a very long sequence of four different nucleotides with bases A, C, G, T. Genomic DNA is a double-stranded helix comprised of two complementary strands, held together by A-T and C-G base pairs. The entire genome is replicated by DNA polymerases (a protein) and passed on to da ...
Trainee Genetic Counsellor
... We are looking for a caring and enthusiastic individual to join our established Genetics Team as a Trainee Genetic Counsellor. We welcome applications both from individuals with an MSc in Genetic Counselling and from nurses or midwives who would be interested in becoming a genetic counsellor. The tr ...
... We are looking for a caring and enthusiastic individual to join our established Genetics Team as a Trainee Genetic Counsellor. We welcome applications both from individuals with an MSc in Genetic Counselling and from nurses or midwives who would be interested in becoming a genetic counsellor. The tr ...
Christ The King School Exampro A-level Biology (7401/7402) DNA
... A sample of DNA was analysed. 28% of the nucleotides contained thymine. Calculate the percentage of nucleotides which contained cytosine. Show your working. ...
... A sample of DNA was analysed. 28% of the nucleotides contained thymine. Calculate the percentage of nucleotides which contained cytosine. Show your working. ...
MASTERY 2.01 ______ 2.04 ______ Biology I Name: Unit 2
... 47. The graph indicates that pepsin would function best in which environment? A. Mouth (pH 6.5) B. Small intestine (8) C. Stomach (pH 2.5) D. Large intestine (pH 9) 48. Pepsin and trypsin are classified as A. Carbohydrates C. Proteins B. Lipids D. Nucleic Acids 49. The graph below shows the change i ...
... 47. The graph indicates that pepsin would function best in which environment? A. Mouth (pH 6.5) B. Small intestine (8) C. Stomach (pH 2.5) D. Large intestine (pH 9) 48. Pepsin and trypsin are classified as A. Carbohydrates C. Proteins B. Lipids D. Nucleic Acids 49. The graph below shows the change i ...
DNA makes up chromosomes!
... 20 amino acids • The function of the protein is determined by number and sequence of amino acids • (A polypeptide is a protein!) ...
... 20 amino acids • The function of the protein is determined by number and sequence of amino acids • (A polypeptide is a protein!) ...
lecture5lifes_chemical_basis
... The elucidation of the structure of α-helix is a landmark in Biochemistry because it was demonstrated that the conformation of a polypeptide chain can be predicted if the properties of its constituents are rigorously and precisely known. For this work Pauling got the Nobel prize in Chemistry in 1954 ...
... The elucidation of the structure of α-helix is a landmark in Biochemistry because it was demonstrated that the conformation of a polypeptide chain can be predicted if the properties of its constituents are rigorously and precisely known. For this work Pauling got the Nobel prize in Chemistry in 1954 ...
Genetic code

The genetic code is the set of rules by which information encoded within genetic material (DNA or mRNA sequences) is translated into proteins by living cells. Biological decoding is accomplished by the ribosome, which links amino acids in an order specified by mRNA, using transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules to carry amino acids and to read the mRNA three nucleotides at a time. The genetic code is highly similar among all organisms and can be expressed in a simple table with 64 entries.The code defines how sequences of these nucleotide triplets, called codons, specify which amino acid will be added next during protein synthesis. With some exceptions, a three-nucleotide codon in a nucleic acid sequence specifies a single amino acid. Because the vast majority of genes are encoded with exactly the same code (see the RNA codon table), this particular code is often referred to as the canonical or standard genetic code, or simply the genetic code, though in fact some variant codes have evolved. For example, protein synthesis in human mitochondria relies on a genetic code that differs from the standard genetic code.While the genetic code determines the protein sequence for a given coding region, other genomic regions can influence when and where these proteins are produced.