Determination of Protein Concentrations Using AAA
... are useful for cleaning the bottom of hydrolysis tubes using the RBS-35. Problematic glassware may also be decontaminated with high temperature in a furnace heated to 450 °C for 2–3 h (without plastic caps and seals) to combust all organic compounds. Hydrolysis tubes are qualified by adding 150 µL o ...
... are useful for cleaning the bottom of hydrolysis tubes using the RBS-35. Problematic glassware may also be decontaminated with high temperature in a furnace heated to 450 °C for 2–3 h (without plastic caps and seals) to combust all organic compounds. Hydrolysis tubes are qualified by adding 150 µL o ...
Phylogenetic, amino acid content and indel analyses
... Y16470) and Weissella paramesenteroides (Morse et al., 1996a) and, therefore, cannot be the cause of the natural rifampicin resistance in these bacteria. Obtaining good sequence alignments is a prerequisite of molecular systematic analysis because each aligned position has to include only homologous ...
... Y16470) and Weissella paramesenteroides (Morse et al., 1996a) and, therefore, cannot be the cause of the natural rifampicin resistance in these bacteria. Obtaining good sequence alignments is a prerequisite of molecular systematic analysis because each aligned position has to include only homologous ...
Purification, Cloning, and Tissue Distribution of a 23
... deduced protein, 187 amino acids long, is rich in glutamic and aspartic acid residues, endowing p23k with a net negative charge at neutral pH. The protein lacks a signal sequence as well as any transmembrane domains. Based on predictions of secondary structure, p23k is a globular protein composed of ...
... deduced protein, 187 amino acids long, is rich in glutamic and aspartic acid residues, endowing p23k with a net negative charge at neutral pH. The protein lacks a signal sequence as well as any transmembrane domains. Based on predictions of secondary structure, p23k is a globular protein composed of ...
Chem*4570 Applied Biochemistry Lecture 7 Overproduction of lysine
... phosphorylation is inefficient. Since the glutamate pathway is the major energy yielding pathway, more glutamate is produced. ...
... phosphorylation is inefficient. Since the glutamate pathway is the major energy yielding pathway, more glutamate is produced. ...
Biochemistry Test Review
... 33. What are carbohydrates that are a) monomers? b) dimers? (double monomers)? c) polymers? 34. Name the bond types between monosaccharides in a polysaccharide. 35. What are several types of carbohydrate polymers and what are their roles in living things? 36. What is an alternative name for "starch" ...
... 33. What are carbohydrates that are a) monomers? b) dimers? (double monomers)? c) polymers? 34. Name the bond types between monosaccharides in a polysaccharide. 35. What are several types of carbohydrate polymers and what are their roles in living things? 36. What is an alternative name for "starch" ...
Genomic Annotation Lab Exercise By Jacob Jipp and Marian
... these similarities can be interpreted as divergent evolution from a common ancestor. While gene predictors have been developed, they are not robust enough to be used as the only source in eukaryotic genomic annotation. There is less information available about eukaryotic genes than prokaryotic genes ...
... these similarities can be interpreted as divergent evolution from a common ancestor. While gene predictors have been developed, they are not robust enough to be used as the only source in eukaryotic genomic annotation. There is less information available about eukaryotic genes than prokaryotic genes ...
Genomic Annotation Lab Exercise By Jacob Jipp and Marian
... these similarities can be interpreted as divergent evolution from a common ancestor. While gene predictors have been developed, they are not robust enough to be used as the only source in eukaryotic genomic annotation. There is less information available about eukaryotic genes than prokaryotic genes ...
... these similarities can be interpreted as divergent evolution from a common ancestor. While gene predictors have been developed, they are not robust enough to be used as the only source in eukaryotic genomic annotation. There is less information available about eukaryotic genes than prokaryotic genes ...
Analysis of 25 underivatized amino acids in human plasma using
... chromatography/electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (LC/ESI-MS) with perfluorinated acids as ion-pairing agents. To date, these studies have used precursor mass, retention time and tandem mass spectrometry (MS/MS) to identify and quantify amino acids. While this is a potentially powerful techni ...
... chromatography/electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (LC/ESI-MS) with perfluorinated acids as ion-pairing agents. To date, these studies have used precursor mass, retention time and tandem mass spectrometry (MS/MS) to identify and quantify amino acids. While this is a potentially powerful techni ...
primary structure
... 3.16 Nucleic acids are information-rich polymers of nucleotides A nucleic acid polymer, a polynucleotide, forms from the nucleotide monomers when the phosphate of one nucleotide bonds to the sugar of the next nucleotide – The result is a repeating sugar-phosphate backbone with protruding nitrogen ...
... 3.16 Nucleic acids are information-rich polymers of nucleotides A nucleic acid polymer, a polynucleotide, forms from the nucleotide monomers when the phosphate of one nucleotide bonds to the sugar of the next nucleotide – The result is a repeating sugar-phosphate backbone with protruding nitrogen ...
peak glossary of terms
... Increased utilization of free fatty acids for energy for increase muscle and heart energy in endurance sports (ergogenic aid) Increased ‘glycogen sparing’ effect in endurance athletes, may provide protection for muscle glycogen stores, which are at risk during periods of increased exercise (anti ...
... Increased utilization of free fatty acids for energy for increase muscle and heart energy in endurance sports (ergogenic aid) Increased ‘glycogen sparing’ effect in endurance athletes, may provide protection for muscle glycogen stores, which are at risk during periods of increased exercise (anti ...
Slides - Websupport1
... • Two pyruvates = 34 ATP • The chemical formula for this process is C6H12O6 + 6 O2 6 CO2 + 6 H2O ...
... • Two pyruvates = 34 ATP • The chemical formula for this process is C6H12O6 + 6 O2 6 CO2 + 6 H2O ...
Assessment of the mathematical issues involved
... assumptions discussed above. There are two ways of expressing enrichment commonly used in stable-isotope studies. In flooding dose experiments, it is common to express enrichment as APE, which is defined as the number of mols of tracer divided by the number of mols of tracer and tracee combined. Enr ...
... assumptions discussed above. There are two ways of expressing enrichment commonly used in stable-isotope studies. In flooding dose experiments, it is common to express enrichment as APE, which is defined as the number of mols of tracer divided by the number of mols of tracer and tracee combined. Enr ...
Chromosomes, Genes and DNA
... The amino acids join together to form a protein molecule. Each gene contains the sequence of bases for one protein. Why is the sequence of bases in DNA called the genetic code? 42 of 47 ...
... The amino acids join together to form a protein molecule. Each gene contains the sequence of bases for one protein. Why is the sequence of bases in DNA called the genetic code? 42 of 47 ...
Relationship between the structure and function of proteins
... Its function is to store and transport oxygen in the skeletal muscles. It is a relatively small protein made up of a single polypeptide chain that contains 153 amino acid residues . It contains a heme group (which is a prosthetic group consisting of a protoporphyrin organic ring and a central iron a ...
... Its function is to store and transport oxygen in the skeletal muscles. It is a relatively small protein made up of a single polypeptide chain that contains 153 amino acid residues . It contains a heme group (which is a prosthetic group consisting of a protoporphyrin organic ring and a central iron a ...
A new genetic screening test for Marfan syndrome
... enough microfibrils, excess TGF-β growth factors are activated and elasticity in many tissues is decreased, leading to overgrowth and instability of tissues and the signs and symptoms of MFS. Individuals with MFS have a 50% chance of transmitting the mutation to their offspring. Approximately 75% of ...
... enough microfibrils, excess TGF-β growth factors are activated and elasticity in many tissues is decreased, leading to overgrowth and instability of tissues and the signs and symptoms of MFS. Individuals with MFS have a 50% chance of transmitting the mutation to their offspring. Approximately 75% of ...
Evidence for Amino Acid Snorkeling from a High
... The TA of Fis1p is necessary (Mozdy et al. 2000; Beilharz 2003) and sufficient (Kemper et al. 2008; Förtsch et al. 2011) for insertion of this polypeptide into the mitochondrial OM. No cellular machinery involved in Fis1p insertion has been identified (Kemper et al. 2008; Krumpe et al. 2012). Fis1p ha ...
... The TA of Fis1p is necessary (Mozdy et al. 2000; Beilharz 2003) and sufficient (Kemper et al. 2008; Förtsch et al. 2011) for insertion of this polypeptide into the mitochondrial OM. No cellular machinery involved in Fis1p insertion has been identified (Kemper et al. 2008; Krumpe et al. 2012). Fis1p ha ...
Chapter 16
... 9. What is the relationship among DNA, a gene, and a chromosome? a. A chromosome contains hundreds of genes, which are composed of protein. b. A chromosome contains hundreds of genes, which are composed of DNA. c. A gene contains hundreds of chromosomes, which are composed of protein. d. A gene is ...
... 9. What is the relationship among DNA, a gene, and a chromosome? a. A chromosome contains hundreds of genes, which are composed of protein. b. A chromosome contains hundreds of genes, which are composed of DNA. c. A gene contains hundreds of chromosomes, which are composed of protein. d. A gene is ...
File
... 3. The 2 new strands are proofread for errors. When a cell copies its DNA (replication), the original DNA ladder is broken apart and new nucleotides are added to the center. This creates two exact copies, each one made from half the original DNA molecule. · DNA polymerase (the enzyme which builds DN ...
... 3. The 2 new strands are proofread for errors. When a cell copies its DNA (replication), the original DNA ladder is broken apart and new nucleotides are added to the center. This creates two exact copies, each one made from half the original DNA molecule. · DNA polymerase (the enzyme which builds DN ...
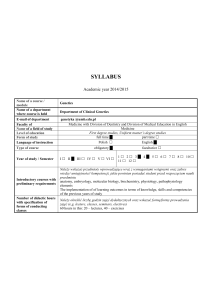
SYLABUS
... 2. Nussbaum RL, McInnes RR, Willard HF. Genetics in Medicine. Sixth edition. 2001, 2004. ...
... 2. Nussbaum RL, McInnes RR, Willard HF. Genetics in Medicine. Sixth edition. 2001, 2004. ...
... c) Full activity of E1 is observed at 37oC and a pH of 7.4. You isolate the active form of E1, subject it to a pH of 2.0 and show that it cannot bind to the substrate. You revert to pH 7.4 and see that the enzyme does not resume its function. Explain why is this so. Altering the pH from 7.4 to 2.0 d ...
Metabolism of bilirubin and bile salts synthesis (uronic acid pathway
... also called direct bilirubin, being water soluble reacts immediately with diazo reagent unconjugated (albumin bound) bilirubin is called indirect bilirubin. Being water insoluble, it has to be first extracted with methanol and then treated with diazo reagent ...
... also called direct bilirubin, being water soluble reacts immediately with diazo reagent unconjugated (albumin bound) bilirubin is called indirect bilirubin. Being water insoluble, it has to be first extracted with methanol and then treated with diazo reagent ...
Booklet 3
... (c) Many different mutations have been described within the PAH gene. The most common mutation leads to an exon being missed out when the messenger RNA is transcribed. The sections of mRNA (the transcripts) are then joined together (spliced) and translated. (i) State what is meant by the term exon. ...
... (c) Many different mutations have been described within the PAH gene. The most common mutation leads to an exon being missed out when the messenger RNA is transcribed. The sections of mRNA (the transcripts) are then joined together (spliced) and translated. (i) State what is meant by the term exon. ...
Mutations and Genetic Diseases
... Earlier in Chapter 2 you learned that genes are like recipes or sets of instructions. You also learned that the sequence of bases in the DNA molecule is comparable to the letters in the words of a written recipe. Imagine that you are copying down a set of instructions in a recipe and you don’t not ...
... Earlier in Chapter 2 you learned that genes are like recipes or sets of instructions. You also learned that the sequence of bases in the DNA molecule is comparable to the letters in the words of a written recipe. Imagine that you are copying down a set of instructions in a recipe and you don’t not ...
Table of Contents - Scholars` Bank
... amino acids that could somehow use the template of the nucleotide encoded within mRNA to distinguish which amino acid was required to construct the desired protein. However, before the “adaptor” could be found, the specifics of the genetic code became known. F. H. C. Crick, J. S. Griffith and L. E. ...
... amino acids that could somehow use the template of the nucleotide encoded within mRNA to distinguish which amino acid was required to construct the desired protein. However, before the “adaptor” could be found, the specifics of the genetic code became known. F. H. C. Crick, J. S. Griffith and L. E. ...
Genetic code

The genetic code is the set of rules by which information encoded within genetic material (DNA or mRNA sequences) is translated into proteins by living cells. Biological decoding is accomplished by the ribosome, which links amino acids in an order specified by mRNA, using transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules to carry amino acids and to read the mRNA three nucleotides at a time. The genetic code is highly similar among all organisms and can be expressed in a simple table with 64 entries.The code defines how sequences of these nucleotide triplets, called codons, specify which amino acid will be added next during protein synthesis. With some exceptions, a three-nucleotide codon in a nucleic acid sequence specifies a single amino acid. Because the vast majority of genes are encoded with exactly the same code (see the RNA codon table), this particular code is often referred to as the canonical or standard genetic code, or simply the genetic code, though in fact some variant codes have evolved. For example, protein synthesis in human mitochondria relies on a genetic code that differs from the standard genetic code.While the genetic code determines the protein sequence for a given coding region, other genomic regions can influence when and where these proteins are produced.