File
... Sentence : Scientists love to explore the universe to learn new things about deep space. ...
... Sentence : Scientists love to explore the universe to learn new things about deep space. ...
Engineering the Heavens
... wonderfully summarized by one nineteenth-century writer and allowed for are as good as nonexistent. In December in The North American Review, 1838, after only a year of final visual observations, Bessel showed the power of this error-quantification approach: When the astronomer undertakes to measure ...
... wonderfully summarized by one nineteenth-century writer and allowed for are as good as nonexistent. In December in The North American Review, 1838, after only a year of final visual observations, Bessel showed the power of this error-quantification approach: When the astronomer undertakes to measure ...
astep - Institut d`Astrophysique de Paris
... The future of transit searches 2 future milestones: •COROT: 60 000 stars (nominal mission), mv=11 to 16, for 150 days, launch oct. 2006 •KEPLER: 100 000 stars, mv=11 to 14 for 4 years, + 70 000 for 1 year, launch end 2008 ...
... The future of transit searches 2 future milestones: •COROT: 60 000 stars (nominal mission), mv=11 to 16, for 150 days, launch oct. 2006 •KEPLER: 100 000 stars, mv=11 to 14 for 4 years, + 70 000 for 1 year, launch end 2008 ...
Two Small Pieces of Glass: The Amazing Telescope
... Objects can be seen if light is available to illuminate them or if they give off their own light. (By end of grade 2). Some materials allow light to pass through them, others allow only some light through and others block all the light and create a dark shadow on any surface beyond them, where the l ...
... Objects can be seen if light is available to illuminate them or if they give off their own light. (By end of grade 2). Some materials allow light to pass through them, others allow only some light through and others block all the light and create a dark shadow on any surface beyond them, where the l ...
Standard
... including constellations and Indigenous astronomy, planets, solar system objects and orbits. Apparent movement of the stars throughout the night and seasons “Solar System”: an interactive orrery model of the solar system showing orbits and relationships of the planets and the sun Point-source of ...
... including constellations and Indigenous astronomy, planets, solar system objects and orbits. Apparent movement of the stars throughout the night and seasons “Solar System”: an interactive orrery model of the solar system showing orbits and relationships of the planets and the sun Point-source of ...
Introduction Notes - Sunflower Astronomy
... Get into groups of three and revise the IAU definition of a planet by considering some or all of the problems that were listed. On the worksheet provided write an alternate definition for a planet. Everyone turns in a copy of the worksheet. Time: 10 minutes. Beyond The Solar System Nearest star to t ...
... Get into groups of three and revise the IAU definition of a planet by considering some or all of the problems that were listed. On the worksheet provided write an alternate definition for a planet. Everyone turns in a copy of the worksheet. Time: 10 minutes. Beyond The Solar System Nearest star to t ...
How can we learn the temperature of stars? Ilya Kovalenko High
... the classification of star spectrum. Then it was very easy to learn its temperature from the book. It appeared to be about 10000 K. Besides they learned that some other stars belong to the same class and that’s why must have similar spectrum. One of the stars is Sirius – the brightest star in the Ea ...
... the classification of star spectrum. Then it was very easy to learn its temperature from the book. It appeared to be about 10000 K. Besides they learned that some other stars belong to the same class and that’s why must have similar spectrum. One of the stars is Sirius – the brightest star in the Ea ...
How many planets are there in our solar system
... 14. Who first discovered and classified galaxies? (1 pt) a. Neil Armstrong b. Edwin Hubble c. Frank Shu d. Robert Hevener 15. List evidence supporting the Big Bang Theory.(2 pts) 16.What is a meteorite? (1 pt) 17.What is space junk and how did it get into space? (1 pts) 18. Who is Dr. Frank Shu? (1 ...
... 14. Who first discovered and classified galaxies? (1 pt) a. Neil Armstrong b. Edwin Hubble c. Frank Shu d. Robert Hevener 15. List evidence supporting the Big Bang Theory.(2 pts) 16.What is a meteorite? (1 pt) 17.What is space junk and how did it get into space? (1 pts) 18. Who is Dr. Frank Shu? (1 ...
Astronomical Observations (Fall 2004) Final Exam
... A photon-counting detector is used to measure a faint source against a background whose count rate is 16 s-1. Assuming that the noise is random and that equal time is spent observing on and off the source, find the total integration time needed to detect a source whose strength is 1% of the backgrou ...
... A photon-counting detector is used to measure a faint source against a background whose count rate is 16 s-1. Assuming that the noise is random and that equal time is spent observing on and off the source, find the total integration time needed to detect a source whose strength is 1% of the backgrou ...
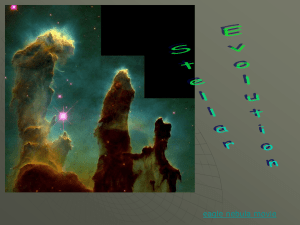
Stellar Evolution Slideshow
... only neutrons are left (Guess where the name “Neutron Stars” came from?) Also called Pulsars because they emit radio waves with incredible regularity. Appear to be rapidly rotating neutron star ...
... only neutrons are left (Guess where the name “Neutron Stars” came from?) Also called Pulsars because they emit radio waves with incredible regularity. Appear to be rapidly rotating neutron star ...
Black Hole
... million years. Our own galaxy is 175 million more years to have another revolution. •Elliptical Galaxy- In an Elliptical Galaxy, the stars have no current rotation, so it cannot have a revolution. ...
... million years. Our own galaxy is 175 million more years to have another revolution. •Elliptical Galaxy- In an Elliptical Galaxy, the stars have no current rotation, so it cannot have a revolution. ...
Skillen HARPS-NEF - University of Hertfordshire
... equivalent to the speed of a rather gentle stroll! Other objects such as white dwarfs and stellar companions on the other hand cause a larger reflex motion in excess of 1 km/sec, and so are much easier to identify. By measuring the wobble of their parent stars, HARPS-NEF will use this technique to ...
... equivalent to the speed of a rather gentle stroll! Other objects such as white dwarfs and stellar companions on the other hand cause a larger reflex motion in excess of 1 km/sec, and so are much easier to identify. By measuring the wobble of their parent stars, HARPS-NEF will use this technique to ...
WOMEN OF ASTRONOMY
... c (accepting the Henry Norris Russell Prize from the American Astronomical Society) ...
... c (accepting the Henry Norris Russell Prize from the American Astronomical Society) ...
Astrophysics
... If galaxies are moving away from us, they must have been closer together millions of years ago. If Hubble’s graph is used, the origin of this movement = approx. 10 000 million years old ...
... If galaxies are moving away from us, they must have been closer together millions of years ago. If Hubble’s graph is used, the origin of this movement = approx. 10 000 million years old ...
Life Cycle of a Star worksheet
... _____ The star begins to run out of fuel and expands into a red giant or red super giant. _____ Stars start out as diffused clouds of gas and dust drifting through space. A single one of these clouds is called a nebula _____ What happens next depends on the mass of the star. _____ Heat and pressure ...
... _____ The star begins to run out of fuel and expands into a red giant or red super giant. _____ Stars start out as diffused clouds of gas and dust drifting through space. A single one of these clouds is called a nebula _____ What happens next depends on the mass of the star. _____ Heat and pressure ...
©M. Rieke 1 Correct responses in BOLDFACE. 1. Why did
... b. the same cloud of gas and dust in which the Sun formed c. a cloud of gas in the Orion nebula d. the Sun (they were flung out of the fast-spinning young sun) 16. Stars on the main sequence all ...
... b. the same cloud of gas and dust in which the Sun formed c. a cloud of gas in the Orion nebula d. the Sun (they were flung out of the fast-spinning young sun) 16. Stars on the main sequence all ...
1 Correct responses in BOLDFACE. 1. Henrietta Leavitt`s period
... a. it was the first significant astronomical discovery by a woman b. it allowed the luminosity of these stars to be determined based on intrinsic properties, and thus their distances from their apparent brightnesses c. it allowed the astronomers of her time to test their models for the interiors of ...
... a. it was the first significant astronomical discovery by a woman b. it allowed the luminosity of these stars to be determined based on intrinsic properties, and thus their distances from their apparent brightnesses c. it allowed the astronomers of her time to test their models for the interiors of ...
Powerpoint - Physics and Astronomy
... The associated dust blocks starlight. Composition mostly H, He. Too cold for optical emission but some radio spectral lines from molecules. Doppler shifts of lines indicate clouds rotate at a few km/s. Clumps within such clouds collapse to form stars or clusters of stars. They are spinning at about ...
... The associated dust blocks starlight. Composition mostly H, He. Too cold for optical emission but some radio spectral lines from molecules. Doppler shifts of lines indicate clouds rotate at a few km/s. Clumps within such clouds collapse to form stars or clusters of stars. They are spinning at about ...
GSO Newtonian - Aperture 150mm - Focal Length 750mm
... This GSO Newtonian is an excellent multi-purpose telescope. It combines a very good mechanical quality with an exceptional optical quality. Moon and the planets are depicted full of contrast and detail. You will be able to see Saturn's Cassini division and details in Jupiter's cloud belts. 150mm ape ...
... This GSO Newtonian is an excellent multi-purpose telescope. It combines a very good mechanical quality with an exceptional optical quality. Moon and the planets are depicted full of contrast and detail. You will be able to see Saturn's Cassini division and details in Jupiter's cloud belts. 150mm ape ...
Supernova Stalking - Susanna Kumlien Reportage
... into perspective. Which is one of the many reasons as to why the sudden flare-up of supernovae on the dynamic starry sky is of such interest to Science. Not only are they spectacular events, but supernovae hold many secrets of great importance for our understanding of the universe, life and everythi ...
... into perspective. Which is one of the many reasons as to why the sudden flare-up of supernovae on the dynamic starry sky is of such interest to Science. Not only are they spectacular events, but supernovae hold many secrets of great importance for our understanding of the universe, life and everythi ...
project.generative.interactive.music
... Hubble telescope picture of the supermassive star Eta Carinae. Even though Eta Carinae is more than 8,000 lightyears away, features 10 billion miles across (about the diameter of our solar system) can be distinguished. Eta Carinae suffered giant outburst about 150 years ago, when it became one of th ...
... Hubble telescope picture of the supermassive star Eta Carinae. Even though Eta Carinae is more than 8,000 lightyears away, features 10 billion miles across (about the diameter of our solar system) can be distinguished. Eta Carinae suffered giant outburst about 150 years ago, when it became one of th ...
TELESCOPE IN THE POCKET Abstract
... In the Galilean telescope a convex lens, objective, focuses the incoming light to the one point, called the focus. The image can be viewed through a concave lens, in everyday talking called an eyepiece or an ocular. The image in the Galilean telescope is formed in the right position, not upside down ...
... In the Galilean telescope a convex lens, objective, focuses the incoming light to the one point, called the focus. The image can be viewed through a concave lens, in everyday talking called an eyepiece or an ocular. The image in the Galilean telescope is formed in the right position, not upside down ...
Spitzer Space Telescope

The Spitzer Space Telescope (SST), formerly the Space Infrared Telescope Facility (SIRTF), is an infrared space observatory launched in 2003. It is the fourth and final of the NASA Great Observatories program.The planned mission period was to be 2.5 years with a pre-launch expectation that the mission could extend to five or slightly more years until the onboard liquid helium supply was exhausted. This occurred on 15 May 2009. Without liquid helium to cool the telescope to the very low temperatures needed to operate, most of the instruments are no longer usable. However, the two shortest-wavelength modules of the IRAC camera are still operable with the same sensitivity as before the cryogen was exhausted, and will continue to be used in the Spitzer Warm Mission. All Spitzer data, from both the primary and warm phases, are archived at the Infrared Science Archive (IRSA).In keeping with NASA tradition, the telescope was renamed after its successful demonstration of operation, on 18 December 2003. Unlike most telescopes that are named after famous deceased astronomers by a board of scientists, the new name for SIRTF was obtained from a contest open to the general public.The contest led to the telescope being named in honor of astronomer Lyman Spitzer, who had promoted the concept of space telescopes in the 1940s. Spitzer wrote a 1946 report for RAND Corporation describing the advantages of an extraterrestrial observatory and how it could be realized with available or upcoming technology. He has been cited for his pioneering contributions to rocketry and astronomy, as well as ""his vision and leadership in articulating the advantages and benefits to be realized from the Space Telescope Program.""The US$800 million Spitzer was launched from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, on a Delta II 7920H ELV rocket, Monday, 25 August 2003 at 13:35:39 UTC-5 (EDT).It follows a heliocentric instead of geocentric orbit, trailing and drifting away from Earth's orbit at approximately 0.1 astronomical unit per year (a so-called ""earth-trailing"" orbit). The primary mirror is 85 centimeters (33 in) in diameter, f/12, made of beryllium and is cooled to 5.5 K (−449.77 °F). The satellite contains three instruments that allow it to perform astronomical imaging and photometry from 3 to 180 micrometers, spectroscopy from 5 to 40 micrometers, and spectrophotometry from 5 to 100 micrometers.