Instrumentation for Cosmology
... Suppose the age of the galaxy is 10 billion years. Its inner regions rotate once in 200 million years… Therefore, we’d expect about 50 turns. The galaxy would look like a clock spring. ...
... Suppose the age of the galaxy is 10 billion years. Its inner regions rotate once in 200 million years… Therefore, we’d expect about 50 turns. The galaxy would look like a clock spring. ...
Slide 1
... Royal Society in 1666, "a system of the world very different from any yet received. It is founded on the following positions. 1. That all the heavenly bodies have not only a gravitation of their parts to their own proper centre, but that they also mutually attract each other within their spheres of ...
... Royal Society in 1666, "a system of the world very different from any yet received. It is founded on the following positions. 1. That all the heavenly bodies have not only a gravitation of their parts to their own proper centre, but that they also mutually attract each other within their spheres of ...
Skywatch Astro Ed Dec13
... of other stars, then hurled into space as the stars died, where they could be incorporated into new stars. Population II stars formed when there were almost no heavier elements around, so they have only tiny amounts of them. But Population I stars, like the Sun, are younger, so they have higher prop ...
... of other stars, then hurled into space as the stars died, where they could be incorporated into new stars. Population II stars formed when there were almost no heavier elements around, so they have only tiny amounts of them. But Population I stars, like the Sun, are younger, so they have higher prop ...
3-1. True or False: Different colors of light are waves with different
... CCDs respond to more of the light falling on them than film does. CCDs have a better resolution than film does. CCDs respond more uniformly to light of different colors. All of the above. X ...
... CCDs respond to more of the light falling on them than film does. CCDs have a better resolution than film does. CCDs respond more uniformly to light of different colors. All of the above. X ...
Tools of Astronomy
... If a star is _____ light years from Earth then the light from that star took 100 years to get here and we are seeing the star as it was _______ years ago! 8. Telescopes are like _______ machines because they look at objects as they were in the past! There are telescopes that “see” all the different ...
... If a star is _____ light years from Earth then the light from that star took 100 years to get here and we are seeing the star as it was _______ years ago! 8. Telescopes are like _______ machines because they look at objects as they were in the past! There are telescopes that “see” all the different ...
How Long is a Light Year?
... certainly not the only one. There are too many stars for us to even begin to count (see how many you can count while gazing up at the sky on a clear night). Not only are there too many stars to count, but the stars are beyond our imagination as to how far away they are. They are so far away that sta ...
... certainly not the only one. There are too many stars for us to even begin to count (see how many you can count while gazing up at the sky on a clear night). Not only are there too many stars to count, but the stars are beyond our imagination as to how far away they are. They are so far away that sta ...
... was near to the center of the system), that only matters with high “boiling points” were able to condense. Therefore, only metals and then also silicates could condense to form solids. At these inner orbits, material with lower boiling points (lighter elements) could not be collected, since it still ...
VI. Preferred Location of Telescopes
... The Keck telescope on Mauna Kea in Hawaii sit at 13,600 ft … above 40% of the atmosphere. * ...
... The Keck telescope on Mauna Kea in Hawaii sit at 13,600 ft … above 40% of the atmosphere. * ...
Chapter 6 Telescopes: Portals of Discovery
... • Infrared and ultraviolet-light telescopes operate like visible-light telescopes but need to be above atmosphere to see all IR and UV wavelengths ...
... • Infrared and ultraviolet-light telescopes operate like visible-light telescopes but need to be above atmosphere to see all IR and UV wavelengths ...
A Dart Board for the Bored An eye opening offer from the editors of
... quite low (with the exception of Mr. Alyea and myself), I submit this article as a reference for anyone who may someday consider a Cassegrainian telescope in defiance of the neck-ringing contortions associated with Newtonian observing, and also to help thicken the WASP. I have chosen to make one mys ...
... quite low (with the exception of Mr. Alyea and myself), I submit this article as a reference for anyone who may someday consider a Cassegrainian telescope in defiance of the neck-ringing contortions associated with Newtonian observing, and also to help thicken the WASP. I have chosen to make one mys ...
CS3_Ch 4 - Leon County Schools
... Which type of telescope collects radio waves and some microwaves using an antenna that looks like a TV satellite dish? A. radio telescope B. reflecting telescope C. refracting telescope D. X-ray telescope ...
... Which type of telescope collects radio waves and some microwaves using an antenna that looks like a TV satellite dish? A. radio telescope B. reflecting telescope C. refracting telescope D. X-ray telescope ...
Bioptic Telescopes - Designs for Vision
... carrier lens, the telescope is “out of the way” while the patient is moving about or doing general work, but is always available for distance spotting. Patients simply need to drop their head slightly to bring the telescope into alignment with their eyes. This is important, because the patient does ...
... carrier lens, the telescope is “out of the way” while the patient is moving about or doing general work, but is always available for distance spotting. Patients simply need to drop their head slightly to bring the telescope into alignment with their eyes. This is important, because the patient does ...
Chapter 26
... A collection of stars, gas, and dust bound together by gravity is called a galaxy. The galaxy we live in is called the Milky Way. The long distances in space are measured in units called light-years and AU’s. A light-year is the distance light travels in one year. Light travels at a rate of 300,000, ...
... A collection of stars, gas, and dust bound together by gravity is called a galaxy. The galaxy we live in is called the Milky Way. The long distances in space are measured in units called light-years and AU’s. A light-year is the distance light travels in one year. Light travels at a rate of 300,000, ...
ASTR 300 Stars and Stellar Systems Fall 2011
... astronomers sometimes put their telescopes in deep valleys? (Chapt. 6, Review Question 4) Optical astronomers hope to get above as much of the atmosphere as possible. For radio astronomers, interference from man-made radio signals is a major problem. Putting a radio telescope in a deep valley may sh ...
... astronomers sometimes put their telescopes in deep valleys? (Chapt. 6, Review Question 4) Optical astronomers hope to get above as much of the atmosphere as possible. For radio astronomers, interference from man-made radio signals is a major problem. Putting a radio telescope in a deep valley may sh ...
December 2015
... ionized by high energy photons emitted from stars that have often been formed within the nebula. These star forming nebula are officially called H II (H two) regions. The color red orange is due to their large amounts of hydrogen. Of course the term nebula means “fuzzy cloud” and came about when ear ...
... ionized by high energy photons emitted from stars that have often been formed within the nebula. These star forming nebula are officially called H II (H two) regions. The color red orange is due to their large amounts of hydrogen. Of course the term nebula means “fuzzy cloud” and came about when ear ...
`A ship flying in space:` Earth seen through the eyes of an astronaut
... Our sun is just one star among the hundreds of billions that make up the Milky Way galaxy, which itself is only one of hundreds of billions of galaxies in the universe. Over the last 15 years, astronomers have found hundreds of planets orbiting stars in our corner of the Milky Way and the list will ...
... Our sun is just one star among the hundreds of billions that make up the Milky Way galaxy, which itself is only one of hundreds of billions of galaxies in the universe. Over the last 15 years, astronomers have found hundreds of planets orbiting stars in our corner of the Milky Way and the list will ...
Chapter 6 Telescopes
... blue wavelengths, the sky is about half as bright as from the ground. Much of the sky background is due to sunlight scattered from interplanetary dust and distant unresolved stars and galaxies. ...
... blue wavelengths, the sky is about half as bright as from the ground. Much of the sky background is due to sunlight scattered from interplanetary dust and distant unresolved stars and galaxies. ...
Big Bang Theory Project
... Spectroscope: Used to identify celestial bodies in distant galaxies. ...
... Spectroscope: Used to identify celestial bodies in distant galaxies. ...
Chapter 21 notes - Clinton Public Schools
... Irregular Galaxies: do not have regular shape: typically smaller, have many bright, young stars and lots of gas and dust to form new stars. Quasars: objects very bright, very far away: active young galaxies with giant black holes at their center: an enormous amount of gas revolves around the black h ...
... Irregular Galaxies: do not have regular shape: typically smaller, have many bright, young stars and lots of gas and dust to form new stars. Quasars: objects very bright, very far away: active young galaxies with giant black holes at their center: an enormous amount of gas revolves around the black h ...
The Universe and Space Travel
... "Hubble's law" although this relation had been discovered previously by Georges Lemaître, who published his work in a less visible journal. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Edwin_Hubble ...
... "Hubble's law" although this relation had been discovered previously by Georges Lemaître, who published his work in a less visible journal. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Edwin_Hubble ...
Light and Telescope
... Most infrared radiation is absorbed in the lower atmosphere. NASA infrared telescope on Mauna Kea, Hawaii ...
... Most infrared radiation is absorbed in the lower atmosphere. NASA infrared telescope on Mauna Kea, Hawaii ...
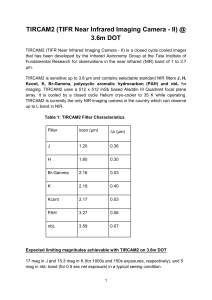
TIRCAM2 (TIFR Near Infrared Imaging Camera - II) @ 3.6m
... TIRCAM2 (TIFR Near Infrared Imaging Camera - II) is a closed cycle cooled imager that has been developed by the Infrared Astronomy Group at the Tata Institute of Fundamental Research for observations in the near infrared (NIR) band of 1 to 3.7 μm. TIRCAM2 is sensitive up to 3.8 μm and contains selec ...
... TIRCAM2 (TIFR Near Infrared Imaging Camera - II) is a closed cycle cooled imager that has been developed by the Infrared Astronomy Group at the Tata Institute of Fundamental Research for observations in the near infrared (NIR) band of 1 to 3.7 μm. TIRCAM2 is sensitive up to 3.8 μm and contains selec ...
Avoiding Run-On Sentences: Practice Exercise I 1. Our solar system
... 5. Marie is never interested in stargazing during the winter however on warm summer nights she often goes to the college observatory. Marie is never interested in stargazing during the winter, however, on warm summer nights she often goes to the college observatory. Marie is never interested in star ...
... 5. Marie is never interested in stargazing during the winter however on warm summer nights she often goes to the college observatory. Marie is never interested in stargazing during the winter, however, on warm summer nights she often goes to the college observatory. Marie is never interested in star ...
Spitzer Space Telescope

The Spitzer Space Telescope (SST), formerly the Space Infrared Telescope Facility (SIRTF), is an infrared space observatory launched in 2003. It is the fourth and final of the NASA Great Observatories program.The planned mission period was to be 2.5 years with a pre-launch expectation that the mission could extend to five or slightly more years until the onboard liquid helium supply was exhausted. This occurred on 15 May 2009. Without liquid helium to cool the telescope to the very low temperatures needed to operate, most of the instruments are no longer usable. However, the two shortest-wavelength modules of the IRAC camera are still operable with the same sensitivity as before the cryogen was exhausted, and will continue to be used in the Spitzer Warm Mission. All Spitzer data, from both the primary and warm phases, are archived at the Infrared Science Archive (IRSA).In keeping with NASA tradition, the telescope was renamed after its successful demonstration of operation, on 18 December 2003. Unlike most telescopes that are named after famous deceased astronomers by a board of scientists, the new name for SIRTF was obtained from a contest open to the general public.The contest led to the telescope being named in honor of astronomer Lyman Spitzer, who had promoted the concept of space telescopes in the 1940s. Spitzer wrote a 1946 report for RAND Corporation describing the advantages of an extraterrestrial observatory and how it could be realized with available or upcoming technology. He has been cited for his pioneering contributions to rocketry and astronomy, as well as ""his vision and leadership in articulating the advantages and benefits to be realized from the Space Telescope Program.""The US$800 million Spitzer was launched from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, on a Delta II 7920H ELV rocket, Monday, 25 August 2003 at 13:35:39 UTC-5 (EDT).It follows a heliocentric instead of geocentric orbit, trailing and drifting away from Earth's orbit at approximately 0.1 astronomical unit per year (a so-called ""earth-trailing"" orbit). The primary mirror is 85 centimeters (33 in) in diameter, f/12, made of beryllium and is cooled to 5.5 K (−449.77 °F). The satellite contains three instruments that allow it to perform astronomical imaging and photometry from 3 to 180 micrometers, spectroscopy from 5 to 40 micrometers, and spectrophotometry from 5 to 100 micrometers.