Notes on Precession in Astronomy
... Celestial Pole, appears to be stationary while other stars appear to rotate around it as the Earth turns daily on its axis [see Star Trail photograph.] However, the specific star that is the North Star varies over time because of the Earth's Precession. Precession was first discovered by the Greek a ...
... Celestial Pole, appears to be stationary while other stars appear to rotate around it as the Earth turns daily on its axis [see Star Trail photograph.] However, the specific star that is the North Star varies over time because of the Earth's Precession. Precession was first discovered by the Greek a ...
Solar System book - Science Link Cafe
... Uranus is the seventh planet from the Sun. It is not visible to the naked eye and became the first planet discovered with the use of a telescope. Uranus is tipped over on its side with an axial tilt of 98o. ...
... Uranus is the seventh planet from the Sun. It is not visible to the naked eye and became the first planet discovered with the use of a telescope. Uranus is tipped over on its side with an axial tilt of 98o. ...
Unit I – The Seasons
... Does the Earth itself really move, orbiting around a static Sun? (Wouldn’t we feel that motion?) Or does the Sun move around the static Earth, as the ancient Greeks thought? We will return to this question later. Whichever is correct, the result is the same! We will see different constellations of t ...
... Does the Earth itself really move, orbiting around a static Sun? (Wouldn’t we feel that motion?) Or does the Sun move around the static Earth, as the ancient Greeks thought? We will return to this question later. Whichever is correct, the result is the same! We will see different constellations of t ...
Astronomy Content from Frameworks
... Moon to a thin crescent. These changes are called phases. The Moon's light comes from the Sun, and the sunlight is reflected off the Moon's surface. The phase of the Moon that we see depends on the orientation of the Earth and Moon, relative to the Sun. The length of time from New Moon to New Moon i ...
... Moon to a thin crescent. These changes are called phases. The Moon's light comes from the Sun, and the sunlight is reflected off the Moon's surface. The phase of the Moon that we see depends on the orientation of the Earth and Moon, relative to the Sun. The length of time from New Moon to New Moon i ...
Document
... • On any given night, you can see about 3000 stars without a telescope, provided the sky is dark. ...
... • On any given night, you can see about 3000 stars without a telescope, provided the sky is dark. ...
Here
... • On any given night, you can see about 3000 stars without a telescope, provided the sky is dark. ...
... • On any given night, you can see about 3000 stars without a telescope, provided the sky is dark. ...
Cycles and Patterns Related to the Earth, Sun
... sun it also spins on its axis to cause day and night. The earth rotates on its axis as it moves (orbits) around the sun. The side facing the sun is lit up by the sun (day). The side facing away from the sun is not being lit up by the sun (night). The cycle is caused by the rotation of the Earth on i ...
... sun it also spins on its axis to cause day and night. The earth rotates on its axis as it moves (orbits) around the sun. The side facing the sun is lit up by the sun (day). The side facing away from the sun is not being lit up by the sun (night). The cycle is caused by the rotation of the Earth on i ...
PHASES OF THE MOON
... We have seasons because of the tilt of the Earth on its axis and the revolution of the axis around the Sun. The Earth takes 365 ¼ days to revolve around the Sun and complete all 4 ...
... We have seasons because of the tilt of the Earth on its axis and the revolution of the axis around the Sun. The Earth takes 365 ¼ days to revolve around the Sun and complete all 4 ...
Homework 12 1. How would phases change if the Moon were the
... same size as Earth, but still had the same mass? Both total and partial solar eclipses would be more frequent because there is a greater chance that the larger Moon would block the Sun. The Earth will have more Moon to block, but a bigger target. Their will be more partial lunar eclipses and fewer t ...
... same size as Earth, but still had the same mass? Both total and partial solar eclipses would be more frequent because there is a greater chance that the larger Moon would block the Sun. The Earth will have more Moon to block, but a bigger target. Their will be more partial lunar eclipses and fewer t ...
Definition - SchoolNotes
... geographer, and astronomer, who lived almost 2,000 years ago, was the first scientist to formulate this idea. In the Ptolemaic system, or geocentric view of the universe, Ptolemy described the planets and stars are revolving around the Earth in perfect circular orbits. Definition: an early model of ...
... geographer, and astronomer, who lived almost 2,000 years ago, was the first scientist to formulate this idea. In the Ptolemaic system, or geocentric view of the universe, Ptolemy described the planets and stars are revolving around the Earth in perfect circular orbits. Definition: an early model of ...
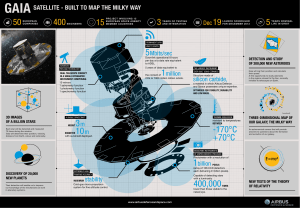
3m 10m -170°C +70°C 400,000
... 1 astrometry function 1 photometry function 1 spectrometry function ...
... 1 astrometry function 1 photometry function 1 spectrometry function ...
Dark Skies Above Downeast Maine
... January 3 – The Quadrantid Meteor Shower Peaks. Look for this beautiful shower to be at its best during the early hours of January 3rd. The Quadrantids have a very small window for when the met ...
... January 3 – The Quadrantid Meteor Shower Peaks. Look for this beautiful shower to be at its best during the early hours of January 3rd. The Quadrantids have a very small window for when the met ...
chapter_5_lecture_notes
... The dying star shrinks into a white dwarf which is a small dim star that is very dense and hot. Or the supernova collapses and the pull of gravity is so strong that nothing can escape, not even light, resulting in a black ...
... The dying star shrinks into a white dwarf which is a small dim star that is very dense and hot. Or the supernova collapses and the pull of gravity is so strong that nothing can escape, not even light, resulting in a black ...
Other Objects in Space
... Stars can also be supergiants When supergiants explode they become supernovas Page 459 Figure 22 The core of the supergiant collapses to form a black hole ...
... Stars can also be supergiants When supergiants explode they become supernovas Page 459 Figure 22 The core of the supergiant collapses to form a black hole ...
Chapter 16 - The Solar System
... • R = length of semisemi-major axis • T = time • When T in years, R in AU, then k = 1 year2 / AU3 ...
... • R = length of semisemi-major axis • T = time • When T in years, R in AU, then k = 1 year2 / AU3 ...
The Sun Worksheet
... Learning Target: I can explain the size of the Sun and its place in the universe. ...
... Learning Target: I can explain the size of the Sun and its place in the universe. ...
31_Finding Earths
... and He such as C, O, Fe…). We think these elements helped form the first solids as the gas cloud cooled and these solids acted as nucleation sites for additional material to condense to form rocky cores of planets. ...
... and He such as C, O, Fe…). We think these elements helped form the first solids as the gas cloud cooled and these solids acted as nucleation sites for additional material to condense to form rocky cores of planets. ...
1. Which of the following statements is incorrect concerning sidereal
... A. One sidereal day is defined as the time taken for the Earth to make one complete rotation on its axis B. One sidereal day is 3.9 minutes longer than one solar day C. The time difference between one sidereal day and one solar day accounts for the daily slight shift in the position of stars D. The ...
... A. One sidereal day is defined as the time taken for the Earth to make one complete rotation on its axis B. One sidereal day is 3.9 minutes longer than one solar day C. The time difference between one sidereal day and one solar day accounts for the daily slight shift in the position of stars D. The ...
Document
... burning helium. It will expand and engulf Mercury, Venus, and Earth. At that point it will become a Red Giant. The Sun is almost a perfect sphere. 1. www.space-facts.com/planets 2. www.tes.com/lessons/mircuk2yTksd_w/the-planets ...
... burning helium. It will expand and engulf Mercury, Venus, and Earth. At that point it will become a Red Giant. The Sun is almost a perfect sphere. 1. www.space-facts.com/planets 2. www.tes.com/lessons/mircuk2yTksd_w/the-planets ...
Lab 21.1 Classifying Stars
... Plot the 36 closest stars on the graph paper and mark each star’s location with a small “x”. Plot the 20 brightest stars on the graph paper and mark each star’s location with a small “o”. Using the diagram on page 382 of the text, label the five groups (four of them are circled). The third group fro ...
... Plot the 36 closest stars on the graph paper and mark each star’s location with a small “x”. Plot the 20 brightest stars on the graph paper and mark each star’s location with a small “o”. Using the diagram on page 382 of the text, label the five groups (four of them are circled). The third group fro ...
Exploring the Universe
... • The moon is able to be illuminated due to the sun’s light reflecting off of its surface • As the moon revolves around Earth, the illuminated portion of the side of the moon facing Earth changes. • When the moon is full, the earth is between the sun and moon and the half that faces you is lit. • Wh ...
... • The moon is able to be illuminated due to the sun’s light reflecting off of its surface • As the moon revolves around Earth, the illuminated portion of the side of the moon facing Earth changes. • When the moon is full, the earth is between the sun and moon and the half that faces you is lit. • Wh ...
Name: Period : _____ Bulldog Review #9 1. The Milky Wa
... A. Gravity is responsible for keeping objects in orbit around one another; gravity is the strongest on the moon and weakest on the Earth. B. Gravity is a force that causes objects to move toward the center of the Earth. Gravity is caused by tectonic plate movement. C. Gravity is the force that is fo ...
... A. Gravity is responsible for keeping objects in orbit around one another; gravity is the strongest on the moon and weakest on the Earth. B. Gravity is a force that causes objects to move toward the center of the Earth. Gravity is caused by tectonic plate movement. C. Gravity is the force that is fo ...
Introduction Notes - Sunflower Astronomy
... b. Curvature of shoes results from walking inside a sphere. 2. Astrology - Claims that specific configurations of the Sun, planets, and constellations influence human affairs. ...
... b. Curvature of shoes results from walking inside a sphere. 2. Astrology - Claims that specific configurations of the Sun, planets, and constellations influence human affairs. ...
Space Explorations - Holy Cross Collegiate
... Heliocentric: a model of the universe that places the Sun at the centre with Earth, the planets, and moons The invention of the telescope enabled astronomers to ...
... Heliocentric: a model of the universe that places the Sun at the centre with Earth, the planets, and moons The invention of the telescope enabled astronomers to ...
Solar System
... out of the atmosphere it can be as cold as 0-20 degrees. The condition is its oval, and circle and also sometimes unreadable. The name of meteoroids are because when its approaching earth it look like falling stars. ...
... out of the atmosphere it can be as cold as 0-20 degrees. The condition is its oval, and circle and also sometimes unreadable. The name of meteoroids are because when its approaching earth it look like falling stars. ...
Geocentric model

In astronomy, the geocentric model (also known as geocentrism, or the Ptolemaic system) is a description of the cosmos where Earth is at the orbital center of all celestial bodies. This model served as the predominant cosmological system in many ancient civilizations such as ancient Greece including the noteworthy systems of Aristotle (see Aristotelian physics) and Ptolemy. As such, they believed that the Sun, Moon, stars, and naked eye planets circled Earth.Two commonly made observations supported the idea that Earth was the center of the Universe. The stars, the sun, and planets appear to revolve around Earth each day, making Earth the center of that system. The stars were thought to be on a celestial sphere, with the earth at its center, that rotated each day, using a line through the north and south pole as an axis. The stars closest to the equator appeared to rise and fall the greatest distance, but each star circled back to its rising point each day. The second observation supporting the geocentric model was that the Earth does not seem to move from the perspective of an Earth-bound observer, and that it is solid, stable, and unmoving.Ancient Roman and medieval philosophers usually combined the geocentric model with a spherical Earth. It is not the same as the older flat Earth model implied in some mythology, as was the case with the biblical and postbiblical Latin cosmology. The ancient Jewish Babylonian uranography pictured a flat Earth with a dome-shaped rigid canopy named firmament placed over it. (רקיע- rāqîa').However, the ancient Greeks believed that the motions of the planets were circular and not elliptical, a view that was not challenged in Western culture until the 17th century through the synthesis of theories by Copernicus and Kepler.The astronomical predictions of Ptolemy's geocentric model were used to prepare astrological and astronomical charts for over 1500 years. The geocentric model held sway into the early modern age, but from the late 16th century onward was gradually superseded by the heliocentric model of Copernicus, Galileo and Kepler. There was much resistance to the transition between these two theories. Christian theologians were reluctant to reject a theory that agreed with Bible passages (e.g. ""Sun, stand you still upon Gibeon"", Joshua 10:12 – King James 2000 Bible). Others felt a new, unknown theory could not subvert an accepted consensus for geocentrism.