Mathematics (P)review
... Light-year (LY): the distance light travels in a year (9.5 trillion km) - nearest star is Proxima Centauri @ 4.3 LY - “solar neighborhood” ~ few thousand LY - diameter of our Galaxy ~ 100,000 LY - nearest major galaxy (M31) ~ 3 Million LY - “diameter” of observable universe ~ 93 Billion LY On small ...
... Light-year (LY): the distance light travels in a year (9.5 trillion km) - nearest star is Proxima Centauri @ 4.3 LY - “solar neighborhood” ~ few thousand LY - diameter of our Galaxy ~ 100,000 LY - nearest major galaxy (M31) ~ 3 Million LY - “diameter” of observable universe ~ 93 Billion LY On small ...
ANSWER KEY Evaluating Scientific Explanations: Why do we have
... How could one of the hemispheres be closer to the sun than the other one? The Earth is one big planet and the tilt doesn’t make any difference in the distance. (Note: This was not modeled in our experiment! The flashlight was so close to the book that when we tilted it, the top part of the book was ...
... How could one of the hemispheres be closer to the sun than the other one? The Earth is one big planet and the tilt doesn’t make any difference in the distance. (Note: This was not modeled in our experiment! The flashlight was so close to the book that when we tilted it, the top part of the book was ...
Friends newsletter december 2011
... later in the evening. The planet sets about 2am on January 1, by midnight on January 31. The planet starts January in Pisces but on the 8th crosses back into Aries, which it left in early December. Mars starts to move into the evening sky in January after having been in the morning sky for the last ...
... later in the evening. The planet sets about 2am on January 1, by midnight on January 31. The planet starts January in Pisces but on the 8th crosses back into Aries, which it left in early December. Mars starts to move into the evening sky in January after having been in the morning sky for the last ...
04 Lines in the Sky
... need to measure the location of objects in the sky. We will look at two methods of measuring locations in the sky. • Both methods require measuring angles. • These methods have long been used not only for timekeeping but for navigation as well. ...
... need to measure the location of objects in the sky. We will look at two methods of measuring locations in the sky. • Both methods require measuring angles. • These methods have long been used not only for timekeeping but for navigation as well. ...
Friends newsletter december 2011
... later in the evening. The planet sets about 2am on January 1, by midnight on January 31. The planet starts January in Pisces but on the 8th crosses back into Aries, which it left in early December. Mars starts to move into the evening sky in January after having been in the morning sky for the last ...
... later in the evening. The planet sets about 2am on January 1, by midnight on January 31. The planet starts January in Pisces but on the 8th crosses back into Aries, which it left in early December. Mars starts to move into the evening sky in January after having been in the morning sky for the last ...
PowerPoint. - teachearthscience.org
... barycenter would be halfway between the stars and the stars would orbit the barycenter. During their revolution, they would be observed to significantly wobble. ...
... barycenter would be halfway between the stars and the stars would orbit the barycenter. During their revolution, they would be observed to significantly wobble. ...
Eratosthenes` Experiment
... know that you can do it with a yardstick? (And you won't have to travel all the way around the world!) The goal of this project is to estimate the circumference of the earth by setting up a mathematical proportion from simple measurements. In this project, you will estimate the circumference of the ...
... know that you can do it with a yardstick? (And you won't have to travel all the way around the world!) The goal of this project is to estimate the circumference of the earth by setting up a mathematical proportion from simple measurements. In this project, you will estimate the circumference of the ...
High School Lab Earth Science Standards
... Energy in the Earth System 4. Energy enters the Earth system primarily as solar radiation and eventually escapes as heat. As a basis for understanding this concept students will know: a. The relative amount of incoming solar energy compared with Earth’s internal energy and the energy used by society ...
... Energy in the Earth System 4. Energy enters the Earth system primarily as solar radiation and eventually escapes as heat. As a basis for understanding this concept students will know: a. The relative amount of incoming solar energy compared with Earth’s internal energy and the energy used by society ...
Topic 2: Measuring the Earth
... - reference line = Equator (0) = a line connecting all points midway between the North & South Poles, at a right angle to the Earth’s axis - lines measure north and south, but run east-west - also called “parallels” - latitude is the same everywhere on a given parallel - in the Northern Hemisphere, ...
... - reference line = Equator (0) = a line connecting all points midway between the North & South Poles, at a right angle to the Earth’s axis - lines measure north and south, but run east-west - also called “parallels” - latitude is the same everywhere on a given parallel - in the Northern Hemisphere, ...
Chapter 2: The Science of Life in the Universe
... 20. Johannes Kepler A) developed a theory of gravity to explain the motions of the planets B) obtained the first observational evidence suggesting the Earth moved about the Sun C) made detailed measurements of the motions of the planets in the sky D) showed that the orbits of the planets were ellips ...
... 20. Johannes Kepler A) developed a theory of gravity to explain the motions of the planets B) obtained the first observational evidence suggesting the Earth moved about the Sun C) made detailed measurements of the motions of the planets in the sky D) showed that the orbits of the planets were ellips ...
Intro ES Sense of Time and Space Test Key
... Part 3: Answer the following questions briefly and clearly! 38. (3 points) Does the spectrum of a star or galaxy which is moving away from the earth moves towards the red or blue end of the visible color spectrum?_______*red_______ This is called the _______*Doppler ____ effect. Is this evidence tha ...
... Part 3: Answer the following questions briefly and clearly! 38. (3 points) Does the spectrum of a star or galaxy which is moving away from the earth moves towards the red or blue end of the visible color spectrum?_______*red_______ This is called the _______*Doppler ____ effect. Is this evidence tha ...
Earth`s Origin & Early Evolution
... More violent and rapid impact accretion. The final stage of accretion has been described as 'runaway accretion'. Planetesimals are swept up into well defined zones around the sun which approximate to the present orbits of the terrestrial planets. The process leads eventually to a small number of lar ...
... More violent and rapid impact accretion. The final stage of accretion has been described as 'runaway accretion'. Planetesimals are swept up into well defined zones around the sun which approximate to the present orbits of the terrestrial planets. The process leads eventually to a small number of lar ...
Solutions to problem set 5
... 37.778 ∼ 310 K. Wien’s Law: λpeak = 3 × 106 K nm/T (proportionality constant can be found in textbook). λpeak = 3 × 106 K nm/310 K = 9680 nm, or 9.68 microns — infrared. Compare to CMBR: TCMBR ∼ 3 K. This is about 100 times cooler than you are, so since peak wavelength is inversely proportional to t ...
... 37.778 ∼ 310 K. Wien’s Law: λpeak = 3 × 106 K nm/T (proportionality constant can be found in textbook). λpeak = 3 × 106 K nm/310 K = 9680 nm, or 9.68 microns — infrared. Compare to CMBR: TCMBR ∼ 3 K. This is about 100 times cooler than you are, so since peak wavelength is inversely proportional to t ...
Chapter 17 - Earth`s Place in Space
... Is this because the Earth rotates on its axis, or because the earth orbits the sun? The stars seem to rotate because the Earth rotates on its ...
... Is this because the Earth rotates on its axis, or because the earth orbits the sun? The stars seem to rotate because the Earth rotates on its ...
AP Physics – Applying Forces
... orbits of the same radius. One satellite is twice as massive as the other. Which of the following statements is true about the speed of these satellites? a) The heavier satellite moves twice as fast as the lighter one. b) The two satellites have the same speed. c) The lighter satellite moves twice a ...
... orbits of the same radius. One satellite is twice as massive as the other. Which of the following statements is true about the speed of these satellites? a) The heavier satellite moves twice as fast as the lighter one. b) The two satellites have the same speed. c) The lighter satellite moves twice a ...
SOLAR SYSTEM
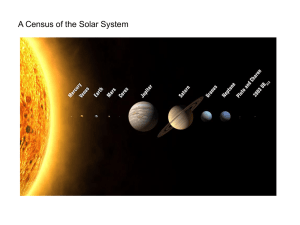
... Asteroids are small, irregularly-shaped bodies made of rock or metal Contains a dwarf planet named Ceres Jupiter - Gas Giant 5th planet from the sun Largest of all planets (all other planets could easily fit inside of it) Enormous ball of gas – mostly hydrogen and helium like the Sun Gre ...
... Asteroids are small, irregularly-shaped bodies made of rock or metal Contains a dwarf planet named Ceres Jupiter - Gas Giant 5th planet from the sun Largest of all planets (all other planets could easily fit inside of it) Enormous ball of gas – mostly hydrogen and helium like the Sun Gre ...
In the Shadow of the Earth
... If you have a telescope or binoculars, then this is a good opportunity to observe the Moon in a new light. Craters and maria (‘seas’) appear different when they don’t have the bright rays of the Sun to cast peculiar shadows on the lunar surface. The red colour of the surface during Totality is actua ...
... If you have a telescope or binoculars, then this is a good opportunity to observe the Moon in a new light. Craters and maria (‘seas’) appear different when they don’t have the bright rays of the Sun to cast peculiar shadows on the lunar surface. The red colour of the surface during Totality is actua ...
Space Key Word Search
... CELESTIAL SPHERE - system of mapping the space around the Earth; an imaginary sphere surrounding Earth. CIRCUMPOLAR - circling the pole star (Polaris). COMET - chunk of dirty, dark ice mixed with dust, rocks, and gases which revolves around the Sun in an elliptical orbit; emits volatiles (gases) in ...
... CELESTIAL SPHERE - system of mapping the space around the Earth; an imaginary sphere surrounding Earth. CIRCUMPOLAR - circling the pole star (Polaris). COMET - chunk of dirty, dark ice mixed with dust, rocks, and gases which revolves around the Sun in an elliptical orbit; emits volatiles (gases) in ...
Chapter 2 Discovering the Universe for Yourself
... • From geographic latitude (northern hemisphere), you see the celestial north pole degrees above the northern horizon; • From geographic latitude – (southern hemisphere), you see the celestial ...
... • From geographic latitude (northern hemisphere), you see the celestial north pole degrees above the northern horizon; • From geographic latitude – (southern hemisphere), you see the celestial ...
5-SolarSystem
... including 58 residing in life-friendly orbits around their parent stars. The census, collected by NASA's Kepler Space Telescope after just four months of work, shows that small planets like Earth are much more prevalent than Jupiter-sized worlds and that multiple-planet systems are common (about 200 ...
... including 58 residing in life-friendly orbits around their parent stars. The census, collected by NASA's Kepler Space Telescope after just four months of work, shows that small planets like Earth are much more prevalent than Jupiter-sized worlds and that multiple-planet systems are common (about 200 ...
Are Cool Stars Popular? Better Ask Sol
... Understanding how this activity affects planets in our solar system is important for determining if far away planet systems could support life. Yet, 70% of the observable universe is made up of red stars that are too dim to see with the naked eye, because they have cooler surfaces and are less than ...
... Understanding how this activity affects planets in our solar system is important for determining if far away planet systems could support life. Yet, 70% of the observable universe is made up of red stars that are too dim to see with the naked eye, because they have cooler surfaces and are less than ...
Chapter 5 Essay Questions
... 3 What is the definition of density? Approximately, what is the average density of the sun? 4 The corona is much hotter than the photosphere, yet we have to wait for a total solar eclipse to see the corona. Why is that? 5 Suppose you have a cool gas cloud of atoms, and you send visible light of all ...
... 3 What is the definition of density? Approximately, what is the average density of the sun? 4 The corona is much hotter than the photosphere, yet we have to wait for a total solar eclipse to see the corona. Why is that? 5 Suppose you have a cool gas cloud of atoms, and you send visible light of all ...
Geocentric model

In astronomy, the geocentric model (also known as geocentrism, or the Ptolemaic system) is a description of the cosmos where Earth is at the orbital center of all celestial bodies. This model served as the predominant cosmological system in many ancient civilizations such as ancient Greece including the noteworthy systems of Aristotle (see Aristotelian physics) and Ptolemy. As such, they believed that the Sun, Moon, stars, and naked eye planets circled Earth.Two commonly made observations supported the idea that Earth was the center of the Universe. The stars, the sun, and planets appear to revolve around Earth each day, making Earth the center of that system. The stars were thought to be on a celestial sphere, with the earth at its center, that rotated each day, using a line through the north and south pole as an axis. The stars closest to the equator appeared to rise and fall the greatest distance, but each star circled back to its rising point each day. The second observation supporting the geocentric model was that the Earth does not seem to move from the perspective of an Earth-bound observer, and that it is solid, stable, and unmoving.Ancient Roman and medieval philosophers usually combined the geocentric model with a spherical Earth. It is not the same as the older flat Earth model implied in some mythology, as was the case with the biblical and postbiblical Latin cosmology. The ancient Jewish Babylonian uranography pictured a flat Earth with a dome-shaped rigid canopy named firmament placed over it. (רקיע- rāqîa').However, the ancient Greeks believed that the motions of the planets were circular and not elliptical, a view that was not challenged in Western culture until the 17th century through the synthesis of theories by Copernicus and Kepler.The astronomical predictions of Ptolemy's geocentric model were used to prepare astrological and astronomical charts for over 1500 years. The geocentric model held sway into the early modern age, but from the late 16th century onward was gradually superseded by the heliocentric model of Copernicus, Galileo and Kepler. There was much resistance to the transition between these two theories. Christian theologians were reluctant to reject a theory that agreed with Bible passages (e.g. ""Sun, stand you still upon Gibeon"", Joshua 10:12 – King James 2000 Bible). Others felt a new, unknown theory could not subvert an accepted consensus for geocentrism.